Zafirlukast
Zafirlulkast Tablets Rx Only
f89a821d-396f-a3aa-e053-6294a90a4577
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Jul 31, 2025
AvKARE
DUNS: 796560394
Products 2
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
zafirlukast
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (8)
zafirlukast
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (8)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL


DESCRIPTION SECTION
DESCRIPTION
Zafirlukast is a synthetic, selective peptide leukotriene receptor antagonist (LTRA), with the chemical name 4-(5-cyclopentyloxy-carbonylamino-1-methyl- indol-3-ylmethyl)-3-methoxy-N-o-tolylsulfonylbenzamide. The molecular weight of zafirlukast is 575.7 and the structural formula is:
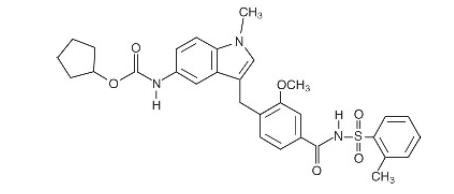
The empirical formula is: C 31H 33N 3O 6S
Zafirlukast, a fine white to pale yellow amorphous powder, is practically insoluble in water. It is slightly soluble in methanol and freely soluble in tetrahydrofuran, dimethylsulfoxide, and acetone.
Zafirlukast is supplied as 10 and 20 mg tablets for oral administration.
**Inactive Ingredients:**Film-coated tablets containing croscarmellose sodium, lactose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, povidone, hypromellose, and titanium dioxide.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Mechanism of Action:
Zafirlukast is a selective and competitive receptor antagonist of leukotriene D 4 and E 4 (LTD 4 and LTE 4), components of slow-reacting substance of anaphylaxis (SRSA). Cysteinyl leukotriene production and receptor occupation have been correlated with the pathophysiology of asthma, including airway edema, smooth muscle constriction, and altered cellular activity associated with the inflammatory process, which contribute to the signs and symptoms of asthma. Patients with asthma were found in one study to be 25 to 100 times more sensitive to the bronchoconstricting activity of inhaled LTD 4 than nonasthmatic subjects.
In vitro studies demonstrated that zafirlukast antagonized the contractile activity of three leukotrienes (LTC 4, LTD 4 and LTE 4) in conducting airway smooth muscle from laboratory animals and humans. Zafirlukast prevented intradermal LTD 4-induced increases in cutaneous vascular permeability and inhibited inhaled LTD 4-induced influx of eosinophils into animal lungs. Inhalational challenge studies in sensitized sheep showed that zafirlukast suppressed the airway responses to antigen; this included both the early- and late-phase response and the nonspecific hyperresponsiveness.
In humans, zafirlukast inhibited bronchoconstriction caused by several kinds of inhalational challenges. Pretreatment with single oral doses of zafirlukast inhibited the bronchoconstriction caused by sulfur dioxide and cold air in patients with asthma. Pretreatment with single doses of zafirlukast attenuated the early- and late-phase reaction caused by inhalation of various antigens such as grass, cat dander, ragweed, and mixed antigens in patients with asthma. Zafirlukast also attenuated the increase in bronchial hyperresponsiveness to inhaled histamine that followed inhaled allergen challenge.
Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Bioavailability:
Absorption
Zafirlukast is rapidly absorbed following oral administration. Peak plasma concentrations are generally achieved 3 hours after oral administration. The absolute bioavailability of zafirlukast is unknown. In two separate studies, one using a high fat and the other a high protein meal, administration of zafirlukast with food reduced the mean bioavailability by approximately 40%.
Distribution
Zafirlukast is more than 99% bound to plasma proteins, predominantly albumin. The degree of binding was independent of concentration in the clinically relevant range. The apparent steady-state volume of distribution (Vss/F) is approximately 70 L, suggesting moderate distribution into tissues. Studies in rats using radiolabeled zafirlukast indicate minimal distribution across the blood-brain barrier.
