ORKAMBI
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ORKAMBI safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ORKAMBI. ORKAMBI (lumacaftor and ivacaftor) tablets, for oral use ORKAMBI (lumacaftor and ivacaftor) oral granules Initial U.S. Approval: 2015
3fc1c40e-cfac-47a1-9e1a-61ead3570600
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Aug 10, 2023
Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated
DUNS: 602478257
Products 5
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
lumacaftor and ivacaftor
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (7)
lumacaftor and ivacaftor
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (7)
lumacaftor and ivacaftor
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (7)
lumacaftor and ivacaftor
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (19)
lumacaftor and ivacaftor
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (19)
Drug Labeling Information
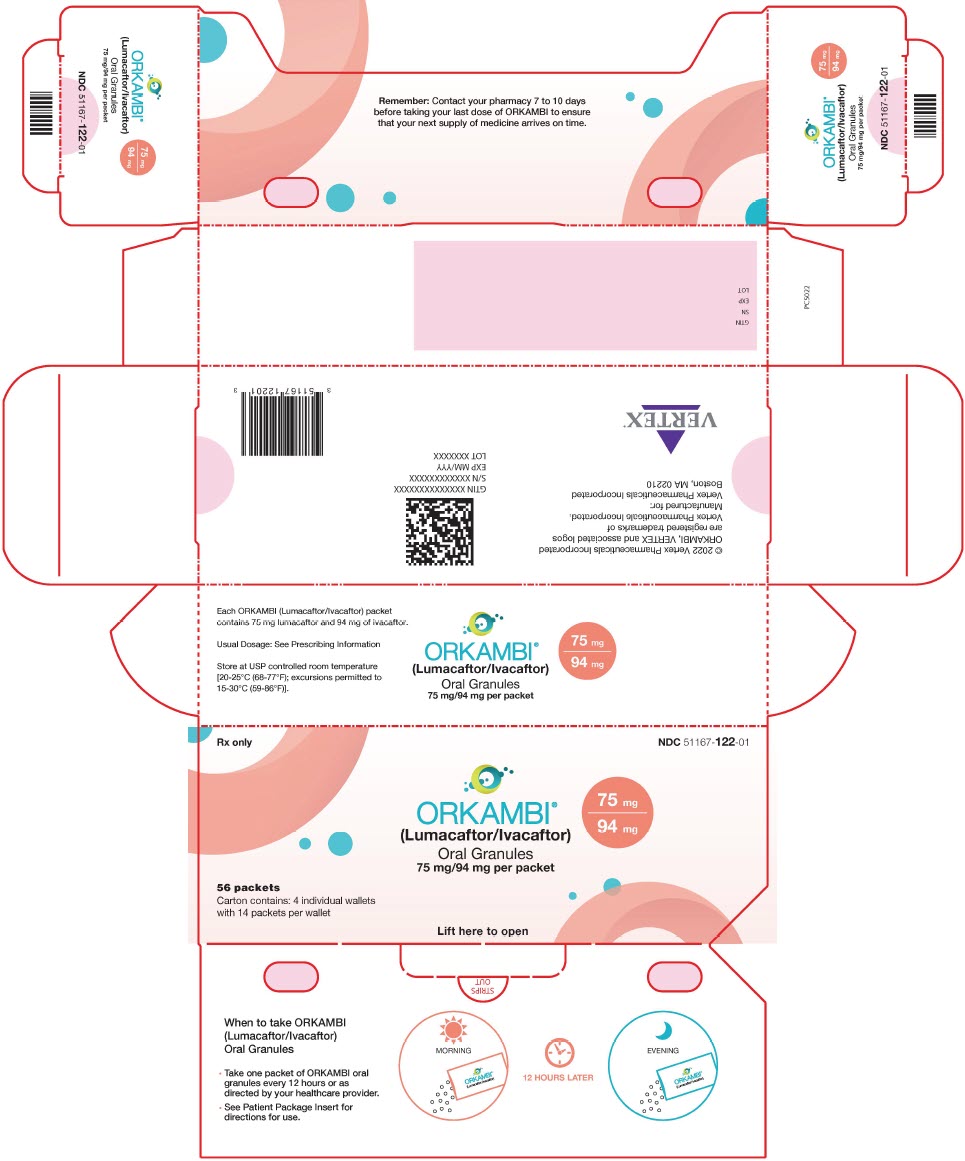
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 75 mg/94 mg packet Carton
Rx only
NDC 51167-122-01
ORKAMBI®
(Lumacaftor/Ivacaftor)
75 mg
94 mg
Oral Granules
75 mg/94 mg per packet
56 packets
Carton contains: 4 individual wallets
with 14 packets per wallet
Lift here to open
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ORKAMBI is indicated for the treatment of cystic fibrosis (CF) in patients aged 1 year and older who are homozygous for the F508del mutation in the CFTR gene. If the patient's genotype is unknown, an FDA-cleared CF mutation test should be used to detect the presence of the F508del mutation on both alleles of the CFTR gene.
