ONGENTYS
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ONGENTYS ® safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ONGENTYS ® . ONGENTYS ( opicapone ) capsules, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 20 20
278a60c4-2353-4657-b486-f392b93181b7
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Apr 26, 2020
Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc.
DUNS: 800981276
Products 2
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
opicapone
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
opicapone
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
Drug Labeling Information
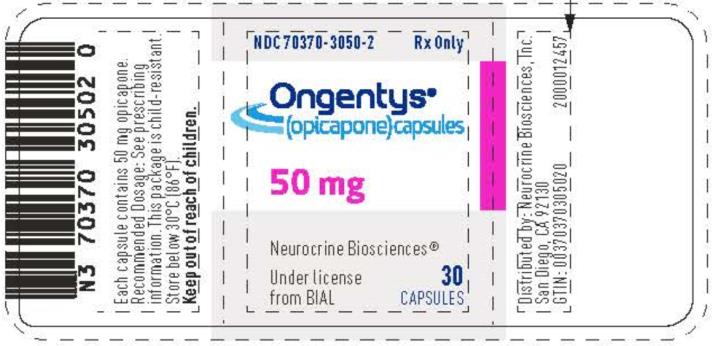
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 70370-3050-2
Ongentys®
(opicapone) capsules
50 mg
30 Capsules
Rx only
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7**DRUG INTERACTIONS**
7.1****Non-Selective Monoamine Oxidase (MAO) Inhibitors
Both ONGENTYS and non-selective MAO inhibitors (e.g., phenelzine, isocarboxazid, and tranylcypromine) inhibit catecholamine metabolism, leading to increased levels of catecholamines. Concomitant use may increase the risk of possible arrhythmias, increased heart rate, and excessive changes in blood pressure.
Concomitant use of ONGENTYS with non-selective MAO inhibitors is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4)]. Selective MAO-B inhibitors can be used concomitantly with ONGENTYS.
7.2****Effect of ONGENTYS on Other Drugs
Drugs Metabolized by Catechol-O-Methyltransferase (COMT)
Concomitant use of ONGENTYS with drugs metabolized by COMT may affect the pharmacokinetics of those drugs, which may increase the risk of possible arrhythmias, increased heart rate, and excessive changes in blood pressure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Drugs known to be metabolized by COMT should be administered with caution. Monitor for changes in heart rate, rhythm, and blood pressure in patients concomitantly treated with ONGENTYS and drugs metabolized by COMT [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2****DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1Dosing and Administration** Information**
The recommended dosage of ONGENTYS is 50 mg administered orally once daily at bedtime. Patients should not eat food for 1 hour before and for at least 1 hour after intake of ONGENTYS [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.2****Dosage Recommendations for Patients with Hepatic Impairment
In patients with moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh B), the recommended dose of ONGENTYS is 25 mg orally once daily at bedtime [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Avoid use of ONGENTYS in patients with severe (Child-Pugh C) hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.3Discontinuation and Missed Dose
When discontinuing ONGENTYS, monitor patients and consider adjustment of other dopaminergic therapies as needed. If a dose of ONGENTYS is missed, the next dose should be taken at the scheduled time the next day.
-
The recommended dosage is 50 mg administered orally once daily at bedtime. (2.1)
-
Patients should not eat food for 1 hour before and for at least 1 hour after intake of ONGENTYS. (2.1)
-
The recommended dosage in patients with moderate hepatic impairment is 25 mg orally once daily at bedtime; avoid use in patients with severe hepatic impairment. (2.2)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8****USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1****Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no adequate data on the developmental risk associated with use of ONGENTYS in pregnant women. In animal studies, oral administration of opicapone during pregnancy resulted in adverse effects on embryofetal development (increased incidence of fetal abnormalities) at clinically relevant plasma exposures in one of two species tested. In addition, opicapone is always given concomitantly with levodopa/carbidopa, which is known to cause developmental toxicity in rabbits (see Data).
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in the U.S. general population is 2-4% and 15-20% of clinically recognized pregnancies, respectively. The background risk for major birth defects and miscarriage in patients with Parkinson’s disease is unknown.
Data
Animal Data
Oral administration of opicapone (0, 150, 375, or 1000 mg/kg/day) to pregnant rats throughout gestation resulted in no adverse effects on embryofetal development. Plasma exposure (AUC) at the highest dose tested (1000 mg/kg/day) was approximately 40 times that in humans at the recommended human dose (50 mg/day).
In pregnant rabbits, oral administration of opicapone (0, 100, 175, or 225 mg/kg/day) during the period of organogenesis resulted in increased incidence of structural abnormalities at all doses tested; maternal toxicity was observed at all but the lowest dose tested. A no-effect dose for adverse effects on embryofetal development was not identified. Plasma exposure (AUC) at the low-effect dose (100 mg/kg/day) was less than that in humans at the RHD.
Oral administration of opicapone (0, 150, 375, or 1000 mg/kg/day) throughout gestation and lactation resulted in no adverse effects on pre- and postnatal development; however, effects on neurobehavioral development in the offspring were not rigorously assessed. Plasma exposure (AUC) at the highest dose tested (1000 mg/kg/day) was approximately 40 times that in humans at the RHD.
Opicapone is always given concomitantly with levodopa/carbidopa, which is known to cause visceral and skeletal malformations in rabbits. The developmental toxicity of opicapone in combination with levodopa/carbidopa was not assessed in animals.
