Dextrose
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use DEXTROSE INJECTION (5% and 10%) safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for DEXTROSE INJECTION (5% and 10%). DEXTROSE Injection, for intravenous use Initial U.S. Approval: 1940
8b25b7e0-703e-4b43-a4eb-52863511602d
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Jun 18, 2025
ICU Medical, Inc.
DUNS: 118380146
ICU Medical Inc.
DUNS: 118380146
Products 3
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
dextrose monohydrate
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (2)
dextrose monohydrate
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (2)
dextrose monohydrate
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (2)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 500 mL Bag Label
500 mL
NDC 0990-7930-03
10% DEXTROSE
Injection, USP
EACH 100 mL CONTAINS DEXTROSE, HYDROUS 10 g IN
WATER FOR INJECTION.
505 mOsmol/LITER (CALC.)
pH 4.3 (3.2 to 6.5)
DEXTROSE SOLUTIONS WITHOUT SALTS SHOULD
NOT BE USED IN BLOOD TRANSFUSIONS BECAUSE
OF POSSIBLE ROULEAU FORMATION. ADDITIVES MAY
BE INCOMPATIBLE. CONSULT WITH PHARMACIST,
IF AVAILABLE. WHEN INTRODUCING ADDITIVES, USE
ASEPTIC TECHNIQUE, MIX THOROUGHLY AND DO NOT
STORE. SINGLE-DOSE CONTAINER. FOR INTRAVENOUS
OR SUBCUTANEOUS USE. USUAL DOSAGE: SEE INSERT.
STERILE, NONPYROGENIC. USE ONLY IF SOLUTION IS
CLEAR AND CONTAINER IS UNDAMAGED. MUST NOT BE
USED IN SERIES CONNECTIONS.
Rx ONLY
3
V
CONTAINS DEHP
icumedical
ICU Medical, Inc., Lake Forest, Illinois, 60045, USA
IM-4454

INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) is indicated as a source of water and calories in adult and pediatric patients, and may also be used as a diluent for reconstitution of a powder or liquid drug product.
Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) is indicated as a source of water and calories in adult and pediatric patients, and may also be used as a diluent for reconstitution of a powder or liquid drug product. (1)
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) is contraindicated in patients with:
- Clinically significant hyperglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Known hypersensitivity to dextrose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- Clinically significant hyperglycemia. (4)
- Known hypersensitivity to dextrose. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Neonatal Hypoglycemia
Neonates, especially preterm neonates with low birth weight, are at increased risk of developing hypoglycemia. Closely monitor blood glucose concentration during treatment with Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) to ensure adequate glycemic control in order to avoid potential long-term adverse effects.
5.2 Hyperglycemia and Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State
The use of Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) in patients with impaired glucose tolerance may worsen hyperglycemia. Administration of dextrose at a rate exceeding the patient's utilization rate may lead to hyperglycemia, coma, and death.
Hyperglycemia is associated with an increase in serum osmolality, resulting in osmotic diuresis, dehydration and electrolyte losses [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6), Use in Specific Populations (8.4)]. Patients with underlying CNS disease and renal impairment who receive dextrose infusions may be at greater risk of developing hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state.
Monitor blood glucose levels and treat hyperglycemia to maintain levels within normal limits while administering Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%). Insulin may be administered or adjusted to maintain optimal blood glucose levels during Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) administration.
5.3 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have been reported with Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) administration [see Adverse Reactions (6)]. Stop administration of Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) immediately if signs or symptoms of a hypersensitivity reaction develop. Initiate appropriate treatment as clinically indicated.
5.4 Phlebitis and Thrombosis
The infusion of hypertonic solutions into a peripheral vein may result in vein irritation, vein damage, and/or thrombosis [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)]. If thrombophlebitis develops, remove the catheter as soon as possible.
5.5 Hyponatremia
Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) may cause hyponatremia. Hyponatremia can lead to acute hyponatremic encephalopathy characterized by headache, nausea, seizures, lethargy, and vomiting. The risk of hospital-acquired hyponatremia is increased in younger pediatric patients, geriatric patients, patients treated with diuretics, and patients with cardiac or pulmonary failure or with the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH) (e.g., postoperative patients, patients concomitantly treated with arginine vasopressin analogs or certain antiepileptic, psychotropic, and cytotoxic drugs) [see Drug Interactions (7.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
Avoid Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) in patients with or at risk for hyponatremia. If use cannot be avoided, closely monitor serum sodium concentrations, chloride concentrations, fluid status, acid-base balance, and neurologic status [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
5.6 Electrolyte Imbalance and Fluid Overload
Electrolyte deficits, particularly serum potassium and phosphate, may occur during prolonged use of Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%).