Limitations of Use
The efficacy and safety of ORKAMBI have not been established in patients with CF other than those homozygous for the F508del mutation.
ORKAMBI is a combination of ivacaftor, a cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR) potentiator, and lumacaftor, indicated for the treatment of cystic fibrosis (CF) in patients aged 1 year and older who are homozygous for the F508del mutation in the CFTR gene. If the patient's genotype is unknown, an FDA-cleared CF mutation test should be used to detect the presence of the F508del mutation on both alleles of the CFTR gene. (1)
Limitations of Use:
The efficacy and safety of ORKAMBI have not been established in patients with CF other than those homozygous for the F508del mutation. (1)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Use in Patients with Advanced Liver Disease
Worsening of liver function, including hepatic encephalopathy, in patients with advanced liver disease has been reported. Liver function decompensation, including liver failure leading to death, has been reported in CF patients with pre-existing cirrhosis with portal hypertension while receiving ORKAMBI. Use ORKAMBI with caution in patients with advanced liver disease and only if the benefits are expected to outweigh the risks. If ORKAMBI is used in these patients, they should be closely monitored after the initiation of treatment and the dose should be reduced [see Dosage and Administration (2.2) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.2 Liver-related Events
Serious adverse reactions related to elevated transaminases have been reported in patients with CF receiving ORKAMBI. In some instances, these elevations have been associated with concomitant elevations in total serum bilirubin.
It is recommended that ALT, AST, and bilirubin be assessed prior to initiating ORKAMBI, every 3 months during the first year of treatment, and annually thereafter. For patients with a history of ALT, AST, or bilirubin elevations, more frequent monitoring should be considered. Patients who develop increased ALT, AST, or bilirubin should be closely monitored until the abnormalities resolve.
Dosing should be interrupted in patients with ALT or AST >5 × upper limit of normal (ULN) when not associated with elevated bilirubin. Dosing should also be interrupted in patients with ALT or AST elevations >3 × ULN when associated with bilirubin elevations >2 × ULN. Following resolution of transaminase elevations, consider the benefits and risks of resuming dosing [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.3 Hypersensitivity Reactions, Including Anaphylaxis
Hypersensitivity reactions, including cases of angioedema and anaphylaxis, have been reported in the postmarketing setting [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. If signs or symptoms of serious hypersensitivity reactions develop during treatment, discontinue ORKAMBI and institute appropriate therapy. Consider the benefits and risks for the individual patient to determine whether to resume treatment with ORKAMBI.
5.4 Respiratory Events
Respiratory events (e.g., chest discomfort, dyspnea, and respiration abnormal) were observed more commonly in patients during initiation of ORKAMBI compared to those who received placebo. These events have led to drug discontinuation and can be serious, particularly in patients with advanced lung disease (percent predicted FEV1 <40). Clinical experience in patients with ppFEV1 <40 is limited, and additional monitoring of these patients is recommended during initiation of therapy [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.5 Effect on Blood Pressure
Increased blood pressure has been observed in some patients treated with ORKAMBI. Blood pressure should be monitored periodically in all patients being treated with ORKAMBI [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.6 Drug Interactions
Substrates of CYP3A
Lumacaftor is a strong inducer of CYP3A. Administration of ORKAMBI may decrease systemic exposure of medicinal products that are substrates of CYP3A, which may decrease therapeutic effect. Co-administration with sensitive CYP3A substrates or CYP3A substrates with a narrow therapeutic index is not recommended.
ORKAMBI may substantially decrease hormonal contraceptive exposure, reducing their effectiveness and increasing the incidence of menstruation-associated adverse reactions, e.g., amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea, menorrhagia, menstrual irregular (27% in women using hormonal contraceptives compared with 3% in women not using hormonal contraceptives). Hormonal contraceptives, including oral, injectable, transdermal, and implantable, should not be relied upon as an effective method of contraception when co-administered with ORKAMBI [see Adverse Reactions (6.1), Drug Interactions (7.3, 7.11), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Strong CYP3A Inducers
Ivacaftor is a substrate of CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 isoenzymes. Use of ORKAMBI with strong CYP3A inducers, such as rifampin, significantly reduces ivacaftor exposure, which may reduce the therapeutic effectiveness of ORKAMBI. Therefore, co-administration with strong CYP3A inducers (e.g., rifampin, St. John's wort [Hypericum perforatum]) is not recommended [see Drug Interactions (7.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.7 Cataracts
Cases of non-congenital lens opacities have been reported in pediatric patients treated with ORKAMBI and ivacaftor, a component of ORKAMBI. Although other risk factors were present in some cases (such as corticosteroid use and exposure to radiation), a possible risk attributable to ivacaftor cannot be excluded [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)]. Baseline and follow-up ophthalmological examinations are recommended in pediatric patients initiating ORKAMBI treatment.