Metabolism
Zafirlukast is extensively metabolized. The most common metabolic products are hydroxylated metabolites which are excreted in the feces. The metabolites of zafirlukast identified in plasma are at least 90 times less potent as LTD 4 receptor antagonists than zafirlukast in a standard in vitro test of activity. In vitro studies using human liver microsomes showed that the hydroxylated metabolites of zafirlukast excreted in the feces are formed through the cytochrome P450 2C9 (CYP2C9) pathway. Additional in vitro studies utilizing human liver microsomes show that zafirlukast inhibits the cytochrome P450 CYP3A4 and CYP2C9 isoenzymes at concentrations close to the clinically achieved total plasma concentrations (seeDrug Interactions).
Excretion
The apparent oral clearance (CL/f) of zafirlukast is approximately 20 L/h. Studies in the rat and dog suggest that biliary excretion is the primary route of excretion. Following oral administration of radiolabeled zafirlukast to volunteers, urinary excretion accounts for approximately 10% of the dose and the remainder is excreted in feces. Zafirlukast is not detected in urine.
In the pivotal bioequivalence study, the mean terminal half-life of zafirlukast is approximately 10 hours in both normal adult subjects and patients with asthma. In other studies, the mean plasma half-life of zafirlukast ranged from approximately 8 to 16 hours in both normal subjects and patients with asthma. The pharmacokinetics of zafirlukast are approximately linear over the range from 5 mg to 80 mg. Steady-state plasma concentrations of zafirlukast are proportional to the dose and predictable from single-dose pharmacokinetic data. Accumulation of zafirlukast in the plasma following twice-daily dosing is approximately 45%.
The pharmacokinetic parameters of zafirlukast 20 mg administered as a single dose to 36 male volunteers are shown with the table below.
Mean (% Coefficient of Variation) pharmacokinetic parameters of zafirlukast following single 20 mg oral dose administration to male volunteers (n=36)|
** C****max** |
** tmax1** |
** AUC** |
** t****1/2** |
** CL/f** | |
|
326 (31.0) |
2 (0.5 - 5.0) |
1137 (34) |
13.3 (75.6) |
19.4 (32) |
1.Median and range
Special Populations
Gender: The pharmacokinetics of zafirlukast are similar in males and females. Weight-adjusted apparent oral clearance does not differ due to gender.
Race: No differences in the pharmacokinetics of zafirlukast due to race have been observed.
Elderly: The apparent oral clearance of zafirlukast decreases with age. In patients above 65 years of age, there is an approximately 2 to 3 fold greater C max and AUC compared to young adult patients.
Children: Following administration of a single 20 mg dose of zafirlukast to 20 boys and girls between 7 and 11 years of age, and in a second study, to 29 boys and girls between 5 and 6 years of age, the following pharmacokinetic parameters were obtained:
|
** Parameter** |
** Children age 5 to 6 years Mean (% Coefficient of Variation)** |
** Children age 7 to 11 years Mean (% Coefficient of Variation)** |
|
C max (ng/mL) |
756 (39%) |
601 (45%) |
|
AUC (ng•h/mL) |
2458 (34%) |
2027 (38%) |
|
t max (h) |
2.1 (61%) |
2.5 (55%) |
|
CL/f (L/h) |
9.2 (37%) |
11.4 (42%) |
Weight unadjusted apparent clearance was 11.4 L/h (42%) in the 7 to 11 year old children and 9.2 L/h (37%) in the 5 to 6 year old children, which resulted in greater systemic drug exposures than that obtained in adults for an identical dose. To maintain similar exposure levels in children compared to adults, a dose of 10 mg twice daily is recommended in children 5 to 11 years of age (seeDOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Zafirlukast disposition was unchanged after multiple dosing (20 mg twice daily) in children and the degree of accumulation in plasma was similar to that observed in adults.
Hepatic Insufficiency: In a study of patients with hepatic impairment (biopsy- proven cirrhosis), there was a reduced clearance of zafirlukast resulting in a 50 to 60% greater C max and AUC compared to normal subjects.
Renal Insufficiency: Based on a cross-study comparison, there are no apparent differences in the pharmacokinetics of zafirlukast between renally-impaired patients and normal subjects.
Drug-Drug Interactions:The following drug interaction studies have been conducted with zafirlukast (seePRECAUTIONS, Drug Interactions).
- Coadministration of multiple doses of zafirlukast (160 mg/day) to steady-state with a single 25 mg dose of warfarin (a substrate of CYP2C9) resulted in a significant increase in the mean AUC (+63%) and half-life (+36%) of S-warfarin. The mean prothrombin time increased by approximately 35%. The pharmacokinetics of zafirlukast were unaffected by coadministration with warfarin.
