Lidocaine
LIDOCAINE PATCH 5%
0bef12dd-6cea-d12b-e063-6394a90a002e
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Sep 9, 2025
Golden State Medical Supply, Inc.
DUNS: 603184490
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
lidocaine
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (16)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Package Label - Principal Display Panel – 30 Count Carton, Lidocaine Patch

DESCRIPTION SECTION
DESCRIPTION
LIDOCAINE PATCH 5% is comprised of an adhesive material containing 5% lidocaine, which is applied to a non‑woven polyester felt backing and covered with a polyethylene terephthalate (PET) film release liner. The release liner is removed prior to application to the skin. The size of the patch is 10 cm x 14 cm.
Lidocaine is chemically designated as acetamide, 2‑(diethylamino)‑N‑(2,6‑ dimethylphenyl), has an octanol: water partition ratio of 43 at pH 7.4, and has the following structure:

Each adhesive patch contains 700 mg of lidocaine (50 mg per gram adhesive) in an aqueous base. It also contains the following inactive ingredients: dihydroxyaluminum aminoacetate, disodium edetate, gelatin, glycerin, kaolin, methylparaben, polyacrylic acid, polyvinyl alcohol, propylene glycol, propylparaben, sodium carboxymethylcellulose, sodium polyacrylate, D-sorbitol, tartaric acid, and urea.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Pharmacodynamics
Lidocaine is an amide-type local anesthetic agent and is suggested to stabilize neuronal membranes by inhibiting the ionic fluxes required for the initiation and conduction of impulses.
The penetration of lidocaine into intact skin after application of LIDOCAINE PATCH 5% is sufficient to produce an analgesic effect, but less than the amount necessary to produce a complete sensory block.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
The amount of lidocaine systemically absorbed from LIDOCAINE PATCH 5% is directly related to both the duration of application and the surface area over which it is applied. In a pharmacokinetic study, three LIDOCAINE PATCH 5% patches were applied over an area of 420 cm 2of intact skin on the back of normal volunteers for 12 hours. Blood samples were withdrawn for determination of lidocaine concentration during the application and for 12 hours after removal of patches. The results are summarized in Table 1.
|
Table 1 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
LIDOCAINE PATCH 5% |
Application Site |
Area |
Dose Absorbed (mg) |
C max |
T max |
|
3 patches |
Back |
420 |
64 ± 32 |
0.13 ± 0.06 |
11 hr |
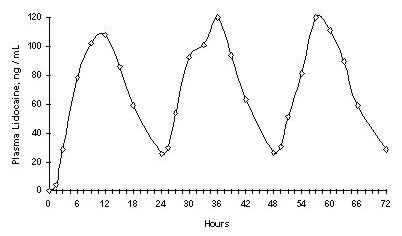
When LIDOCAINE PATCH 5% is used according to the recommended dosing instructions, only 3 ± 2% of the dose applied is expected to be absorbed. At least 95% (665 mg) of lidocaine will remain in a used patch. Mean peak blood concentration of lidocaine is about 0.13 mcg/mL (about 1/10 of the therapeutic concentration required to treat cardiac arrhythmias). Repeated application of three patches simultaneously for 12 hours (recommended maximum daily dose), once per day for three days, indicated that the lidocaine concentration does not increase with daily use. The mean plasma pharmacokinetic profile for the 15 healthy volunteers is shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1
Mean lidocaine blood concentrations after three consecutive daily applications of three LIDOCAINE PATCH 5% patches simultaneously for 12 hours per day in healthy volunteers (n = 15).
Distribution
****When lidocaine is administered intravenously to healthy volunteers, the
volume of distribution is 0.7 to 2.7 L/kg (mean 1.5 ± 0.6 SD, n=15). At
concentrations produced by application of LIDOCAINE PATCH 5%, lidocaine is
approximately 70% bound to plasma proteins, primarily alpha‑1‑acid
glycoprotein. At much higher plasma concentrations (1 to 4 mcg/mL of free
base), the plasma protein binding of lidocaine is concentration dependent.
Lidocaine crosses the placental and blood brain barriers, presumably by
passive diffusion.
Metabolism
****It is not known if lidocaine is metabolized in the skin. Lidocaine is
metabolized rapidly by the liver to a number of metabolites, including
monoethylglycinexylidide (MEGX) and glycinexylidide (GX), both of which have
pharmacologic activity similar to, but less potent than that of lidocaine. A
minor metabolite, 2, 6-xylidine, has unknown pharmacologic activity but is
carcinogenic in rats. The blood concentration of this metabolite is negligible
following application of LIDOCAINE PATCH 5%. Following intravenous
administration, MEGX and GX concentrations in serum range from 11 to 36% and
from 5 to 11% of lidocaine concentrations, respectively.
Excretion
****Lidocaine and its metabolites are excreted by the kidneys. Less than 10%
of lidocaine is excreted unchanged. The half-life of lidocaine elimination
from the plasma following IV administration is 81 to 149 minutes (mean 107 ±
22 SD, n = 15). The systemic clearance is 0.33 to 0.90 L/min (mean 0.64 ± 0.18
SD, n = 15).
