Regulatory Information
HSA regulatory responsibility and product classification details
Regulatory Responsibility
Product Classification
Formulation Information
TABLET, FILM COATED
**DOSE AND METHOD OF ADMINISTRATION** **ENTECA** (0.5 mg/1 mg tablets) may not be suitable for all dosages and therefore, other suitable available strengths and/or dosage forms of entecavir should be used in such cases. **Recommended Dosage** _**Compensated Liver Disease**_ The recommended dose of **ENTECA** for chronic hepatitis B virus infection in nucleoside-treatment-naïve adults and adolescents 16 years of age and older is 0.5 mg once daily, with or without food. The recommended dose of **ENTECA** in adults and adolescents (≥16 years of age) with a history of hepatitis B viremia while receiving lamivudine or known lamivudine resistance mutations is 1 mg once daily, which must be taken on an empty stomach (at least 2 hours after a meal and 2 hours before the next meal). _**Decompensated Liver Disease**_ The recommended dose of **ENTECA** for chronic hepatitis B virus infection in adults with decompensated liver disease is 1 mg once daily, which must be taken on an empty stomach (at least 2 hours after a meal and 2 hours before the next meal). **Renal Impairment** In subjects with renal impairment, the apparent oral clearance of entecavir decreased as creatinine clearance decreased \[see **PHARMACODYNAMIC AND PHARMACOKINETIC PROPERTIES**, **Pharmacodynamic effects** – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_\]. Dosage adjustment is recommended for patients with creatinine clearance less than 50 mL/min, including patients on hemodialysis or continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD), as shown in Table 1. The once-daily dosing regimens are preferred. 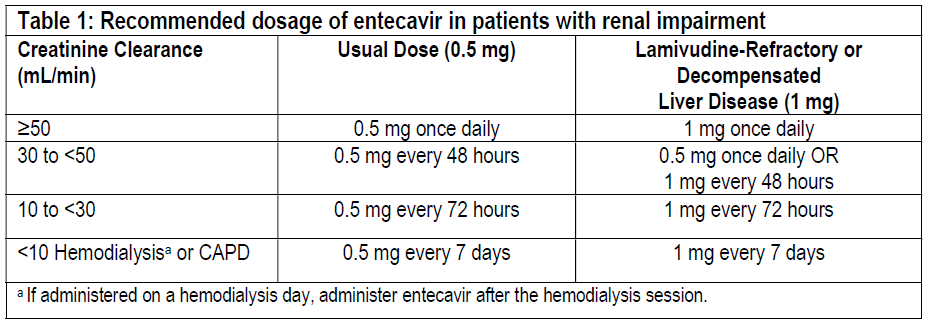 **Hepatic Impairment** No dosage adjustment is necessary for patients with hepatic impairment. **Duration of Therapy** The optimal duration of treatment with **ENTECA** for patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection and the relationship between treatment and long-term outcomes such as cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma are unknown. **USE IN SPECIAL POPULATIONS** **Pregnancy** There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of entecavir in pregnant women. When pregnant rats and rabbits received entecavir at 28 and 212 times the human exposure at the highest human dose, there were no signs of embryofetal toxicity. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, entecavir should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed and after careful consideration of the risks and benefits. Developmental toxicity studies were performed in rats and rabbits. There were no signs of embryofetal or maternal toxicity when pregnant animals received oral entecavir at approximately 28 (rat) and 212 (rabbit) times the human exposure achieved at the highest recommended human dose of 1 mg/day. In rats, maternal toxicity, embryofetal toxicity (resorptions), lower fetal body weights, tail and vertebral malformations, reduced ossification (vertebrae, sternebrae, and phalanges), and extra lumbar vertebrae and ribs were observed at exposures 3100 times those in humans. In rabbits, embryofetal toxicity (resorptions), reduced ossification (hyoid), and an increased incidence of 13th rib were observed at exposures 883 times those in humans. In a peripostnatal study, no adverse effects on offspring occurred when rats received oral entecavir at exposures greater than 94 times those in humans. **Labor and Delivery** There are no studies in pregnant women and no data on the effect of entecavir on transmission of HBV from mother to infant. Therefore, appropriate interventions should be used to prevent neonatal acquisition of HBV. **Nursing Mothers** It is not known whether entecavir is excreted into human milk; however, entecavir is excreted into the milk of rats. Because many drugs are excreted into human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from entecavir, a decision should be made to discontinue nursing or to discontinue entecavir taking into consideration the importance of continued hepatitis B therapy to the mother and the known benefits of breastfeeding. **Pediatric Use** Safety and effectiveness of entecavir in pediatric patients below the age of 16 years have not been established. **Geriatric Use** Clinical studies of entecavir did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Entecavir is substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function \[see **DOSE AND METHOD OF ADMINISTRATION**\]. **Racial/Ethnic Groups** There are no significant racial differences in entecavir pharmacokinetics. The safety and efficacy of entecavir 0.5 mg once daily were assessed in a single-arm, open-label trial of HBeAg-positive or -negative, nucleoside-naïve, Black/African American (n=40) and Hispanic (n=6) subjects with