Humalog
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use HUMALOG safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for HUMALOG. HUMALOG (insulin lispro) injection, for subcutaneous or intravenous use Initial U.S. Approval: 1996
c8ecbd7a-0e22-4fc7-a503-faa58c1b6f3f
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Aug 2, 2023
Eli Lilly and Company
DUNS: 006421325
Products 9
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Insulin lispro
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
diluent
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (7)
Insulin lispro
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
Insulin lispro
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
Insulin lispro
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
Insulin lispro
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
Insulin lispro
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
Insulin lispro
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
Insulin lispro
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE CARTON – HUMALOG U-200 Tempo Pen
Dispense in this sealed carton.
NDC 0002-8208-27
Humalog® Tempo PenTM
insulin lispro injection
For Single Patient Use Only
200 units per mL (U-200)
prefilled insulin delivery device
2 x 3 mL Prefilled Pens
Rx Only
For subcutaneous use.
Read Insulin Delivery Device Instructions for Use.
NEEDLES NOT INCLUDED
This device is recommended for use with Becton, Dickinson and Company's insulin pen needles.
 DO NOT TRANSFER TO A
SYRINGE SEVERE OVERDOSE CAN RESULT
DO NOT TRANSFER TO A
SYRINGE SEVERE OVERDOSE CAN RESULT

WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Never Share a HUMALOG Prefilled Pen, Cartridge, Reusable Pen Compatible
with Lilly 3 mL Cartridges1, or Syringe Between Patients
HUMALOG prefilled pens, cartridges, and reusable pens compatible with Lilly 3 mL cartridges must never be shared between patients, even if the needle is changed. Patients using HUMALOG vials must never share needles or syringes with another person. Sharing poses a risk for transmission of blood-borne pathogens.
5.2 Hyperglycemia or Hypoglycemia with Changes in Insulin Regimen
Changes in an insulin regimen (e.g., insulin strength, manufacturer, type, injection site or method of administration) may affect glycemic control and predispose to hypoglycemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)] or hyperglycemia. Repeated insulin injections into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis have been reported to result in hyperglycemia; and a sudden change in the injection site (to an unaffected area) has been reported to result in hypoglycemia [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
Make any changes to a patient's insulin regimen under close medical supervision with increased frequency of blood glucose monitoring. Advise patients who have repeatedly injected into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis to change the injection site to unaffected areas and closely monitor for hypoglycemia. For patients with type 2 diabetes, dosage adjustments of concomitant antidiabetic products may be needed.
5.3 Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia is the most common adverse reaction associated with insulins, including HUMALOG. Severe hypoglycemia can cause seizures, may be life- threatening, or cause death. Hypoglycemia can impair concentration ability and reaction time; this may place an individual and others at risk in situations where these abilities are important (e.g., driving or operating other machinery).
Hypoglycemia can happen suddenly, and symptoms may differ in each individual and change over time in the same individual. Symptomatic awareness of hypoglycemia may be less pronounced in patients with longstanding diabetes, in patients with diabetic nerve disease, in patients using medications that block the sympathetic nervous system (e.g., beta-blockers) [see Drug Interactions (7)], or in patients who experience recurrent hypoglycemia.
Risk Factors for Hypoglycemia
The risk of hypoglycemia after an injection is related to the duration of action of the insulin and, in general, is highest when the glucose lowering effect of the insulin is maximal. As with all insulins, the glucose lowering effect time course of HUMALOG may vary in different individuals or at different times in the same individual and depends on many conditions, including the area of injection as well as the injection site blood supply and temperature [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. Other factors which may increase the risk of hypoglycemia include changes in meal pattern (e.g., macronutrient content or timing of meals), changes in level of physical activity, or changes to co-administered medication [see Drug Interactions (7)]. Patients with renal or hepatic impairment may be at higher risk of hypoglycemia [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6, 8.7)].
Risk Mitigation Strategies for Hypoglycemia
Patients and caregivers must be educated to recognize and manage hypoglycemia. Self-monitoring of blood glucose plays an essential role in the prevention and management of hypoglycemia. In patients at higher risk for hypoglycemia and patients who have reduced symptomatic awareness of hypoglycemia, increased frequency of blood glucose monitoring is recommended.
5.4 Hypoglycemia Due to Medication Errors
Accidental mix-ups between insulin products have been reported. To avoid medication errors between HUMALOG and other insulins, instruct patients to always check the insulin label before each injection.
Do not transfer HUMALOG U-200 from the HUMALOG prefilled pens to a syringe. The markings on the insulin syringe will not measure the dose correctly and can result in overdosage and severe hypoglycemia [see Dosage and Administration (2.1) and Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
5.5 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Severe, life-threatening, generalized allergy, including anaphylaxis, can occur with insulins, including HUMALOG. If hypersensitivity reactions occur, discontinue HUMALOG; treat per standard of care and monitor until symptoms and signs resolve [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. HUMALOG is contraindicated in patients who have had hypersensitivity reactions to insulin lispro or any of the excipients in HUMALOG [see Contraindications (4)].
5.6 Hypokalemia
All insulins, including HUMALOG, cause a shift in potassium from the extracellular to intracellular space, possibly leading to hypokalemia. Untreated hypokalemia may cause respiratory paralysis, ventricular arrhythmia, and death. Monitor potassium levels in patients at risk for hypokalemia if indicated (e.g., patients using potassium-lowering medications, patients taking medications sensitive to serum potassium concentrations).
5.7 Fluid Retention and Heart Failure with Concomitant Use of PPAR-gamma
Agonists
Thiazolidinediones (TZDs), which are peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR)-gamma agonists, can cause dose-related fluid retention, particularly when used in combination with insulin. Fluid retention may lead to or exacerbate heart failure. Patients treated with insulin, including HUMALOG, and a PPAR-gamma agonist should be observed for signs and symptoms of heart failure. If heart failure develops, it should be managed according to current standards of care, and discontinuation or dose reduction of the PPAR- gamma agonist must be considered.
5.8 Hyperglycemia and Ketoacidosis Due to Insulin Pump Device Malfunction
Malfunction of the insulin pump or insulin infusion set or insulin degradation can rapidly lead to hyperglycemia and ketoacidosis. Prompt identification and correction of the cause of hyperglycemia or ketosis is necessary. Interim subcutaneous injections with HUMALOG may be required. Patients using continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion pump therapy must be trained to administer insulin by injection and have alternate insulin therapy available in case of pump failure [see How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16.2) and Patient Counseling Information (17)].