8.2****Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of opicapone in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. In lactating rats, oral administration of opicapone resulted in levels of opicapone or metabolites in milk similar to those in maternal plasma. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for ONGENTYS and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from ONGENTYS or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4****Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5****Geriatric Use
No dose adjustment is required for elderly patients. Of the total number of patients who received ONGENTYS 50 mg in Study 1 and Study 2, 52% of patients were 65 years and older. No overall differences in safety and effectiveness were observed between these patients and younger patients, but greater sensitivity to adverse reactions of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
8.6** Renal Impairment**
The renal route of elimination plays a minor role in the clearance of opicapone [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Avoid use of ONGENTYS in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) (CLcr <15 mL/min). No dosage adjustment is required for patients with mild, moderate, or severe renal impairment. However, because of a potential for increased exposure, monitor patients with severe renal impairment for adverse reactions and discontinue ONGENTYS if tolerability issues arise.
8.7Hepatic Impairment
Opicapone exposure is increased in patients with hepatic impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Avoid use of ONGENTYS in patients with severe (Child-Pugh C) hepatic impairment. Dosage adjustment is recommended for patients with moderate (Child-Pugh B) hepatic impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)]. No dosage adjustment is required in patients with mild (Child-Pugh A) hepatic impairment.
-
Pregnancy: Based on animal data, may cause fetal harm (8.1)
-
Avoid use in patients with end-stage renal disease. (8.6)
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11****DESCRIPTION
ONGENTYS contains opicapone, a peripheral, selective and reversible catechol- O-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitor. The chemical name of opicapone is 2,5-dichloro-3-(5-(3,4-dihydroxy-5-nitrophenyl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl)-4,6-dimethylpyridine-1-oxide with the following structure:

The opicapone molecular formula is C15H10Cl2N4O6; and its molecular weight is 413.17.
Opicapone is a yellow powder/crystalline solid with limited aqueous solubility.
ONGENTYS capsules are intended for oral administration. Each capsule contains 25 mg or 50 mg of opicapone. ONGENTYS also contains the following inactive ingredients: lactose, magnesium stearate, pregelatinized starch, and sodium starch glycolate. The capsule shells contain: FD&C Blue#2, FD&C Red#3, gelatin, and titanium dioxide.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13****NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1****Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
No increase in tumors was observed when opicapone was administered orally to mice (0, 100, 375, or 750 mg/kg/day) for up to 2 years (84-93 weeks at the high dose). The highest dose tested is approximately 70 times the recommended dose (RHD) in humans (50 mg/day) on a body surface area (mg/m2) basis.
No increase in tumors was observed when opicapone was administered orally to rats (0, 100, 500, or 1000 mg/kg/day) for 2 years. Plasma exposure (AUC) at the highest dose tested is approximately 24 times that in humans at the RHD (50 mg/day).
Mutagenesis
Opicapone was negative in in vitro (bacterial reverse mutation test (Ames), chromosomal aberrations in human peripheral blood lymphocytes) and in in vivo (rat bone marrow micronucleus) assays.
Impairment of Fertility
In male and female rats, oral administration of opicapone (0, 100, 500, or 1000 mg/kg/day) prior to and during mating and continuing in females to gestation day 6, resulted in no adverse effects on fertility or general reproductive performance. Plasma exposure (AUC) at the highest dose tested is approximately 40 times that in humans at the RHD.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16****HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1****How Supplied
ONGENTYS (opicapone) capsules are available as:
• 50 mg hard gelatin capsules, Size 1; dark blue opaque cap and dark pink opaque body; axially printed with “OPC” over “50” in white ink, on both the cap and body
- Bottle of 30 with child-resistant closure: NDC 70370-3050-2
• 25 mg hard gelatin capsules, Size 1; light blue opaque cap and light pink opaque body; axially printed with “OPC” over “25” in blue ink, on both the cap and body
- Bottle of 30 with child-resistant closure: NDC 70370-3025-2
16.2Storage and Handling
Store at a temperature below 30°C (86°F).
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17****PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Administration
Instruct patients and/or caregivers that ONGENTYS capsules should be taken at bedtime. Inform patients to not eat food for 1 hour before and for at least 1 hour after intake of ONGENTYS [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
Concomitant Medications
Certain medications can cause an interaction with ONGENTYS. Advise patients and/or caregivers to inform their healthcare provider of all the medicines the patient is taking, including over-the-counter medicines, dietary supplements, and herbal products [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Drug Interactions (7)].
Falling Asleep During Activities of Daily Living
Advise patients and/or caregivers that somnolence has been reported with ONGENTYS. Patients treated with dopaminergic medications have reported falling asleep while engaged in activities of daily living. These adverse reactions may affect some patients’ ability to drive and operate machinery safely [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Hypotension/Syncope
Advise patients that ONGENTYS may cause hypotension or syncope [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Dyskinesia
Advise patients that ONGENTYS may cause dyskinesia or exacerbate pre-existing dyskinesia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Hallucinations and Psychosis
Advise patients that ONGENTYS may cause hallucinations, delusions, or aggressive behavior and they should report any of these adverse reactions to their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Impulse Control/Compulsive Disorders
Inform patients of the potential for experiencing intense urges to gamble, increased sexual urges, intense urges to spend money, binge eating, and other intense urges and the inability to control these urges while taking ONGENTYS and one or more medications that increase central dopaminergic tone that are generally used for the treatment of PD. Advise patients that they should report any of these adverse reactions to their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Withdrawal-Emergent Hyperpyrexia and Confusion
Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider before stopping ONGENTYS. Tell patients to inform their healthcare provider if they develop symptoms such as fever, confusion, or severe muscle stiffness after stopping ONGENTYS [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
For further information on ONGENTYS, call 1-833-ONGENTYS (833-664-3689) or visit www.ongentys.com
Distributed by:
Neurocrine Biosciences, Inc., San Diego, CA 92130
Under license from BIAL-Portela & Ca, S.A.
ONGENTYS is a registered trademark of BIAL-Portela & Ca, S.A.
91067001