- Use in patients with advanced liver disease: ORKAMBI should be used with caution in these patients and only if the benefits are expected to outweigh the risks. If ORKAMBI is used in these patients, they should be closely monitored after the initiation of treatment and the dose should be reduced. Liver function decompensation, including liver failure leading to death, has been reported in CF patients with pre-existing cirrhosis with portal hypertension. (2.2, 5.1, 6.1)
- Liver-related events: Elevated transaminases (ALT/AST) have been observed in some cases associated with elevated bilirubin. Measure serum transaminases and bilirubin before initiating ORKAMBI, every 3 months during the first year of treatment, and annually thereafter. For patients with a history of ALT, AST, or bilirubin elevations, more frequent monitoring should be considered. Interrupt dosing in patients with ALT or AST >5 × upper limit of normal (ULN), or ALT or AST >3 × ULN with bilirubin >2 × ULN. Following resolution, consider the benefits and risks of resuming dosing. (5.2, 6.1)
- Hypersensitivity reactions: Angioedema and anaphylaxis have been reported with ORKAMBI in the postmarketing setting. Initiate appropriate therapy in the event of a hypersensitivity reaction. (5.3)
- Respiratory events: Chest discomfort, dyspnea, and respiration abnormal were observed more commonly during initiation of ORKAMBI. Clinical experience in patients with percent predicted FEV1 (ppFEV1) <40 is limited, and additional monitoring of these patients is recommended during initiation of therapy. (5.4, 6.1)
- Blood pressure: Increased blood pressure has been observed in some patients. Periodically monitor blood pressure in all patients. (5.5, 6.1)
- Drug interactions: Use with sensitive CYP3A substrates or CYP3A substrates with a narrow therapeutic index may decrease systemic exposure of the medicinal products and co-administration is not recommended. Hormonal contraceptives should not be relied upon as an effective method of contraception and their use is associated with increased menstruation-related adverse reactions. Use with strong CYP3A inducers may diminish exposure of ivacaftor, which may diminish its effectiveness; therefore, co-administration is not recommended. (5.6, 6.1, 7, 12.3)
- Cataracts: Non-congenital lens opacities/cataracts have been reported in pediatric patients treated with ORKAMBI and ivacaftor, a component of ORKAMBI. Baseline and follow-up examinations are recommended in pediatric patients initiating ORKAMBI. (5.7)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the label:
- Use in Patients with Advanced Liver Disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Liver-related Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions, Including Anaphylaxis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Respiratory Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Effect on Blood Pressure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Cataracts [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The overall safety profile of ORKAMBI is based on the pooled data from 1108 patients with CF aged 12 years and older who are homozygous for the F508del mutation in the CFTR gene and who received at least one dose of study drug in two double-blind, placebo-controlled, Phase 3 clinical trials, each with 24 weeks of treatment (Trials 1 and 2).
In addition, the following clinical trials have been conducted:
- A 24-week, open-label trial (Trial 3) in 58 patients with CF aged 6 through 11 years homozygous for the F508del-CFTR mutation.
- A 24-week, placebo-controlled trial (Trial 4) in 204 patients aged 6 through 11 years homozygous for the F508del-CFTR mutation.
- A 24-week, open-label trial (Trial 5) in 46 patients aged 12 years and older homozygous for the F508del-CFTR mutation and with advanced lung disease (ppFEV1 <40).
- A 24-week, open-label trial (Trial 6) in 60 patients aged 2 through 5 years homozygous for the F508del-CFTR mutation.
- A 24-week, open-label trial (Trial 7) in 46 patients aged 1 through 2 years homozygous for the F508del-CFTR mutation.
Of the 1108 patients, in the pooled analyses of Trial 1 and Trial 2, 49% were female and 99% were Caucasian; 369 patients received ORKAMBI every 12 hours and 370 patients received placebo.
The proportion of patients who prematurely discontinued study drug due to adverse events was 5% for patients treated with ORKAMBI and 2% for patients who received placebo.
Serious adverse reactions, whether considered drug-related or not by the investigators, that occurred more frequently in patients treated with ORKAMBI included pneumonia, hemoptysis, cough, increased blood creatine phosphokinase, and transaminase elevations. These occurred in 1% or less of patients.
Table 3 shows adverse reactions occurring in ≥5% of patients with CF aged 12 years and older treated with ORKAMBI who are homozygous for the F508del mutation in the CFTR gene that also occurred at a higher rate than in patients who received placebo in the two double-blind, placebo-controlled trials.