- Never share a HUMALOG prefilled pen, cartridge, reusable pen compatible with Lilly 3 mL cartridges, or syringe between patients, even if the needle is changed. (5.1)
- Hyperglycemia or Hypoglycemia with Changes in Insulin Regimen: Make changes to a patient's insulin regimen (e.g., insulin strength, manufacturer, type, injection site or method of administration) under close medical supervision with increased frequency of blood glucose monitoring. (5.2)
- Hypoglycemia: May be life-threatening. Monitor blood glucose and increase monitoring frequency with changes to insulin dosage, use of glucose lowering medications, meal pattern, physical activity; in patients with renal or hepatic impairment; and in patients with hypoglycemia unawareness. (5.3, 7, 8.6, 8.7)
- Hypoglycemia Due to Medication Errors: Accidental mix-ups between insulin products can occur. Instruct patients to check insulin labels before injection. Do not transfer HUMALOG U-200 from the HUMALOG prefilled pen to a syringe as overdosage and severe hypoglycemia can result. (5.4)
- Hypersensitivity Reactions: May be life-threatening. Discontinue HUMALOG, monitor and treat if indicated. (5.5)
- Hypokalemia: May be life-threatening. Monitor potassium levels in patients at risk of hypokalemia and treat if indicated. (5.6)
- Fluid Retention and Heart Failure with Concomitant Use of Thiazolidinediones (TZDs): Observe for signs and symptoms of heart failure; consider dosage reduction or discontinuation if heart failure occurs. (5.7)
- Hyperglycemia and Ketoacidosis Due to Insulin Pump Device Malfunction: Monitor glucose and administer HUMALOG U-100 by subcutaneous injection if pump malfunction occurs. (5.8)
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
The table below includes clinically significant drug interactions with HUMALOG.
|
Drugs That May Increase the Risk of Hypoglycemia | |
|
Drugs: |
Antidiabetic agents, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blocking agents, disopyramide, fibrates, fluoxetine, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, pentoxifylline, pramlintide, salicylates, somatostatin analogs (e.g., octreotide), and sulfonamide antibiotics. |
|
Intervention: |
Dose adjustment and increased frequency of glucose monitoring may be required when HUMALOG is co-administered with these drugs. |
|
Drugs That May Decrease the Blood Glucose Lowering Effect of HUMALOG | |
|
Drugs: |
Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., olanzapine and clozapine), corticosteroids, danazol, diuretics, estrogens, glucagon, isoniazid, niacin, oral contraceptives, phenothiazines, progestogens (e.g., in oral contraceptives), protease inhibitors, somatropin, sympathomimetic agents (e.g., albuterol, epinephrine, terbutaline), and thyroid hormones. |
|
Intervention: |
Dose adjustment and increased frequency of glucose monitoring may be required when HUMALOG is co-administered with these drugs. |
|
Drugs That May Increase or Decrease the Blood Glucose Lowering Effect of HUMALOG | |
|
Drugs: |
Alcohol, beta-blockers, clonidine, and lithium salts. Pentamidine may cause hypoglycemia, which may sometimes be followed by hyperglycemia. |
|
Intervention: |
Dose adjustment and increased frequency of glucose monitoring may be required when HUMALOG is co-administered with these drugs. |
|
Drugs That May Blunt Signs and Symptoms of Hypoglycemia | |
|
Drugs: |
Beta-blockers, clonidine, guanethidine and reserpine. |
|
Intervention: |
Increased frequency of glucose monitoring may be required when HUMALOG is co- administered with these drugs. |
- Drugs that may increase the risk of hypoglycemia: antidiabetic agents, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blocking agents, disopyramide, fibrates, fluoxetine, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, pentoxifylline, pramlintide, salicylates, somatostatin analog (e.g., octreotide), and sulfonamide antibiotics (7).
- Drugs that may decrease the blood glucose lowering effect: atypical antipsychotics, corticosteroids, danazol, diuretics, estrogens, glucagon, isoniazid, niacin, oral contraceptives, phenothiazines, progestogens (e.g., in oral contraceptives), protease inhibitors, somatropin, sympathomimetic agents (e.g., albuterol, epinephrine, terbutaline), and thyroid hormones (7).
- Drugs that may increase or decrease the blood glucose lowering effect: alcohol, beta-blockers, clonidine, lithium salts, and pentamidine (7).
- Drugs that may blunt the signs and symptoms of hypoglycemia: beta-blockers, clonidine, guanethidine, and reserpine (7).
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES SECTION
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
|
Dosage and Administration (2.2) |
05/2025 |
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Regulation of glucose metabolism is the primary activity of insulins and insulin analogs, including insulin lispro. Insulins lower blood glucose by stimulating peripheral glucose uptake by skeletal muscle and fat, and by inhibiting hepatic glucose production. Insulins inhibit lipolysis and proteolysis, and enhance protein synthesis.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
HUMALOG has been shown to be equipotent to human insulin on a molar basis. One unit of HUMALOG has the same glucose-lowering effect as one unit of regular human insulin. Studies in normal volunteers and patients with diabetes demonstrated that HUMALOG has a more rapid onset of action and a shorter duration of activity than regular human insulin when given subcutaneously.
The time course of action of insulin and insulin analogs, such as HUMALOG, may vary considerably in different individuals or within the same individual. The parameters of HUMALOG activity (time of onset, peak time, and duration) as designated in Figure 1 should be considered only as general guidelines. The rate of insulin absorption, and consequently the onset of activity are known to be affected by the site of injection, exercise, and other variables [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
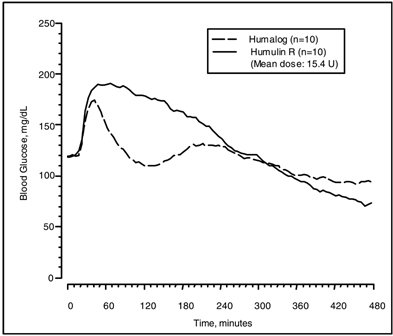
Figure 1: Blood Glucose Levels After Subcutaneous Injection of Regular Human Insulin or HUMALOG (0.2 unit/kg) Immediately Before a High Carbohydrate Meal in 10 Patients with Type 1 Diabetesa.
a Baseline insulin concentration was maintained by infusion of 0.2 mU/min/kg human insulin.
Intravenous Administration of HUMALOG U-100 — The glucose lowering effect of intravenously administered HUMALOG was tested in 21 patients with type 1 diabetes. For the study, the patients' usual doses of insulin were held and blood glucose concentrations were allowed to reach a stable range of 200 to 260 mg/dL during a one to three hours run-in phase. The run-in phase was followed by a 6-hour assessment phase. During the assessment phase, patients received intravenous HUMALOG at an initial infusion rate of 0.5 units/hour. The infusion rate of HUMALOG could be adjusted at regular timed intervals to achieve and maintain blood glucose concentrations between 100 to 160 mg/dL.
The mean blood glucose levels during the assessment phase for patients on HUMALOG therapy are summarized below in Table 4. All patients achieved the targeted glucose range at some point during the 6-hour assessment phase. At the endpoint, blood glucose was within the target range (100 to 160 mg/dL) for 17 of 20 patients treated with HUMALOG. The average time (±SE) required to attain near normoglycemia was 129 ± 14 minutes for HUMALOG.
Table 4: Mean Blood Glucose Concentrations (mg/dL) During Intravenous Infusions of HUMALOG U-100|
a Results shown as mean ± SD | |
|
Time from Start of Infusion (minutes) |
Mean Blood Glucose (mg/dL) Intravenousa |
|
0 |
224 ± 16 |
|
30 |
205 ± 21 |
|
60 |
195 ± 20 |
|
120 |
165 ± 26 |
|
180 |
140 ± 26 |
|
240 |
123 ± 20 |
|
300 |
120 ± 27 |
|
360 |
122 ± 25 |
The pharmacodynamics of a single 20 unit dose of HUMALOG U-200 administered subcutaneously were compared to the pharmacodynamics of a single 20 unit dose of HUMALOG U-100 administered subcutaneously in a euglycemic clamp study enrolling healthy subjects. In this study, the overall, maximum, and time to maximum glucose lowering effect were similar between HUMALOG U-200 and HUMALOG U-100. The mean area under the glucose infusion rate curves (measure of overall pharmacodynamic effect) were 125 g and 126 g for HUMALOG U-200 and HUMALOG U-100, respectively. The maximum glucose infusion rate was 534 mg/min and 559 mg/min and the corresponding median time (min, max) to maximum effect were 2.8 h (0.5 h – 6.3 h) and 2.4 h (0.5 h – 4.7 h) for HUMALOG U-200 and HUMALOG U-100, respectively.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption and Bioavailability — Studies in healthy volunteers and patients with diabetes demonstrated that HUMALOG is absorbed more quickly than regular human insulin. In healthy volunteers given subcutaneous doses of HUMALOG ranging from 0.1 to 0.4 unit/kg, peak serum levels were seen 30 to 90 minutes after dosing. When healthy volunteers received equivalent doses of regular human insulin, peak insulin levels occurred between 50 to 120 minutes after dosing. Similar results were seen in patients with type 1 diabetes (see Figure 2).