Depending on the administered volume and the infusion rate, Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) can cause fluid overload, including pulmonary edema.
Avoid Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) in patients at risk for fluid and/or solute overload. If use cannot be avoided in these patients, monitor fluid balance, electrolyte concentrations, and acid-base balance, especially during prolonged use. Additional monitoring is recommended for patients with water and electrolyte disturbances that could be aggravated by increased glucose, insulin administration and/or free water load.
5.7 Refeeding Syndrome
Refeeding severely undernourished patients may result in refeeding syndrome, characterized by the intracellular shift of potassium, phosphorus, and magnesium as the patient becomes anabolic. Thiamine deficiency and fluid retention may also develop. To prevent these complications, monitor severely undernourished patients and slowly increase nutrient intake.
- Neonatal Hypoglycemia: Closely monitor blood glucose concentrations to ensure adequate glycemic control. (5.1)
- Hyperglycemia and Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State: Use with caution in patients with known subclinical or overt diabetes mellitus. (5.2)
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: Monitor for signs and symptoms and discontinue infusion immediately if reaction occurs. (5.3)
- Phlebitis and Thrombosis: Remove catheter as soon as possible if thrombophlebitis develops. (2.1, 5.4)
- Hyponatremia: Monitor serum sodium and chloride concentrations, fluid status, acid-base balance, and neurologic status. (5.5)
- Electrolyte Imbalance and Fluid Overload: Monitor changes in fluid balance, electrolyte concentrations, and acid-base balance during administration. (5.6)
- Refeeding Syndrome: Monitor laboratory parameters. (5.7)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Neonatal Hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hyperglycemia and Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Phlebitis and Thrombosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Hyponatremia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Electrolyte Imbalance and Fluid Overload [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Refeeding syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
The following adverse reactions associated with the use of Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) were identified in clinical studies or postmarketing reports. Because some of these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Administration site conditions: blister, erythema, extravasation, pain, phlebitis, vein damage, thrombosis
Immune system disorders: anaphylaxis, angioedema, bronchospasm, chills, hypotension, pruritis, pyrexia, rash
Cardiovascular disorders: cyanosis, volume overload
The most common adverse reactions are hyperglycemia, hypersensitivity reactions, hyponatremia, infection, both systemic and at the injection site, vein thrombosis or phlebitis, and electrolyte imbalance. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact ICU Medical, Inc. at 1-800-441-4100 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Drugs with Effects on Glycemic Control and Electrolyte Balance
Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) can affect glycemic control, vasopressin, and fluid and/or electrolyte balance [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.4, 5.5)]. Monitor patients' blood glucose concentrations, fluid balance, serum electrolyte concentrations, and acid-base balance.
Concomitant administration of Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) with drugs associated with hyponatremia may increase the risk of developing hyponatremia. Drugs associated with hyponatremia include diuretics and those that cause SIADH (e.g., selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), arginine vasopressin analogs, certain antiepileptic, psychotropic, and cytotoxic drugs). Avoid use of Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) in patients receiving drugs associated with hyponatremia. If use cannot be avoided, closely monitor serum sodium concentrations during concomitant use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Drugs with Effects on Glycemic Control and Electrolyte Balance: Monitor blood glucose concentrations, fluid balance, serum electrolyte concentrations, and acid-base balance. Avoid use of Dextrose Injection in patients receiving drugs associated with hyponatremia. (7.1)
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
IFU0000541
icumedical
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES SECTION
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
|
Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.2, 2.3) |
06/2025 |
|
Contraindications (4) |
06/2025 |
|
Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 5.5, 5.6, 5.7) |
06/2025 |
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Administration Instructions
Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) is intended for intravenous use.
- Use a peripheral vein to administer if the final dextrose concentration is 5% or less and the osmolarity is less than 900 mOsm/L.
- Consider using a central vein to administer hypertonic solutions with osmolarity of 900 mOsm/L or greater to avoid venous irritation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- Do not administer Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) simultaneously with blood products through the same administration set because of the possibility of pseudoagglutination or hemolysis.
- Use of a final filter is recommended during administration of parenteral solutions, where possible.
- Discard the unused portion.
- Avoid use with chemotherapy agents. Consult the specific chemotherapy agent prescribing information to determine the appropriate diluent.
2.2 Important Preparation Information
Visually inspect the Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) for particulate matter and discoloration. Do not administer Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) if the solution is cloudy, there are precipitates, or the container is damaged.
To reduce the risk of air embolism, adhere to the following preparation instructions for Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%):
- Use a non-vented infusion set or close the vent on a vented set.