Table 3: Incidence of Adverse Drug Reactions in ≥5% of ORKAMBI-Treated Patients Aged 12 Years and Older Who are Homozygous for the F508del Mutation in the CFTR Gene in 2 Placebo-Controlled Phase 3 Clinical Trials of 24 Weeks Duration|
Adverse Reaction |
ORKAMBI |
Placebo |
|---|---|---|
|
Dyspnea |
48 (13) |
29 (8) |
|
Nasopharyngitis |
48 (13) |
40 (11) |
|
Nausea |
46 (13) |
28 (8) |
|
Diarrhea |
45 (12) |
31 (8) |
|
Upper respiratory tract infection |
37 (10) |
20 (5) |
|
Fatigue |
34 (9) |
29 (8) |
|
Respiration abnormal |
32 (9) |
22 (6) |
|
Blood creatine phosphokinase increased |
27 (7) |
20 (5) |
|
Rash |
25 (7) |
7 (2) |
|
Flatulence |
24 (7) |
11 (3) |
|
Rhinorrhea |
21 (6) |
15 (4) |
|
Influenza |
19 (5) |
8 (2) |
The safety profile from two pediatric trials in CF patients aged 6 through 11 years who are homozygous for the F508del-CFTR mutation, a 24-week, open-label, multicenter safety trial in 58 patients (Trial 3) and a 24-week, placebo- controlled, clinical trial (Trial 4) in 204 patients (103 received lumacaftor 200 mg/ivacaftor 250 mg every 12 hours and 101 received placebo), was similar to that observed in Trials 1 and 2. Adverse reactions that are not listed in Table 3, and that occurred in ≥5% of lumacaftor/ivacaftor-treated patients with an incidence of ≥3% higher than placebo included: productive cough (17.5% vs 5.9%), nasal congestion (16.5% vs 7.9%), headache (12.6% vs 8.9%), abdominal pain upper (12.6% vs 6.9%), and sputum increased (10.7% vs 2.0%).
In a 24-week, open-label, multicenter, study in 60 patients aged 2 through 5 years with CF who are homozygous for the F508del-CFTR mutation (Trial 6) the safety profile was similar to that observed in studies in patients aged 6 years and older [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
In a 24-week, open-label, multicenter, study in 46 patients aged 1 through 2 years with CF who are homozygous for the F508del-CFTR mutation (Trial 7) the safety profile was similar to that observed in studies in patients aged 2 years and older [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)].
Additional information on selected adverse reactions from trials is detailed below:
Description of Selected Adverse Drug Reactions
Liver-related Adverse Reactions
In Trials 1 and 2, the incidence of maximum transaminase (ALT or AST) levels
8, >5, and >3 × ULN elevations were similar between patients treated with ORKAMBI and those who received placebo. Three patients who received ORKAMBI had liver-related serious adverse reactions, including two reported as transaminase elevations and one as hepatic encephalopathy, compared to none in the placebo group. Of these three, one had elevated transaminases (>3 × ULN) associated with bilirubin elevation >2 × ULN. Following discontinuation or interruption of ORKAMBI, transaminases decreased to <3 × ULN.
Among six patients with pre-existing cirrhosis and/or portal hypertension who received ORKAMBI, worsening liver function with increased ALT, AST, bilirubin, and hepatic encephalopathy was observed in one patient. The event occurred within five days of the start of dosing and resolved following discontinuation of ORKAMBI [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2)].
During the 24-week, open-label, clinical trial in 58 patients aged 6 through 11 years (Trial 3), the incidence of maximum transaminase (ALT or AST) levels
8, >5, and >3 × ULN was 5%, 9%, and 19%. No patients had total bilirubin levels >2 × ULN. Lumacaftor/ivacaftor dosing was maintained or successfully resumed after interruption in all patients with transaminase elevations, except one patient who discontinued treatment permanently.
During the 24-week, placebo-controlled, clinical trial in 204 patients aged 6 through 11 years (Trial 4), the incidence of maximum transaminase (ALT or AST) levels >8, >5, and >3 × ULN was 1%, 5%, and 13% in the lumacaftor/ivacaftor patients, and 2%, 3%, and 8% in the placebo-treated patients. No patients had total bilirubin levels >2 × ULN. Two patients in the lumacaftor/ivacaftor group and two patients in the placebo group discontinued treatment permanently due to transaminase elevations.
During the 24-week, open-label, clinical trial in 60 patients aged 2 through 5 years (Trial 6), the incidence of maximum transaminase (ALT or AST) levels >8,
5, and >3 × ULN was 8.3% (5/60), 11.7% (7/60), and 15.0% (9/60). No patients had total bilirubin levels >2 × ULN. Three patients discontinued lumacaftor/ivacaftor treatment permanently due to transaminase elevations.
During the 24-week, open-label, clinical trial in 46 patients aged 1 through 2 years (Trial 7), the incidence of maximum transaminase (ALT or AST) levels >8,
5, and >3 × ULN was 2.2% (1/46), 4.3% (2/46), and 10.9% (5/46), respectively. No patients had total bilirubin levels >2 × ULN. One patient discontinued lumacaftor/ivacaftor treatment permanently due to transaminase elevations.