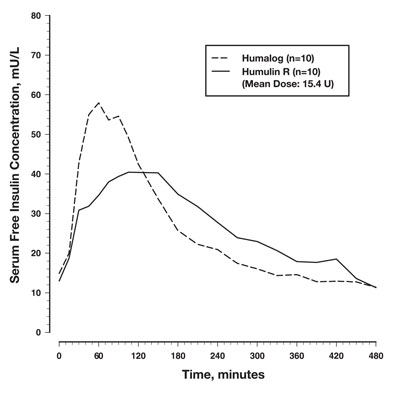
Figure 2: Serum HUMALOG and Insulin Levels After Subcutaneous Injection of Regular Human Insulin or HUMALOG (0.2 unit/kg) Immediately Before a High Carbohydrate Meal in 10 Patients with Type 1 Diabetesa.
a Baseline insulin concentration was maintained by infusion of 0.2 mU/min/kg human insulin.
HUMALOG U-100 was absorbed at a consistently faster rate than regular human insulin in healthy male volunteers given 0.2 unit/kg at abdominal, deltoid, or femoral subcutaneous sites. After HUMALOG was administered in the abdomen, serum drug levels were higher and the duration of action was slightly shorter than after deltoid or thigh administration. Bioavailability of HUMALOG is similar to that of regular human insulin. The absolute bioavailability after subcutaneous injection ranges from 55% to 77% with doses between 0.1 to 0.2 unit/kg, inclusive.
The results of a study in healthy subjects demonstrated that HUMALOG U-200 is bioequivalent to HUMALOG U-100 following administration of a single 20 unit dose.
The mean observed area under the serum insulin concentration-time curve from time zero to infinity was 2360 pmol hr/L and 2390 pmol hr/L for HUMALOG U-200 and HUMALOG U-100, respectively. The corresponding mean peak serum insulin concentration was 795 pmol/L and 909 pmol/L for HUMALOG U-200 and HUMALOG U-100, respectively. The median time to maximum concentration was 1.0 hour for both formulations.
Distribution — When administered intravenously as bolus injections of 0.1 and 0.2 U/kg dose in two separate groups of healthy subjects, the mean volume of distribution of HUMALOG appeared to decrease with increase in dose (1.55 and 0.72 L/kg, respectively) in contrast to that of regular human insulin for which, the volume of distribution was comparable across the two dose groups (1.37 and 1.12 L/kg for 0.1 and 0.2 U/kg dose, respectively).
Metabolism — Human metabolism studies have not been conducted. However, animal studies indicate that the metabolism of HUMALOG is identical to that of regular human insulin.
Elimination — After subcutaneous administration of HUMALOG, the t1/2 is shorter than that of regular human insulin (1 versus 1.5 hours, respectively). When administered intravenously, HUMALOG and regular human insulin demonstrated similar dose-dependent clearance, with a mean clearance of 21.0 mL/min/kg and 21.4 mL/min/kg, respectively (0.1 unit/kg dose), and 9.6 mL/min/kg and 9.4 mL/min/kg, respectively (0.2 unit/kg dose). Accordingly, HUMALOG demonstrated a mean t1/2 of 0.85 hours (51 minutes) and 0.92 hours (55 minutes), respectively for 0.1 unit/kg and 0.2 unit/kg doses, and regular human insulin mean t1/2 was 0.79 hours (47 minutes) and 1.28 hours (77 minutes), respectively for 0.1 unit/kg and 0.2 unit/kg doses.
Specific Populations
The effects of age, gender, race, obesity, pregnancy, or smoking on the pharmacokinetics of HUMALOG have not been studied.
Renal Impairment — Type 2 diabetic patients with varying degree of renal impairment showed no difference in pharmacokinetics of regular insulin and HUMALOG. However, the sensitivity of the patients to insulin did change, with an increased response to insulin as the renal function declined. Some studies with human insulin have shown increased circulating levels of insulin in patients with renal impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Hepatic Impairment — Type 2 diabetic patients with impaired hepatic function showed no effect on the pharmacokinetics of HUMALOG as compared to patients with no hepatic dysfunction. However, some studies with human insulin have shown increased circulating levels of insulin in patients with liver failure [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)].
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The safety and efficacy of HUMALOG U-100 were studied in pediatric and adult patients with type 1 diabetes (n=789) and adult patients with type 2 diabetes (n=722).
14.1 Type 1 Diabetes – Adults and Pediatric Patients Aged 12 Years and
Older
A 12-month, randomized, parallel, open-label, active-controlled study was conducted in patients with type 1 diabetes to assess the safety and efficacy of HUMALOG (n=81) compared with Humulin® R [insulin human injection (100 units/mL)] (n=86). HUMALOG was administered by subcutaneous injection immediately prior to meals and Humulin R was administered 30 to 45 minutes before meals. Humulin® U [ULTRALENTE® human insulin (rDNA origin) extended zinc suspension] was administered once or twice daily as the basal insulin. There was a 2- to 4-week run-in period with Humulin R and Humulin U before randomization. Most patients were Caucasian (97%). Forty-seven percent of the patients were male. The mean age was 31 years (range 12 to 70 years). Glycemic control, the total daily doses of HUMALOG and Humulin R, and the incidence of severe hypoglycemia (as determined by the number of events that were not self- treated) were similar in the two treatment groups. There were no episodes of diabetic ketoacidosis in either treatment group.
Table 5: Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus – Adults and Pediatric Patients Aged 12 years and Older|
a Values are Mean ± SD | ||
|
b Severe hypoglycemia refers to hypoglycemia for which patients were not able to self-treat. | ||
|
Treatment Duration |
12 months | |
|
HUMALOG |
Humulin R | |
|
N |
81 |
86 |
|
Baseline HbA1c (%)a |
8.2 ± 1.4 |
8.3 ± 1.7 |
|
Change from baseline HbA1c (%)a |
-0.1 ± 0.9 |
0.1 ± 1.1 |
|
Treatment Difference in HbA1c Mean (95% confidence interval) |
0.4 (0.0, 0.8) | |
|
Baseline short-acting insulin dose (units/kg/day) |
0.3 ± 0.1 |
0.3 ± 0.1 |
|
End-of-Study short-acting insulin dose (units/kg/day) |
0.3 ± 0.1 |
0.3 ± 0.1 |
|
Change from baseline short-acting insulin dose (units/kg/day) |
0.0 ± 0.1 |
0.0 ± 0.1 |
|
Baseline Body weight (kg) |
72 ± 12.7 |
71 ± 11.3 |
|
Weight change from baseline (kg) |
1.4 ± 3.6 |
1.0 ± 2.6 |
|
Patients with severe hypoglycemia (n, %)b |
14 (17%) |
18 (21%) |
14.2 Type 1 Diabetes – Pediatric Patients
An 8-month, crossover study of pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes (n=463), aged 9 to 19 years, compared two subcutaneous multiple-dose treatment regimens: HUMALOG or Humulin R, both administered with Humulin N (NPH human insulin) as the basal insulin. HUMALOG achieved glycemic control comparable to Humulin R, as measured by HbA1c (see Table 6), and both treatment groups had a comparable incidence of hypoglycemia. In a 9-month, crossover study of pediatric patients (n=60) with type 1 diabetes, aged 3 to 11 years, HUMALOG administered immediately before meals, HUMALOG administered immediately after meals and Humulin R administered 30 minutes before meals resulted in similar glycemic control, as measured by HbA1c, and incidence of hypoglycemia, regardless of treatment group.