- Use a dedicated line without any connections (do not connect flexible containers in series).
- Donot pressurize the flexible container to increase flow rates.
- If using a pumping device to administer Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%), turn off the pump before the container is empty.
To Open:
Tear outer wrap at notch and remove solution container. If supplemental medication is desired, follow directions below before preparing for administration.
To Add Medication:
- Prepare additive port.
- Using aseptic technique and an additive delivery needle of appropriate length, puncture resealable additive port at target area, inner diaphragm and inject. Withdraw needle after injecting medication.
- The additive port may be protected by covering with an additive cap.
- Mix container contents thoroughly.
Preparation for Administration
(Use aseptic technique)
- Close flow control clamp of administration set.
- Remove cover from outlet port at bottom of container.
- Insert piercing pin of administration set into port with a twisting motion until the set is firmly seated.NOTE: When using a vented administration set, replace bacterial retentive air filter with piercing pin cover. Insert piercing pin with twisting motion until shoulder of air filter housing rests against the outlet port flange.
- Suspend container from hanger.
- Squeeze and release drip chamber to establish proper fluid level in chamber.
- Attach venipuncture device to set.
- Open clamp to expel air from set and venipuncture device. Close clamp.
- Perform venipuncture.
- Regulate rate of administration with flow control clamp.
2.3 Dosage Considerations
The choice of dextrose concentration, rate, and volume depends on the age, weight, clinical and metabolic conditions of the patient and concomitant therapy.
Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) administration rate should be based on the patient's tolerance of dextrose, especially for premature infants with low birth weight.
Increase the infusion rate gradually as needed; frequently monitor blood glucose concentrations to avoid hyperglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
- Only for intravenous infusion. (2.1)
- Infusion rate depends on the age, weight, clinical and metabolic conditions of the patient and concomitant therapy. See full prescribing information for more information on preparation, administration, and dosing considerations. (2.1, 2.2, 2.3)
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection:
- 5% (5 g/100 mL) (50 mg/mL) of dextrose hydrous in a clear, sterile, and nonpyrogenic solution in single-dose flexible containers: 25 mL, 50 mL, 100 mL, 150 mL, 250 mL, 500 mL, and 1000 mL
- 10% (10 g/100 mL) (100 mg/mL) of dextrose hydrous in a clear, sterile, and nonpyrogenic solution in single-dose flexible containers: 250 mL, 500 mL, and 1000 mL
Injection:
- 5% (5 g/100 mL) (50 mg/mL) of dextrose hydrous in single-dose flexible containers: 25 mL, 50 mL, 100 mL, 150 mL, 250 mL, 500 mL, and 1000 mL. (3)
- 10% (10 g/100 mL) (100 mg/mL) of dextrose hydrous in single-dose flexible containers: 250 mL, 500 mL, and 1000 mL. (3)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) has been used for decades during labor and delivery. Although there are a few case reports that describe adverse effects of dextrose use in other stages of pregnancy, exposure during pregnancy in general is not expected to cause major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with dextrose.
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) has been used for decades and is not expected to cause harm to a breastfed infant. There are no data on the effects of Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) on levels of glucose in human milk, on the breastfed infant, or on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) is indicated in pediatric patients as a source of water and calories, and may also be used as a diluent for reconstitution of a powder or liquid drug product.
Neonates, especially premature infants with low birth weight, are at increased risk of developing hypo-or hyperglycemia. Therefore, they need close monitoring during treatment with intravenous glucose infusions to ensure adequate glycemic control in order to avoid potential long-term adverse effects.
Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) can cause imbalances in fluid and electrolytes in pediatric patients and requires close monitoring of volume status and plasma electrolyte concentrations, particularly in pediatric patients who may have impaired ability to regulate fluids and electrolytes. Pediatric patients are at increased risk for developing hyponatremic encephalopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5, 5.6)].
In very low birth weight neonates, excessive or rapid administration of Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) may result in increased serum osmolality and risk of intracerebral hemorrhage.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) has not been studied in sufficient number of patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. Geriatric patients are at increased risk of developing hyponatremia and hyponatremic encephalopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the geriatric and younger adult patients. In general, the infusion rate for geriatric patients should start slow and be titrated up cautiously, reflecting their greater risk for electrolyte abnormalities and fluid overload.
Dextrose is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because geriatric patients are more likely to have impaired renal function, care should be taken in selection of infusion rate and patients should be closely monitored during Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) treatment.
Pediatric Use: Increased risk of hypoglycemia/hyperglycemia and imbalances in fluid/electrolytes; monitor serum glucose concentrations, volume status, and electrolytes. (8.4)
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
A medication error resulting in a high infusion rate of Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) can cause hyperglycemia, hyperosmolality, and adverse effects on fluid and electrolyte balance [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.6)].