Respiratory Adverse Reactions
In Trials 1 and 2, the incidence of respiratory symptom-related adverse reactions (e.g., chest discomfort, dyspnea, and respiration abnormal) was more common in patients treated with ORKAMBI (22%) compared to patients who received placebo (14%). The incidence of these adverse reactions was more common in patients treated with ORKAMBI with lower pre-treatment FEV1. In patients treated with ORKAMBI, the majority of the events began during the first week of treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
During the 24-week, open-label, clinical trial in 46 patients aged 12 years and older (Trial 5) with advanced lung disease (ppFEV1 <40) [mean ppFEV1 29.1 at baseline (range: 18.3 to 42.0)], the incidence of respiratory symptom- related adverse reactions was 65% [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
During the 24-week, open-label, clinical trial (Trial 3) in 58 patients aged 6 through 11 years (mean baseline ppFEV1 was 91.4), the incidence of respiratory symptom-related adverse reactions was 3% (2/58).
During the 24-week, placebo-controlled, clinical trial (Trial 4) in patients aged 6 through 11 years [mean ppFEV1 89.8 at baseline (range: 48.6 to 119.6)], the incidence of respiratory symptom-related adverse reactions was 11% in lumacaftor/ivacaftor patients and 9% in placebo patients. A decline in ppFEV1 at initiation of therapy was observed during serial post-dose spirometry assessments. The absolute change from pre-dose at 4-6 hours post-dose was -7.7 on Day 1 and -1.3 on Day 15 in lumacaftor/ivacaftor patients. The post-dose decline was resolved by Week 16.
Menstrual Abnormalities
In Trials 1 and 2, the incidence of combined menstrual abnormality adverse reactions (e.g., amenorrhea, dysmenorrhea, menorrhagia, menstrual irregular) was more common in female patients treated with ORKAMBI (10%) compared to placebo (2%). These events occurred more frequently in the subset of female patients treated with ORKAMBI who were using hormonal contraceptives (27%) compared to those not using hormonal contraceptives (3%) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6) and Drug Interactions (7.11)].
Increased Blood Pressure
In Trials 1 and 2, adverse reactions related to increases in blood pressure (e.g., hypertension, blood pressure increased) were reported in 1.1% (4/369) of patients treated with ORKAMBI and in no patients who received placebo.
The proportion of patients who experienced a systolic blood pressure value
140 mmHg or a diastolic blood pressure >90 mmHg on at least two occasions was 3.6% and 2.2% in patients treated with ORKAMBI, respectively, compared with 1.6% and 0.5% in patients who received placebo [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post approval use of ORKAMBI. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Hepatobiliary: liver function decompensation including liver failure leading to death in patients with pre-existing cirrhosis with portal hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Immune System Disorders: anaphylaxis, angioedema
The most common adverse reactions to ORKAMBI (occurring in ≥5% of patients with CF homozygous for the F508del mutation in the CFTR gene) were dyspnea, nasopharyngitis, nausea, diarrhea, upper respiratory tract infection, fatigue, respiration abnormal, blood creatine phosphokinase increased, rash, flatulence, rhinorrhea, influenza. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated at 1-877-634-8789 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No studies of carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, or impairment of fertility were conducted with ORKAMBI; however, studies are available for individual components, lumacaftor and ivacaftor, as described below.
Lumacaftor
A two-year study in Sprague-Dawley rats and a 26-week study in transgenic Tg.rasH2 mice were conducted to assess carcinogenic potential of lumacaftor. No evidence of tumorigenicity was observed in rats at lumacaftor oral doses up to 1000 mg/kg/day (approximately 5 and 13 times the MRHD on a lumacaftor AUC basis in males and females, respectively). No evidence of tumorigenicity was observed in Tg.rasH2 mice at lumacaftor oral doses up to 1500 and 2000 mg/kg/day in female and male mice, respectively. Lumacaftor was negative for genotoxicity in the following assays: Ames test for bacterial gene mutation, in vitro chromosomal aberration assay in Chinese hamster ovary cells, and in vivo mouse micronucleus test.
Lumacaftor had no effects on fertility and reproductive performance indices in male and female rats at an oral dose of 1000 mg/kg/day (approximately 3 and 8 times, respectively, the MRHD on a lumacaftor AUC basis).
Ivacaftor
Two-year studies were conducted in mice and rats to assess carcinogenic potential of ivacaftor. No evidence of tumorigenicity was observed in mice and rats at ivacaftor oral doses up to 200 mg/kg/day and 50 mg/kg/day, respectively (approximately equivalent to 3 and 10 times the MRHD based on summed AUCs of ivacaftor and its metabolites).