Table 6: Pediatric Subcutaneous Administration of HUMALOG in Type 1 Diabetes|
a Values are Mean ± SD | |||
|
b Severe hypoglycemia refers to hypoglycemia that required glucagon or glucose injection or resulted in coma. | |||
|
End point | |||
|
Baseline |
HUMALOG |
Humulin R | |
|
HbA1c (%)a |
8.6 ± 1.5 |
8.7 ± 1.5 |
8.7 ± 1.6 |
|
Change from baseline HbA1c (%)a |
— |
0.1 ± 1.1 |
0.1 ± 1.3 |
|
Short-acting insulin dose (units/kg/day)a |
0.5 ± 0.2 |
0.5 ± 0.2 |
0.5 ± 0.2 |
|
Change from baseline short-acting insulin dose (units/kg/day)a |
— |
0.01 ± 0.1 |
-0.01 ± 0.1 |
|
Body weight (kg)a |
59.1 ± 13.1 |
61.1 ± 12.7 |
61.4 ± 12.9 |
|
Weight change from baseline (kg)a |
— |
2.0 ± 3.1 |
2.3 ± 3.0 |
|
Patients with severe hypoglycemia (n, %)b |
— |
5 (1.1%) |
5 (1.1%) |
|
Diabetic ketoacidosis (n, %) |
— |
11 (2.4%) |
9 (1.9%) |
14.3 Type 1 Diabetes – Adults Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion
To evaluate the administration of HUMALOG U-100 via external insulin pumps, two open-label, crossover design studies were performed in patients with type 1 diabetes. One study involved 39 patients, ages 19 to 58 years, treated for 24 weeks with HUMALOG or regular human insulin. After 12 weeks of treatment, the mean HbA1c values decreased from 7.8% to 7.2% in the HUMALOG-treated patients and from 7.8% to 7.5% in the regular human insulin-treated patients. Another study involved 60 patients (mean age 39, range 15 to 58 years) treated for 24 weeks with either HUMALOG or buffered regular human insulin. After 12 weeks of treatment, the mean HbA1c values decreased from 7.7% to 7.4% in the HUMALOG-treated patients and remained unchanged from 7.7% in the buffered regular human insulin-treated patients. Rates of hypoglycemia were comparable between treatment groups in both studies.
14.4 Type 1 Diabetes – Pediatric Patients: Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin
Infusion
A randomized, 16-week, open-label, parallel design, study of pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes (n=298) aged 4 to 18 years compared two subcutaneous infusion regimens administered via an external insulin pump: insulin aspart (n=198) or HUMALOG U-100 (n=100). These two treatments resulted in comparable changes from baseline in HbA1c and comparable rates of hypoglycemia after 16 weeks of treatment (see Table 7). Infusion site reactions were similar between groups.
Table 7: Pediatric Insulin Pump Study in Type 1 Diabetes (16 weeks; n=298)|
a Values are Mean ± SD | ||
|
b Severe hypoglycemia refers to hypoglycemia associated with central nervous system symptoms and requiring the intervention of another person or hospitalization. | ||
|
HUMALOG |
Aspart | |
|
N |
100 |
198 |
|
Baseline HbA1c (%)a |
8.2 ± 0.8 |
8.0 ± 0.9 |
|
Change from Baseline HbA1c (%) |
-0.1 ± 0.7 |
-0.1 ± 0.8 |
|
Treatment Difference in HbA1c, Mean (95% confidence interval) |
0.1 (-0.3, 0.1) | |
|
Baseline insulin dose (units/kg/24 hours)a |
0.9 ± 0.3 |
0.9 ± 0.3 |
|
End-of-Study insulin dose (units/kg/24 hours)a |
0.9 ± 0.2 |
0.9 ± 0.2 |
|
Patients with severe hypoglycemia (n, %)b |
8 (8%) |
19 (10%) |
|
Diabetic ketoacidosis (n, %) |
0 (0) |
1 (0.5%) |
|
Baseline body weight (kg)a |
55.5 ± 19.0 |
54.1 ± 19.7 |
|
Weight Change from baseline (kg)a |
1.6 ± 2.1 |
1.8 ± 2.1 |
14.5 Type 2 Diabetes – Adults
A 6-month randomized, crossover, open-label, active-controlled study was conducted in insulin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes (n=722) to assess the safety and efficacy of HUMALOG for 3 months followed by Humulin R for 3 months or the reverse sequence. HUMALOG was administered by subcutaneous injection immediately before meals and Humulin R was administered 30 to 45 minutes before meals. Humulin® N [NPH human insulin (rDNA origin) isophane suspension] or Humulin U was administered once or twice daily as the basal insulin. All patients participated in a 2- to 4-week run-in period with Humulin R and Humulin N or Humulin U. Most of the patients were Caucasian (88%), and the numbers of men and women in each group were approximately equal. The mean age was 58.6 years (range 23.8 to 85 years). The average body mass index (BMI) was 28.2 kg/m2. During the study, the majority of patients used Humulin N (84%) compared with Humulin U (16%) as their basal insulin. The reductions from baseline in HbA1c and the incidence of severe hypoglycemia (as determined by the number of events that were not self-treated) were similar between the two treatments from the combined groups (see Table 8).
Table 8: Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus — Adults|
a Values are Mean ± SD | |||
|
b Severe hypoglycemia refers to hypoglycemia for which patients were not able to self-treat. | |||
|
End point | |||
|
Baseline |
HUMALOG |
Humulin R | |
|
HbA1c (%)a |
8.9 ± 1.7 |
8.2 ± 1.3 |
8.2 ± 1.4 |
|
Change from baseline HbA1c (%)a |
— |
-0.7 ± 1.4 |
-0.7 ± 1.3 |
|
Short-acting insulin dose (units/kg/day)a |
0.3 ± 0.2 |
0.3 ± 0.2 |
0.3 ± 0.2 |
|
Change from baseline short-acting insulin dose (units/kg/day)a |
— |
0.0 ± 0.1 |
0.0 ± 0.1 |
|
Body weight (kg)a |
80 ± 15 |
81 ± 15 |
81 ± 15 |
|
Weight change from baseline |
— |
0.8 ± 2.7 |
0.9 ± 2.6 |
|
Patients with severe hypoglycemia (n, %)b |
— |
15 (2%) |
16 (2%) |
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Administration Instructions
- Always check insulin labels before administration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- Inspect HUMALOG visually before use. It should appear clear and colorless. Do not use HUMALOG if particulate matter or coloration is seen.
- Use HUMALOG prefilled pens with caution in patients with visual impairment that may rely on audible clicks to dial their dose.
- Do NOT mix HUMALOG U-100 with other insulins when using a continuous subcutaneous infusion pump.
- Do NOT transfer HUMALOG U-200 from the prefilled pen to a syringe for administration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- Do NOT perform dose conversion when using any HUMALOG U-100 or U-200 prefilled pens. The dose window shows the number of insulin units to be delivered and no conversion is needed.