chronic HBV infection. In this trial, 76% of subjects were male, the mean age was 42 years, 57% were HBeAg-positive, the mean baseline HBV DNA was 7.0 log10 international units/mL, and the mean baseline ALT was 162 units/L. At Week 48 of treatment, 32 of 46 (70%) subjects had HBV DNA <50 international units/mL (approximately 300 copies/mL), 31 of 46 (67%) subjects had ALTnormalization (≤1 × ULN), and 12 of 26 (46%) HBeAg-positive subjects had HBe seroconversion. Safety data were similar to those observed in the larger controlled clinical trials. Because of low enrollment, safety and efficacy have not been established in the US Hispanic population. **Renal Impairment** Dosage adjustment of entecavir is recommended for patients with creatinine clearance less than 50 mL/min, including patients on hemodialysis or CAPD \[see **DOSE AND METHOD OF ADMINISTRATION** and **PHARMACODYNAMIC AND PHARMACOKINETIC PROPERTIES**, **Pharmacodynamic effects** – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_\]. **Liver Transplant Recipients** The safety and efficacy of entecavir were assessed in a single-arm, open-label trial in 65 subjects who received a liver transplant for complications of chronic HBV infection. Eligible subjects who had HBV DNA less than 172 international units/mL (approximately 1000 copies/mL) at the time of transplant were treated with entecavir 1 mg once daily in addition to usual post-transplantation management, including hepatitis B immune globulin. The trial population was 82% male, 39% Caucasian, and 37% Asian, with a mean age of 49 years; 89% of subjects had HBeAg-negative disease at the time of transplant. Four of the 65 subjects received 4 weeks or less of entecavir (2 deaths, 1 retransplantation, and 1 protocol violation) and were not considered evaluable. Of the 61 subjects who received more than 4 weeks of entecavir, 60 received hepatitis B immune globulin post-transplant. Fifty-three subjects (82% of all 65 subjects treated) completed the trial and had HBV DNA measurements at or after 72 weeks treatment post-transplant. All 53 subjects had HBV DNA <50 international units/mL (approximately 300 copies/mL). Eight evaluable subjects did not have HBV DNA data available at 72 weeks, including 3 subjects who died prior to study completion. No subjects had HBV DNA values ≥50 international units/mL while receiving entecavir (plus hepatitis B immune globulin). All 61 evaluable subjects lost HBsAg post-transplant; 2 of these subjects experienced recurrence of measurable HBsAg without recurrence of HBV viremia. This trial was not designed to determine whether addition of entecavir to hepatitis B immune globulin decreased the proportion of subjects with measurable HBV DNA post-transplant compared to hepatitis B immune globulin alone. If entecavir treatment is determined to be necessary for a liver transplant recipient who has received or is receiving an immunosuppressant that may affect renal function, such as cyclosporine or tacrolimus, renal function must be carefully monitored both before and during treatment with entecavir \[see **DOSE AND METHOD OF ADMINISTRATION** and **PHARMACODYNAMIC AND PHARMACOKINETIC PROPERTIES**, **Pharmacodynamic effects** – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_\].
ORAL
Medical Information
**INDICATIONS** **ENTECA** is indicated for the treatment of chronic hepatitis B virus infection in adults with evidence of active viral replication and either evidence of persistent elevations in serum aminotransferases (ALT or AST) or histologically active disease. The following points should be considered when initiating therapy with entecavir: This indication is based on histologic, virologic, biochemical, and serologic responses in nucleoside-treatment-naïve and lamivudine-resistant adult subjects with HBeAg-positive or HBeAg-negative chronic HBV infection with compensated liver disease \[see **CLINICAL STUDIES** – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_\]. - Virologic, biochemical, serologic, and safety data are available from a controlled study in adult subjects with chronic HBV infection and decompensated liver disease \[see **UNDESIRABLE EFFECTS** and **CLINICAL STUDIES** – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_\]. Virologic, biochemical, serologic, and safety data are available for a limited number of adult subjects with HIV/HBV co-infection who have received prior lamivudine therapy \[see **WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS** and **CLINICAL STUDIES** – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_\].
**CONTRAINDICATIONS** **ENTECA** is contraindicated in patients with previously demonstrated hypersensitivity to entecavir or any component of the product.
J05AF10
entecavir
Manufacturer Information
RANBAXY (MALAYSIA) SDN. BHD.
SUN PHARMACEUTICAL INDUSTRIES LIMITED
Active Ingredients
Documents
Package Inserts
Enteca Tablets PI.pdf
Approved: September 12, 2022