Ivacaftor was negative for genotoxicity in the following assays: Ames test for bacterial gene mutation, in vitro chromosomal aberration assay in Chinese hamster ovary cells, and in vivo mouse micronucleus test.
Ivacaftor impaired fertility and reproductive performance indices in male and female rats at an oral dose of 200 mg/kg/day (approximately 15 and 7 times the MRHD based on summed AUCs of ivacaftor and its metabolites). Increases in prolonged diestrus were observed in females at 200 mg/kg/day. Ivacaftor also increased the number of females with all nonviable embryos and decreased corpora lutea, implantations, and viable embryos in rats at 200 mg/kg/day (approximately 7 times the MRHD based on summed AUCs of ivacaftor and its metabolites) when dams were dosed prior to and during early pregnancy. These impairments of fertility and reproductive performance in male and female rats at 200 mg/kg/day were attributed to severe toxicity. No effects on male or female fertility and reproductive performance indices were observed at an oral dose of ≤100 mg/kg/day (approximately 8 and 5 times the MRHD based on summed AUCs of ivacaftor and its metabolites).
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
ORKAMBI (lumacaftor 200 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg) is supplied as pink, oval-shaped tablets; each tablet contains 200 mg of lumacaftor and 125 mg of ivacaftor, printed with "2V125" in black ink on one side and plain on the other, and is packaged as follows:
|
112–count tablet box containing a 4-week supply (4 weekly cartons of 7 daily blister strips with 4 tablets per strip). |
NDC 51167-809-01 |
ORKAMBI (lumacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg) is supplied as pink, oval-shaped tablets; each tablet contains 100 mg of lumacaftor and 125 mg of ivacaftor, printed with "1V125" in black ink on one side and plain on the other, and is packaged as follows:
|
112–count tablet box containing a 4-week supply (4 weekly cartons of 7 daily blister strips with 4 tablets per strip). |
NDC 51167-700-02 |
ORKAMBI (lumacaftor/ivacaftor) oral granules are supplied as small white to off-white granules and enclosed in unit-dose packets as follows:
|
56-count carton (contains 56 unit-dose packets of lumacaftor 75 mg/ivacaftor 94 mg per packet) |
NDC 51167-122-01 |
|
56-count carton (contains 56 unit-dose packets of lumacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg per packet) |
NDC 51167-900-01 |
|
56-count carton (contains 56 unit-dose packets of lumacaftor 150 mg/ivacaftor 188 mg per packet) |
NDC 51167-500-02 |
Store at 20°C - 25°C (68°F - 77°F); excursions permitted to 15°C - 30°C (59°F
- 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
SPL PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT SECTION
|
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. |
Revised: 08/2023 | ||
|
PATIENT INFORMATION | |||
|
What is ORKAMBI?
It is not known if ORKAMBI is safe and effective in children under 1 year of age. | |||
|
Before taking ORKAMBI, tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions, including if you: | |||
| |||
|
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. ORKAMBI may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how ORKAMBI works. The dose of ORKAMBI may need to be adjusted when taken with certain medicines. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for a list of these medicines if you are not sure. Especially tell your doctor if you take: | |||
| |||
|
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your doctor and pharmacist when you get a new medicine. | |||
|
How should I take ORKAMBI? | |||
| |||
|
What should I avoid while taking ORKAMBI? | |||
|
What are the possible side effects of ORKAMBI? ORKAMBI can cause serious side effects, including: | |||
|
*Worsening of liver functionin people with severe liver disease. The worsening of liver function can be serious or cause death. Talk to your doctor if you have been told you have liver disease as your doctor may need to adjust the dose of ORKAMBI. *High liver enzymes in the blood, which can be a sign of liver injury in people receiving ORKAMBI. Your doctor will do blood tests to check your liver: | |||
|
Call your doctor right away if you have any of the following symptoms of liver problems: | |||
|
| ||
|
*Serious Allergic Reactions can happen to people who are treated with ORKAMBI. Call your doctor or go to the emergency room right away if you have any symptoms of an allergic reaction. Symptoms of an allergic reaction may include: | |||
|
| ||
|
*Breathing problemssuch as trouble breathing, shortness of breath or chest tightness in people when starting ORKAMBI, especially in people who have poor lung function. If you have poor lung function, your doctor may monitor you more closely when you start ORKAMBI. Call your doctor right away if you have trouble breathing, shortness of breath or chest tightness. *An increase in blood pressurein some people receiving ORKAMBI. Your doctor should monitor your blood pressure during treatment with ORKAMBI. Call your doctor right away if you have an increase in blood pressure. *Abnormality of the eye lens (cataract) in some children and adolescents receiving ORKAMBI. If you are a child or adolescent, your doctor should perform eye examinations before and during treatment with ORKAMBI to look for cataracts. The most common side effects of ORKAMBI include: | |||
|
| ||
|
Additional side effects in children Side effects seen in children are similar to those seen in adults and adolescents. Additional common side effects seen in children include: | |||
|
| ||
|
Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not
go away. | |||
|
How should I store ORKAMBI? | |||
| |||
|
Keep ORKAMBI and all medicines out of the reach of children. | |||
|
General information about the safe and effective use of ORKAMBI. Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use ORKAMBI for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give ORKAMBI to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about ORKAMBI that is written for health professionals. | |||
|
What are the ingredients in ORKAMBI? ORKAMBI tablets: The tablet film coat contains: carmine, FD&C Blue #1, FD&C Blue #2, polyethylene glycol, polyvinyl alcohol, talc, and titanium dioxide. The printing ink contains: ammonium hydroxide, iron oxide black, propylene
glycol, and shellac. | |||
|
Manufactured for: Vertex Pharmaceuticals Incorporated; 50 Northern Avenue,
Boston, MA 02210 |
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage in Adults and Pediatric Patients Aged 1 Year and
Older
The recommended dosage of ORKAMBI in adults and pediatric patients aged one year and older is based on patient's age and weight as described in Table 1.