2.2 Administration Instructions for the Approved Routes of Administration
Subcutaneous Injection: HUMALOG U-100 or U-200
- Administer the dose of HUMALOG U-100 or HUMALOG U-200 within fifteen minutes before a meal or immediately after a meal by injection into the subcutaneous tissue of the abdominal wall, thigh, upper arm, or buttocks.
- Rotate the injection site within the same region from one injection to the next (abdominal wall, thigh, upper arm, or buttocks) to reduce the risk of lipodystrophy and localized cutaneous amyloidosis. Do not inject into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Adverse Reactions (6)].
- During changes to a patient's insulin regimen, increase the frequency of blood glucose monitoring [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- HUMALOG administered by subcutaneous injection should generally be used in regimens with an intermediate- or long-acting insulin.
- The HUMALOG U-100 KwikPen, HUMALOG U-100 Tempo Pen, HUMALOG U-200 KwikPen, and HUMALOG U-200 Tempo Pen each dial in 1 unit increments and delivers a maximum dose of 60 units per injection.
- The HUMALOG U-100 Junior KwikPen dials in 0.5 unit increments and delivers a maximum dose of 30 units per injection.
Subcutaneous Injection: Diluted HUMALOG U-100
- HUMALOG U-100 may be diluted with Sterile Diluent for HUMALOG for subcutaneous injection ONLY under medical supervision. Dilute one part HUMALOG U-100 to:
- Nine parts diluent to yield a concentration one-tenth that of HUMALOG U-100 (equivalent to U-10).
- One part diluent to yield a concentration one-half that of HUMALOG U-100 (equivalent to U-50).
- Diluted HUMALOG for subcutaneous injection may be stored for 28 days when refrigerated at 41°F (5°C) and for 14 days at room temperature up to 86°F (30°C).
Continuous Subcutaneous Infusion (Insulin Pump): HUMALOG U-100 ONLY
- Do NOT administer HUMALOG U-200 using a continuous subcutaneous infusion pump.
- Refer to the continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion pump user manual to see if HUMALOG can be used with the insulin pump. Use HUMALOG in accordance with the insulin pump system's instructions for use.
- Administer HUMALOG U-100 by continuous subcutaneous infusion in a region recommended in the instructions from the pump manufacturer. Rotate infusion sites within the same region to reduce the risk of lipodystrophy and localized cutaneous amyloidosis. Do not inject into areas of lipodystrophy or localized cutaneous amyloidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Adverse Reactions (6)].
- Train patients using continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion therapy to administer insulin by injection and have alternate insulin therapy available in case of insulin pump failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
- During changes to a patient's insulin regimen, increase the frequency of blood glucose monitoring [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Change HUMALOG U-100 in the pump reservoir at least every 7 days or according to the pump user manual, whichever is shorter.
- Change the infusion set and the infusion set insertion site according to the manufacturer's user manual.
- Do NOT dilute or mix HUMALOG U-100 when administering by continuous subcutaneous infusion.
- Do NOT expose HUMALOG U-100 in the pump reservoir to temperatures greater than 98.6°F (37°C).
Intravenous Administration: HUMALOG U-100 ONLY
- Do NOT administer HUMALOG U-200 intravenously.
- Administer HUMALOG U-100 intravenously ONLY under medical supervision with close monitoring of blood glucose and potassium levels to avoid hypoglycemia and hypokalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.6)].
- Dilute HUMALOG U-100 to concentrations from 0.1 unit/mL to 1.0 unit/mL using 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP.
- Infusion bags prepared with HUMALOG U-100 are stable when stored in a refrigerator (2° to 8°C [36° to 46°F]) for 48 hours and then may be used at room temperature for up to an additional 48 hours.
2.3 Dosage Recommendations
- Individualize and adjust the dosage of HUMALOG based on route of administration, the individual's metabolic needs, blood glucose monitoring results and glycemic control goal.
- When switching from another insulin to HUMALOG, a different dosage of HUMALOG may be needed [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Dosage modifications may be needed with changes in physical activity, changes in meal patterns (i.e., macronutrient content or timing of food intake), changes in renal or hepatic function or during acute illness [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3) and Use in Specific Populations (8.6, 8.7)].
- Do NOT perform dose conversion when using any HUMALOG U-100 or U-200 prefilled pens. The dose window shows the number of insulin units to be delivered and no conversion is needed.
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Drug Interactions
Dosage modification may be needed when HUMALOG is used concomitantly with certain drugs [see Drug Interactions (7)].
2.5 Instructions for Mixing with Other Insulins
The table below includes administration instructions regarding mixing HUMALOG U-100 and HUMALOG U-200 with other insulins.
|
HUMALOG U-100 subcutaneous injection route |
|
|
HUMALOG U-100 continuous subcutaneous infusion route (Insulin Pump) |
Do NOT mix HUMALOG U-100 with any other insulin. |
|
HUMALOG U-200 subcutaneous injection route |
Do NOT mix with any other insulin. |
- See Full Prescribing Information for important administration instructions. (2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4)
- Subcutaneous injection (2.2):
- Administer HUMALOG® U-100 or U-200 by subcutaneous injection into the abdominal wall, thigh, upper arm, or buttocks within 15 minutes before a meal or immediately after a meal.
- Rotate injection sites to reduce risk of lipodystrophy and localized cutaneous amyloidosis.
- Continuous subcutaneous infusion (Insulin Pump) (2.2):
- Refer to the insulin infusion pump user manual to see if HUMALOG can be used. Use in accordance with the insulin pump instructions for use.
- Administer HUMALOG U-100 by continuous subcutaneous infusion using an insulin pump in a region recommended in the instructions from the pump manufacturer.
- Rotate infusion sites to reduce risk of lipodystrophy and localized cutaneous amyloidosis.
- DO NOT administer HUMALOG U-200 by continuous subcutaneous infusion.
- Intravenous Infusion (2.2):
- Administer HUMALOG U-100 by intravenous infusion ONLY after dilution and under medical supervision. DO NOT administer HUMALOG U-200 by intravenous infusion.
- The dosage of HUMALOG must be individualized based on the route of administration and the individual's metabolic needs, blood glucose monitoring results and glycemic control goal. (2.3)
- Do not perform dose conversion when using the HUMALOG U-100 or U-200 prefilled pens. The dose window shows the number of insulin units to be delivered and no conversion is needed. (2.1, 2.3)
- Do not mix HUMALOG U-200 with any other insulin. (2.4)
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: 100 units/mL (U-100) clear and colorless solution available as:
- 10 mL multiple-dose vial
- 3 mL multiple-dose vial
- 3 mL single-patient-use KwikPen prefilled pen
- 3 mL single-patient-use Tempo Pen prefilled pen
- 3 mL single-patient-use Junior KwikPen prefilled pen
- 3 mL single-patient-use cartridges
Injection: 200 units/mL (U-200) clear and colorless solution available as:
- 3 mL single-patient-use KwikPen prefilled pen
- 3 mL single-patient-use Tempo Pen prefilled pen
Injection: 100 units/mL (U-100) is available as: (3)
- 10 mL multiple-dose vial
- 3 mL multiple-dose vial
- 3 mL single-patient-use KwikPen® prefilled pen
- 3 mL single-patient-use Tempo Pen™ prefilled pen
- 3 mL single-patient-use Junior KwikPen® prefilled pen
- 3 mL single-patient-use cartridges
Injection: 200 units/mL (U-200) is available as: (3)
- 3 mL single-patient-use KwikPen® prefilled pen
- 3 mL single-patient-use Tempo PenTM prefilled pen
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
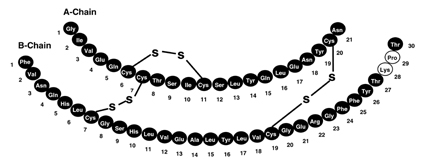
Insulin lispro is a rapid-acting human insulin analog produced by recombinant DNA technology utilizing a non-pathogenic laboratory strain of Escherichia coli. Insulin lispro differs from human insulin in that the amino acid proline at position B28 is replaced by lysine and the lysine in position B29 is replaced by proline. Chemically, it is Lys(B28), Pro(B29) human insulin analog and has the empirical formula C257H383N65O77S6 and a molecular weight of 5.808 kDa, both identical to that of human insulin.