- Coadministration of zafirlukast (80 mg/day) at steady-state with a single dose of a liquid theophylline preparation (6 mg/kg) in 13 asthmatic patients, 18 to 44 years of age, resulted in decreased mean plasma concentrations of zafirlukast by approximately 30%, but no effect on plasma theophylline concentrations was observed.
- Coadministration of zafirlukast (20 mg/day) or placebo at steady-state with a single dose of sustained release theophylline preparation (16 mg/kg) in 16 healthy boys and girls (6 through 11 years of age) resulted in no significant differences in the pharmacokinetic parameters of theophylline.
- Coadministration of zafirlukast dosed at 40 mg twice daily in a single-blind, parallel-group, 3-week study in 39 healthy female subjects taking oral contraceptives, resulted in no significant effect on ethinyl estradiol plasma concentrations or contraceptive efficacy.
- Coadministration of zafirlukast (40 mg/day) with aspirin (650 mg four times daily) resulted in mean increased plasma concentrations of zafirlukast by approximately 45%.
- Coadministration of a single dose of zafirlukast (40 mg) with erythromycin (500 mg three times daily for 5 days) to steady-state in 11 asthmatic patients resulted in decreased mean plasma concentrations of zafirlukast by approximately 40% due to a decrease in zafirlukast bioavailability.
- Coadministration of zafirlukast with fluconazole, a moderate CYP2C9 inhibitor, resulted in increased plasma levels of zafirlukast, by approximately 58% (90% CI:28, 95). The clinical significance of this interaction is unknown. Zafirlukast exposure is likely to be increased by other moderate and strong CYP2C9 inhibitors. Coadministration of zafirlukast with itraconazole, a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor, caused no change in plasma levels of zafirlukast.
Clinical Studies:
Three U.S. double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, 13-week clinical trials in 1380 adults and children 12 years of age and older with mild-to- moderate asthma demonstrated that zafirlukast improved daytime asthma symptoms, nighttime awakenings, mornings with asthma symptoms, rescue beta 2-agonist use, FEV 1, and morning peak expiratory flow rate. In these studies, the patients had a mean baseline FEV 1 of approximately 75% of predicted normal and a mean baseline beta 2-agonist requirement of approximately 4 to 5 puffs of albuterol per day. The results of the largest of the trials are shown in the table below.
Mean Change from Baseline at Study End Point|
** Zafirlukast 20 mg twice daily** |
** Placebo** | |
|
Daytime Asthma symptom score |
-0.44 1 |
-0.25 |
|
Nighttime Awakenings |
-1.27 1 |
-0.43 |
|
Mornings with Asthma Symptoms |
-1.32 1 |
-0.75 |
|
Rescue β 2-agonist use |
-1.15 1 |
-0.24 |
|
FEV 1 (L) |
+0.15 1 |
+0.05 |
|
Morning PEFR (L/min) |
+22.06 1 |
+7.63 |
|
Evening PEFR (L/min) |
+13.12 |
+10.14 |
1. p<0.05, compared to placebo
In a second and smaller study, the effect of zafirlukast on most efficacy parameters was comparable to the active control (inhaled cromolyn sodium 1600 mcg four times per day) and superior to placebo at end point for decreasing rescue beta 2-agonist use (figure below).
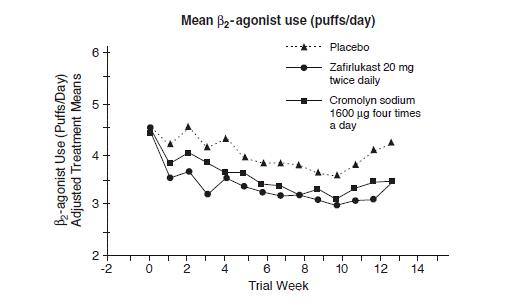
In these trials, improvement in asthma symptoms occurred within one week of initiating treatment with zafirlukast. The role of zafirlukast in the management of patients with more severe asthma, patients receiving antiasthma therapy other than as-needed, inhaled beta 2-agonists, or as an oral or inhaled corticosteroid-sparing agent remains to be fully characterized.