Table 1: Recommended Oral Dosage of ORKAMBI in Patients Aged 1 Year and Older|
Age Group |
Weight |
ORKAMBI Daily Dose (every 12 hours) | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Morning Dose |
Evening Dose | ||
|
1 through 2 years |
7 kg to <9 kg |
1 packet of lumacaftor 75 mg/ivacaftor 94 mg oral granules |
1 packet of lumacaftor 75 mg/ivacaftor 94 mg oral granules |
|
9 kg to <14 kg |
1 packet of lumacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg oral granules |
1 packet of lumacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg oral granules | |
|
≥14 kg |
1 packet of lumacaftor 150 mg/ivacaftor 188 mg oral granules |
1 packet of lumacaftor 150 mg/ivacaftor 188 mg oral granules | |
|
2 through 5 years |
<14 kg |
1 packet of lumacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg oral granules |
1 packet of lumacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg oral granules |
|
≥14 kg |
1 packet of lumacaftor 150 mg/ivacaftor 188 mg oral granules |
1 packet of lumacaftor 150 mg/ivacaftor 188 mg oral granules | |
|
6 through 11 years |
|
2 tablets of lumacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg |
2 tablets of lumacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg |
|
12 years and older |
|
2 tablets of lumacaftor 200 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg |
2 tablets of lumacaftor 200 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg |
Administration Instructions for ORKAMBI Oral Granules
The entire content of each packet of oral granules should be mixed with one teaspoon (5 mL) of age-appropriate soft food or liquid and the mixture completely consumed. Some examples of soft foods or liquids include puréed fruits or vegetables, flavored yogurt or pudding, applesauce, water, milk, breast milk, infant formula or juice. Food should be at room temperature or below. Each packet is for single use only. Once mixed, the product has been shown to be stable for one hour, and therefore should be ingested during this period.
Administration with Fat-Containing Food for ORKAMBI Tablets and Oral Granules
A fat-containing meal or snack should be consumed just before or just after dosing for all formulations. Examples of appropriate fat-containing foods include eggs, avocados, nuts, butter, peanut butter, cheese pizza, breast milk, infant formula, whole-milk dairy products (such as whole milk, cheese, and yogurt), etc.
Missed Dose
If a patient misses a dose and remembers the missed dose within 6 hours, the patient should take the dose with fat-containing food. If more than 6 hours elapsed after the usual dosing time, the patient should skip that dose and resume the normal schedule for the following dose. A double dose should not be taken to make up for the forgotten dose [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Patient Counseling Information (17)].
2.2 Dosage Adjustment for Patients with Hepatic Impairment
For dose adjustment for patients with hepatic impairment, refer to Table 2.
Studies have not been conducted in patients with severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class C), but exposure is expected to be higher than in patients with moderate hepatic impairment. Therefore, use with caution at a maximum dose of 1 tablet in the morning and 1 tablet in the evening or less frequently, or 1 packet of oral granules once daily or less frequently in patients with severe hepatic impairment after weighing the risks and benefits of treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), and Patient Counseling Information (17)].