Insulin lispro has the following primary structure:
HUMALOG (insulin lispro) injection is a sterile, clear, and colorless solution for subcutaneous or intravenous use.
Each mL of HUMALOG U-100 contains 100 units of insulin lispro, and the inactive ingredients: dibasic sodium phosphate (1.0 mg), glycerin (16 mg), metacresol (3.15 mg), trace amounts of phenol, zinc oxide (content adjusted to provide 0.0197 mg zinc ion), and Water for Injection, USP.
Each mL of HUMALOG U-200 contains 200 units of insulin lispro, and the inactive ingredients: glycerin (16 mg), metacresol (3.15 mg), trace amounts of phenol, tromethamine (5 mg), zinc oxide (content adjusted to provide 0.046 mg zinc ion), and Water for Injection, USP.
HUMALOG has a pH of 7.0 to 7.8.
Hydrochloric acid 10% and/or sodium hydroxide 10% is added to adjust the pH.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
HUMALOG (insulin lispro) injection is a clear and colorless solution available as:
|
a Tempo Pen contains a component that allows for data connectivity when used with a compatible transmitter. | ||||
|
HUMALOG |
Total Volume |
Concentration |
NDC Number |
Package Size |
|
U-100 multiple-dose vial |
10 mL |
100 units/mL |
0002-7510-01 |
1 vial |
|
U-100 multiple-dose vial |
3 mL |
100 units/mL |
0002-7510-17 |
1 vial |
|
U-100 multiple-dose vial |
3 mL |
100 units/mL |
0002-7533-01 |
1 vial |
|
U-100 single-patient-use cartridge1 |
3 mL |
100 units/mL |
0002-7516-59 |
5 cartridges |
|
U-100 single-patient-use KwikPen |
3 mL |
100 units/mL |
0002-8799-59 |
5 pens |
|
U-100 single-patient-use Tempo Pena |
3 mL |
100 units/mL |
0002-8213-05 |
5 pens |
|
U-100 single-patient-use Junior KwikPen |
3 mL |
100 units/mL |
0002-7714-59 |
5 pens |
|
U-200 single-patient-use KwikPen |
3 mL |
200 units/mL |
0002-7712-27 |
2 pens |
|
U-200 single-patient-use Tempo Pena |
3 mL |
200 units/mL |
0002-8208-27 |
2 pens |
The U-100 KwikPen, U-100 Tempo Pen, U-200 KwikPen, and U-200 Tempo Pen dial in 1-unit increments. The U-100 Junior KwikPen dials in 0.5-unit increments.
Each prefilled pen, cartridge, and reusable pen compatible with Lilly 3 mL cartridges is for single-patient-use only. HUMALOG prefilled pens, cartridges, and reusable pens compatible with Lilly 3 mL cartridges must never be shared between patients, even if the needle is changed. Patients using HUMALOG vials must never share needles or syringes with another person.
16.2 Storage and Handling
Dispense in the original sealed carton with the enclosed Instructions for Use.
Protect from direct heat and light. Do not freeze and do not use if it has been frozen.
See table below for storage information:
| |||
|
Not In-Use (Unopened) Room Temperature (Up to 86°F [30°C]) |
Not In-Use (Unopened) Refrigerated |
In-Use (Opened) | |
|
HUMALOG U-100* | |||
|
10 mL multiple-dose vial |
28 days |
Until expiration date |
28 days |
|
3 mL multiple-dose vial |
28 days |
Until expiration date |
28 days |
|
3 mL single-patient-use cartridge |
28 days |
Until expiration date |
28 days |
|
3 mL single-patient-use Humalog KwikPen |
28 days |
Until expiration date |
28 days |
|
3 mL single-patient-use Humalog Tempo Pen |
28 days |
Until expiration date |
28 days |
|
3 mL single-patient-use Humalog Junior KwikPen |
28 days |
Until expiration date |
28 days |
|
HUMALOG U-200* | |||
|
3 mL single-patient-use Humalog KwikPen |
28 days |
Until expiration date |
28 days |
|
3 mL single-patient-use Humalog Tempo Pen |
28 days |
Until expiration date |
28 days |
Use in an External Insulin Pump — Change the HUMALOG U-100 in the reservoir at least every 7 days, or according to the pump user manual, whichever is shorter, or after exposure to temperatures that exceed 98.6°F (37°C).
Storage of Diluted HUMALOG U-100 for Subcutaneous Injection — Diluted HUMALOG for subcutaneous injection may be stored for 28 days when refrigerated at 41°F (5°C) and for 14 days at room temperature up to 86°F (30°C) [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. Do not dilute HUMALOG contained in a cartridge or HUMALOG used in an external insulin pump.
Storage of Intravenous Infusion Preparations with HUMALOG U-100
Intravenous infusion bags prepared with HUMALOG U-100 may be stored for 48 hours when refrigerated at 36° to 46°F (2° to 8°C). The prepared intravenous infusions bags may then be used at room temperature for up to an additional 48 hours [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information and Instructions for Use).
Never Share a HUMALOG Prefilled Pen, Cartridge, Reusable Pen Compatible with Lilly 3 mL Cartridges, or Syringe Between Patients
Advise patients that they must never share a HUMALOG prefilled pen, cartridge, or reusable pen compatible with Lilly 3 mL cartridges with another person, even if the needle is changed. Advise patients using HUMALOG vials not to share needles or syringes with another person. Sharing poses a risk for transmission of blood-borne pathogens [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Hyperglycemia or Hypoglycemia
Instruct patients on self-management procedures including glucose monitoring, proper injection technique, and management of hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, especially at initiation of HUMALOG therapy. Instruct patients on handling of special situations such as intercurrent conditions (illness, stress, or emotional disturbances), an inadequate or skipped insulin dose, inadvertent administration of an increased insulin dose, inadequate food intake, and skipped meals. Instruct patients on the management of hypoglycemia.
Inform patients that their ability to concentrate and react may be impaired as a result of hypoglycemia. Advise patients who have frequent hypoglycemia or reduced or absent warning signs of hypoglycemia to use caution when driving or operating machinery [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Advise patients that changes in insulin regimen can predispose to hyperglycemia or hypoglycemia and that changes in insulin regimen should be made under close medical supervision [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Hypoglycemia due to Medication Errors
Instruct patients to always check the insulin container label before each injection to avoid mix-ups between insulin products [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Inform patients that HUMALOG U-200 contains 2 times as much insulin per mL as HUMALOG U-100. The HUMALOG U-200 prefilled pen dose window shows the number of units of HUMALOG U-200 to be injected so no dose conversion is required [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Instruct patients to NOT transfer HUMALOG U-200 from the HUMALOG U-200 prefilled pen to a syringe. The markings on the syringe will not measure the dose correctly and this can result in overdosage and severe hypoglycemia. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Advise patients that hypersensitivity reactions have occurred with HUMALOG. Inform patients on the symptoms of hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Administration Instruction for HUMALOG U-200
Instruct patients to NOT mix HUMALOG U-200 with any other insulin.