Severe hyperglycemia and severe dilutional hyponatremia, and their complications, can be fatal. In the event of overdosage (overhydration or solute overload) during Dextrose Injection (5% and 10%) treatment, discontinue the infusion. Institute corrective measures such as administration of exogenous insulin, and treat adverse effects on the CNS, respiratory, and cardiovascular systems [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.6)].
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Dextrose, USP is chemically designated D-glucose monohydrate (C6H12O6 ∙ H2O), a hexose sugar freely soluble in water.
The molecular weight of dextrose (D-glucose) monohydrate is 198.17. It has the following structural formula:
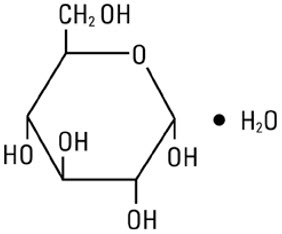
Water for Injection, USP is chemically designated H2O.
Dextrose Injection, USP (5% and 10%) solutions are sterile and nonpyrogenic. They are parenteral solutions containing various concentrations of dextrose in water for injection intended for intravenous administration.
Each 100 mL of 5% Dextrose Injection, USP, contains dextrose, hydrous 5 g in water for injection. The caloric value is 170 kcal/L. The osmolarity is 252 mOsmol/L (calc.), which is slightly hypotonic.
Each 100 mL of 10% Dextrose Injection, USP, contains dextrose, hydrous 10 g in water for injection. The caloric value is 340 kcal/L. The osmolarity is 505 mOsmol/L (calc.), which is hypertonic.
The pH for both concentrations is 4.3 (range is 3.2 to 6.5).
The solutions contain no bacteriostatic, antimicrobial agent or added buffer and each is supplied as single-dose containers.
Dextrose is derived from corn.
Exposure to temperatures above 25°C/77°F during transport and storage will lead to minor losses in moisture content. Higher temperatures lead to greater losses. It is unlikely that these minor losses will lead to clinically significant changes within the expiration period.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Dextrose provides a source of carbohydrate calories and is used to supplement nutrition by providing glucose parenterally.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The exposure-response relationship and time course of pharmacodynamic response for the safety and effectiveness of dextrose have not been fully characterized.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Dextrose is oxidized to carbon dioxide and water.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Studies with dextrose to evaluate the drug's carcinogenic potential, mutagenic potential, or effects on fertility have not been performed.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Dextrose Injection, USP (5% and 10%) is a clear, sterile, nonpyrogenic solution of dextrose supplied in single-dose flexible plastic containers as shown in the accompanying Table.
|
NDC No. |
Product |
Container size |
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
0990-7922-61* |
5% Dextrose Injection, USP (5 g / 100 mL (50 mg/mL)) |
150 |
|
0990-7922-53† |
5% Dextrose Injection, USP (5 g / 100 mL (50 mg/mL)) |
250 |
|
0990-7922-02* |
5% Dextrose Injection, USP (5 g / 100 mL (50 mg/mL)) |
250 |
|
0990-7922-03*,† |
5% Dextrose Injection, USP (5 g / 100 mL (50 mg/mL)) |
500 |
|
0990-7922-55*,† |
5% Dextrose Injection, USP (5 g / 100 mL (50 mg/mL)) |
500 |
|
0990-7922-09*,† |
5% Dextrose Injection, USP (5 g / 100 mL (50 mg/mL)) |
1000 |
|
0990-7923-20* |
5% Dextrose Injection, USP (5 g / 100 mL (50 mg/mL)) |
25 |
|
0990-7923-36* |
5% Dextrose Injection, USP (5 g / 100 mL (50 mg/mL)) |
50 |
|
0990-7923-13* |
5% Dextrose Injection, USP (5 g / 100 mL (50 mg/mL)) |
50 |
|
0990-7923-23* |
5% Dextrose Injection, USP (5 g / 100 mL (50 mg/mL)) |
100 |
|
0990-7923-37* |
5% Dextrose Injection, USP (5 g / 100 mL (50 mg/mL)) |
100 |
|
0990-7930-02* |
10% Dextrose Injection, USP (10 g / 100 mL (100 mg/mL)) |
250 |
|
0990-7930-03*,† |
10% Dextrose Injection, USP (10 g / 100 mL (100 mg/mL)) |
500 |
|
0990-7930-09*,† |
10% Dextrose Injection, USP (10 g / 100 mL (100 mg/mL)) |
1000 |
Storage and Handling
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Protect from freezing.