Table 2: Recommended Dosage for Patients with Hepatic Impairment|
Age Group |
Weight |
Morning Dose |
Evening Dose | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||
|
Mild (Child-Pugh Class A) |
1 through 2 years |
7 kg to <9 kg |
1 packet of lumacaftor 75 mg/ivacaftor 94 mg oral granules |
1 packet of lumacaftor 75 mg/ivacaftor 94 mg oral granules |
|
9 kg to <14 kg |
1 packet of lumacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg oral granules |
1 packet of lumacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg oral granules | ||
|
≥14 kg |
1 packet of lumacaftor 150 mg/ivacaftor 188 mg oral granules |
1 packet of lumacaftor 150 mg/ivacaftor 188 mg oral granules | ||
|
2 through 5 years |
<14 kg |
1 packet of lumacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg oral granules |
1 packet of lumacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg oral granules | |
|
≥14 kg |
1 packet of lumacaftor 150 mg/ivacaftor 188 mg oral granules |
1 packet of lumacaftor 150 mg/ivacaftor 188 mg oral granules | ||
|
6 through 11 years |
|
2 tablets of lumacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg |
2 tablets of lumacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg | |
|
12 years and older |
|
2 tablets of lumacaftor 200 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg |
2 tablets of lumacaftor 200 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg | |
|
Moderate (Child-Pugh Class B) |
1 through 2 years |
7 kg to <9 kg |
1 packet of lumacaftor 75 mg/ivacaftor 94 mg oral granules |
1 packet of lumacaftor 75 mg/ivacaftor 94 mg oral granulesevery other day |
|
9 kg to <14 kg |
1 packet of lumacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg oral granules |
1 packet of lumacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg oral granulesevery other day | ||
|
≥14 kg |
1 packet of lumacaftor 150 mg/ivacaftor 188 mg oral granules |
1 packet of lumacaftor 150 mg/ivacaftor 188 mg oral granulesevery other day | ||
|
2 through 5 years |
<14 kg |
1 packet of lumacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg oral granules |
1 packet of lumacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg oral granulesevery other day | |
|
≥14 kg |
1 packet of lumacaftor 150 mg/ivacaftor 188 mg oral granules |
1 packet of lumacaftor 150 mg/ivacaftor 188 mg oral granulesevery other day | ||
|
6 through 11 years |
|
2 tablets of lumacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg |
1 tablet of lumacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg | |
|
12 years and older |
|
2 tablets of lumacaftor 200 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg |
1 tablet of lumacaftor 200 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg | |
|
Severe (Child-Pugh Class C) |
1 through 2 years |
7 kg to <9 kg |
1 packet of lumacaftor 75 mg/ivacaftor 94 mg oral granules* |
N/A |
|
9 kg to <14 kg |
1 packet of lumacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg oral granules* | |||
|
≥14 kg |
1 packet of lumacaftor 150 mg/ivacaftor 188 mg oral granules* | |||
|
2 through 5 years |
<14 kg |
1 packet of lumacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg oral granules* | ||
|
≥14 kg |
1 packet of lumacaftor 150 mg/ivacaftor 188 mg oral granules* | |||
|
6 through 11 years |
|
1 tablet of lumacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg* |
1 tablet of lumacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg* | |
|
12 years and older |
|
1 tablet of lumacaftor 200 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg* |
1 tablet of lumacaftor 200 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg* |
2.3 Dosage Adjustment for Patients Taking CYP3A Inhibitors
No dose adjustment is necessary when CYP3A inhibitors are initiated in patients already taking ORKAMBI. However, when initiating ORKAMBI in patients currently taking strong CYP3A inhibitors, reduce the ORKAMBI dosage for the first week of treatment based on age as follows [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and Drug Interactions (7.1)]:
- 1 through 5 years of age: 1 packet of granules every other day
- 6 years of age and older: 1 tablet daily
Following this one-week period, resume the recommended daily dosage.
If ORKAMBI is interrupted for more than one-week and then re-initiated while taking strong CYP3A inhibitors, reduce the ORKAMBI dosage for the first week of treatment re-initiation based on age as follows:
- 1 through 5 years of age: 1 packet of granules every other day
- 6 years of age and older: 1 tablet daily
Following this one-week period, resume the recommended daily dosage.
|
Age Group |
Weight |
Dose |
Administration |
|---|---|---|---|
|
1 through 2 years |
7 kg to < 9 kg |
1 packet of lumacaftor 75 mg/ivacaftor 94 mg granules |
Mixed with one teaspoon (5 mL) of soft food or liquid and administered orally every 12 hours with fat-containing food |
|
9 kg to < 14 kg |
1 packet of lumacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg granules | ||
|
≥14 kg |
1 packet of lumacaftor 150 mg/ivacaftor 188 mg granules | ||
|
2 through 5 years |
<14 kg |
1 packet of lumacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg granules | |
|
≥14 kg |
1 packet of lumacaftor 150 mg/ivacaftor 188 mg granules | ||
|
6 through 11 years |
|
2 tablets of lumacaftor 100 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg |
Taken orallyevery 12 hours with fat-containing food |
|
12 years and older |
|
2 tablets of lumacaftor 200 mg/ivacaftor 125 mg |
- Reduce dosage in patients with moderate or severe hepatic impairment. (2.2, 8.6, 12.3)
- When initiating ORKAMBI in patients taking strong CYP3A inhibitors, reduce ORKAMBI dosage for the first week of treatment. (2.3, 7.1, 12.3)