Instructions For Patients Using Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Pumps
- Do not use HUMALOG U-200 in a subcutaneous insulin pump.
- Train patients in intensive insulin therapy with multiple injections and in the function of their pump and pump accessories.
- Instruct patients to follow healthcare provider recommendations when setting pump basal rates and bolus settings.
- Refer to the continuous subcutaneous infusion pump user manual to see if HUMALOG can be used with the pump. See recommended reservoir and infusion sets in the insulin pump user manual.
- Instruct patients to replace insulin in the reservoir at least every 7 days, or according to the pump user manual, whichever is shorter; infusion sets and infusion set insertion sites should be changed in accordance with the manufacturers' user manual. By following this schedule, patients avoid insulin degradation, infusion set occlusion, and loss of the insulin preservative.
- Instruct patients to discard insulin exposed to temperatures higher than 98.6°F (37°C). The temperature of the insulin may exceed ambient temperature when the pump housing, cover, tubing or sport case is exposed to sunlight or radiant heat.
- Instruct patients to inform healthcare provider and select a new site for infusion if infusion site becomes erythematous, pruritic, or thickened.
- Instruct patients on the risk of rapid hyperglycemia and ketosis due to pump malfunction, infusion set occlusion, leakage, disconnection or kinking, and degraded insulin. Instruct patients on the risk of hypoglycemia from pump malfunction. If these problems cannot be promptly corrected, instruct patients to resume therapy with subcutaneous insulin injection and contact their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5) and How Supplied/Storage and Handling (16.2)].
Manufactured by:
Eli Lilly and Company
Indianapolis, IN 46285, USA
US License Number 1891
1 3 mL cartridge is for use in compatible insulin delivery devices, including HumaPen® Luxura® HD
Humalog®, Humalog KwikPen®, Humalog Tempo PenTM, Humalog® Junior KwikPen®, HumaPen®, HumaPen® Luxura® and HumaPen® Luxura® HD are trademarks of Eli Lilly and Company.
www.humalog.com
Copyright © 1996, 2025, Eli Lilly and Company. All rights reserved.
LOG-0012-USPI-20250507
SPL PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT SECTION
Patient Package Insert
|
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration |
Revised: May 2025 |
|
PATIENT INFORMATION | |
|
Do not share your HUMALOG prefilled pens, cartridges, reusable pen
compatible with 3 mL cartridges of HUMALOG U-100, needles, or syringes with
other people, even if the needle has been changed. You may give other people a
serious infection or get a serious infection from them.
| |
|
Who should not take HUMALOG?
| |
|
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking HUMALOG?
| |
|
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including
prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. | |
|
How should I use HUMALOG?
| |
|
Keep HUMALOG and all medicines out of reach of children. | |
|
Your dose of HUMALOG may need to change because of a:
| |
|
What should I avoid while using HUMALOG?
| |
|
What are the possible side effects of HUMALOG? *low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). Signs and symptoms of low blood sugar may include: | |
|
|
|
Your healthcare provider may prescribe a glucagon product for emergency use so that someone else can give you glucagon if your blood sugar becomes too low (severe hypoglycemia) and you are unable to take sugar by mouth. *severe allergic reaction (whole body reaction). Get medical help right away, if you have any of these signs or symptoms of a severe allergic reaction: | |
|
|
|
*low potassium in your blood (hypokalemia). *heart failure. Taking certain diabetes pills called thiazolidinediones or “TZDs” with HUMALOG may cause heart failure in some people. This can happen even if you have never had heart failure or heart problems before. If you already have heart failure it may get worse while you take TZDs with HUMALOG. Your healthcare provider should monitor you closely while you are taking TZDs with HUMALOG. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any new or worse symptoms of heart failure including: | |
|
|
|
Treatment with TZDs and HUMALOG may need to be adjusted or stopped by your
healthcare provider if you have new or worse heart failure. | |
|
|
|
The most common side effects of HUMALOG include: | |
|
|
|
These are not all of the possible side effects of HUMALOG. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088. | |
|
General Information about the safe and effective use of HUMALOG. | |
|
What are the ingredients in HUMALOG U-100? | |
|
What are the ingredients in HUMALOG U-200? |
LOG-0008-PPI-20250507
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE SECTION
Tempo Pen U-200 Instructions for Use
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
HUMALOG**®**** (HU-ma-log) Tempo Pen™**
(insulin lispro)
injection, for subcutaneous use
3 mL single-patient-use pen (200 units per mL)

Read the Instructions for Use before you start taking HUMALOG and each time you get another Tempo Pen There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
Do not share your HUMALOG Tempo Pen with other people, even if the needle has been changed. You may give other people a serious infection or get a serious infection from them.
HUMALOG Tempo Pen 200 units/mL (“Pen”) is a disposable single-patient-use prefilled pen containing 600 units of HUMALOG. You can give yourself more than 1 dose from the Pen. Each turn (click) of the Dose Knob dials 1 unit of insulin. You can give from 1 to 60 units in a single injection.If your dose is more than 60 units, you will need to give yourself more than 1 injection. The Plunger only moves a little with each injection, and you may not notice that it moves. The Plunger will only reach the end of the cartridge when you have used all 600 units in the Pen.
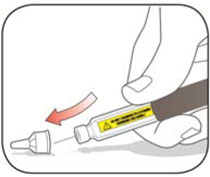
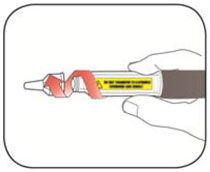
Do not transfer insulin from your Pen to a syringe. Syringes will not measure 200 units/mL insulin correctly. A severe overdose can result, causing very low blood sugar which may put your life in danger.
People who are blind or have vision problems should not use the Pen without help from a person trained to use the Pen.
This HUMALOG Tempo Pen contains a component that allows for data connectivity when used with a compatible transmitter.
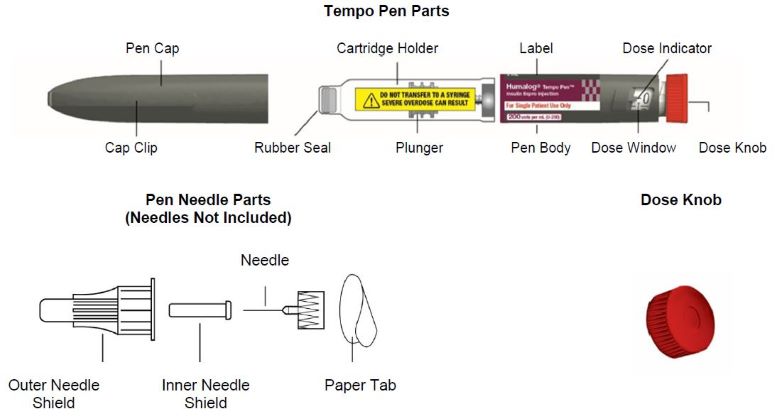
How to recognize your HUMALOG 200 units/mL Tempo Pen
- Pen color: Dark grey
- Dose Knob: Red
- Label: Burgundy label with "200 units per mL (U-200)" in white stripe and a grey and burgundy checker board design.
Supplies needed to give your injection
- HUMALOG Tempo Pen
- Tempo Pen compatible Needle (Becton, Dickinson and Company Pen Needles recommended)
- Alcohol swab
- Gauze
Preparing your Pen
- Wash your hands with soap and water.
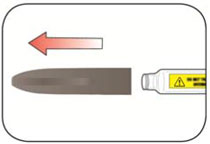
- Check your Pen to make sure you are taking the right type of insulin. This is especially important if you use more than 1 type of insulin. *Do not use your Pen past the expiration date printed on the Label or for more than 28 days after you first start using the Pen. *Always use a new needle for each injection to help prevent infections and blocked needles. Do not reuse or share your needles with other people. You may give other people a serious infection or get a serious infection from them.
|
Step 1:
-
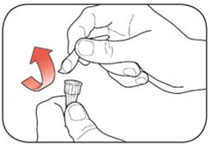
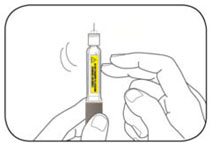
Step 2: *Check the liquid in the Pen. |
|
|
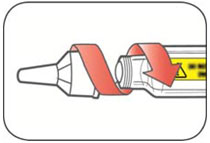
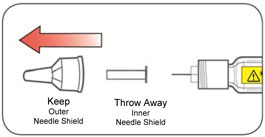
Step 3: *Select a new Needle.
|
|
|
Step 4:
|
|
|
Step 5:
|
|
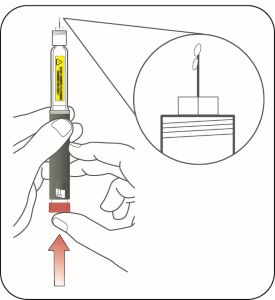
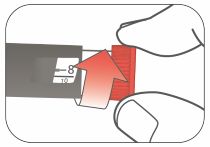
Priming your Pen
Prime before each injection.
- Priming your Pen means removing the air from the Needle and Cartridge that may collect during normal use and ensures that the Pen is working correctly.
- If youdo not prime before each injection, you may get too much or too little insulin.
|
Step 6:
|
|
|
Step 7:
|
|
|
Step 8:
You should see insulin at the tip of the Needle. - - Small air bubbles are normal and will not affect your dose. |
|
|
|
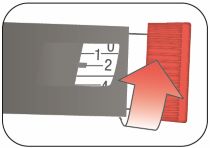
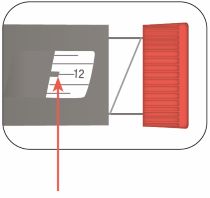
Selecting your dose
This Pen has been made to deliver the dose that is shown in the Dose Window. Dial your usual dose as instructed by your healthcare provider.
- You can give from 1 to 60 units in a single injection.
- If your dose is more than 60 units, you will need to give more than 1 injection.
-
If you need help with dividing up your dose the right way, ask your healthcare provider.
-
Use a new Needle for each injection and repeat the priming step.
|
Step 9:
- - - - - - *Always check the number in the Dose Window to make sure you have dialed the correct dose. |
|
|
| |
|
|
- The Pen will not let you dial more than the number of units left in the Pen.
- If you need to inject more than the number of units left in the Pen, you may either:
-
inject the amount left in your Pen and then use a new Pen to give the rest of your dose,**or**
-
get a new Pen and inject the full dose.
- It is normal to see a small amount of insulin left in the Pen that you cannot inject.Do not transfer this to a syringe. Severe overdose can result.
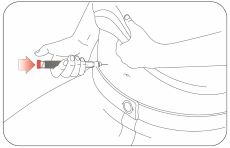
Giving your injection
- Inject your insulin as your healthcare provider has shown you.
- Change (rotate) your injection sites within the area you choose for each dose to reduce your risk of getting lipodystrophy (pits in skin or thickened skin) and localized cutaneous amyloidosis (skin with lumps) at the injection sites. *Do not use the exact same spot for each injection. *Do not inject where the skin has pits, is thickened, or has lumps. *Do not inject where the skin is tender, bruised, scaly or hard, or into scars or damaged skin. *Do not try to change your dose while injecting.
|
Step 10:
|
|
|
Step 11:
|
|
|
Step 12:
- - - - The Plunger only moves a little with each injection, and you may not notice
that it moves. |
|
After your injection
|
Step 13:
|
|
|
Step 14:
|
|
|
Step 15:
|
|
Disposing of Pens and Needles
- The used Pen may be discarded in your household trash after you have removed the needle.
- Put your used needles in a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container right away after use. Do not throw away (dispose of) loose needles in your household trash.
- If you do not have a FDA-cleared sharps disposal container, you may use a household container that is:
-
made of a heavy-duty plastic,
-
can be closed with a tight-fitting, puncture-resistant lid, without sharps being able to come out,
-
upright and stable during use,
-
leak-resistant, and
-
properly labeled to warn of hazardous waste inside the container.
- When your sharps disposal container is almost full, you will need to follow your community guidelines for the right way to dispose of your sharps disposal container. There may be state or local laws about how you should throw away used needles and syringes. For more information about safe sharps disposal, and for specific information about sharps disposal in the state that you live in, go to the FDA's website at: http://www.fda.gov/safesharpsdisposal
- Do not dispose of your used sharps disposal container in your household trash unless your community guidelines permit this. Do not recycle your used sharps disposal container.
Storing your Pen
Unused Pens
- Store unused Pens in the refrigerator at 36°F to 46°F (2°C to 8°C). *Do not freeze your insulin.Do not use if it has been frozen.
- Unused Pens may be used until the expiration date printed on the Label, if the Pen has been kept in the refrigerator.
In-use Pen
- Store the Pen you are currently using at room temperature [up to 86°F (30°C)]. Keep away from heat and light.
- Throw away the HUMALOG Tempo Pen you are using after 28 days, even if it still has insulin left in it.
General information about the safe and effective use of your Pen
*Keep your Pen and needles out of the sight and reach of children. *Do not use your Pen if any part looks broken or damaged.
- Always carry an extra Pen in case yours is lost or damaged.
Troubleshooting
- If you cannot remove the Pen Cap, gently twist the cap back and forth, and then pull the cap straight off.
- If the Dose Knob is hard to push:
-
Pushing the Dose Knob more slowly will make it easier to inject.
-
Your Needle may be blocked. Put on a new Needle and prime the Pen.
-
You may have dust, food, or liquid inside the Pen. Throw the Pen away and get a new Pen.
If you have any questions or problems with your HUMALOG Tempo Pen, contact Lilly at 1-800-LillyRx (1-800-545-5979) or call your healthcare provider for help. For more information on HUMALOG Tempo Pen and insulin, go to www.humalog.com.
Manufactured by:
Eli Lilly and Company
Indianapolis, IN 46285, USA
US License Number 1891
This Instructions for Use has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administraion.
Revised: 05/2025
Scan this code to launch (www.humalog.com)

HUMALOG® is a registered trademark and HUMALOG Tempo PenTM is a trademark of Eli Lilly and Company.
Copyright © 2025, Eli Lilly and Company. All rights reserved.
|
HUMALOG Tempo Pen meets the current dose accuracy and functional requirements of ISO 11608-1. |
LOGTP200-0001-IFU-20250507

 (Example: 12
units shown in the Dose Window)
(Example: 12
units shown in the Dose Window)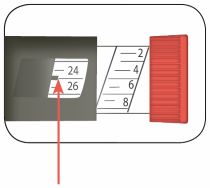 (Example: 25
units shown in the Dose Window)
(Example: 25
units shown in the Dose Window)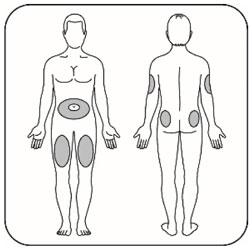
 Do not try to
inject your insulin by turning the Dose Knob. You willnot receive your
insulin by turning the Dose Knob.
Do not try to
inject your insulin by turning the Dose Knob. You willnot receive your
insulin by turning the Dose Knob.