Doxercalciferol
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use doxercalciferol capsules safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for doxercalciferol capsules.Doxercalciferol capsules, for oral useInitial U.S. Approval: 1999
2ed2f592-27a7-4c10-a18a-21a3f221d3b1
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Oct 28, 2021
Heritage Pharmaceuticals Inc. d/b/a Avet Pharmaceuticals Inc.
DUNS: 780779901
Products 3
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Doxercalciferol
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (10)
Doxercalciferol
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (11)
Doxercalciferol
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (9)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL 2.5 mcg
NDC 23155-540-25
Doxercalciferol Capsules
2.5 mcg
50 Capsules
Rx only

INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- Doxercalciferol capsules are indicated for the treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism in adult patients with Stage 3 or Stage 4 chronic kidney disease (CKD) and adult patients with CKD on dialysis.
Doxercalciferol Capsules is a synthetic vitamin D2 analog:
- Doxercalciferol capsules are indicated for the treatment of secondary hyperparathyroidism in adult patients with Stage 3 or Stage 4 chronic kidney disease (CKD) and adult patients with CKD on dialysis. (1)
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Doxercalciferol is contraindicated in patients with:
- Hypercalcemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Vitamin D toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Known hypersensitivity to doxercalciferol or any of the inactive ingredients of doxercalciferol capsules; serious hypersensitivity reactions including anaphylaxis and angioedema have been reported [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3), Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
- Hypercalcemia (4)
- Vitamin D toxicity (4)
- Know hypersensitivity to doxercalciferol or any of the inactive ingredients of doxercalciferol capsules (4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in another section of the label:
- Hypercalcemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Serious Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Adynamic Bone Disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adverse reactions in patients with stage 3 or 4 CKD
Doxercalciferol capsules have been evaluated in two placebo-controlled, double-blind 24 week studies in patients with Stage 3 or 4 CKD. Patients were treated with doxercalciferol capsules (n=27) or placebo (n=28) [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Adverse reactions occurring in the doxercalciferol capsules group at a frequency of 5% or greater and more frequently than in the placebo group are presented in Table 1.
Table 1: Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥5% Doxercalciferol Capsule- Treated Patients with CKD on Predialysis and Greater than Placebo in Two Double-Blind Clinical Studies
| ||
|
** Adverse Reaction******* |
** Doxercalciferol (n=27)** |
** Placebo (n=28)** |
|
Infection/bacterial infection/viral infection |
30 |
25 |
|
Constipation |
26 |
11 |
|
Rhinitis |
22 |
11 |
|
Anemia |
19 |
4 |
|
Cough |
19 |
4 |
|
Dyspnea |
19 |
11 |
|
Paresthesia |
15 |
11 |
|
Asthenia |
15 |
11 |
|
Insomnia |
15 |
4 |
|
Hypertonia |
11 |
4 |
|
Angina pectoris |
8 |
0 |
|
Dehydration |
7 |
4 |
|
Depression |
7 |
0 |
|
Dyspepsia |
7 |
4 |
|
Edema |
7 |
4 |
|
Urinary tract infection |
7 |
4 |
|
Leukopenia |
7 |
0 |
|
Chest pain |
7 |
4 |
|
Pruritus |
7 |
4 |
|
Sinusitis |
7 |
4 |
Adverse reactions in patients with CKD on dialysis
Doxercalciferol capsules have been evaluated in two placebo-controlled, double-blind studies in patients with CKD on hemodialysis. Patients were treated with doxercalciferol capsules (n=61) or placebo (n=61) [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. After randomization to two groups, eligible patients underwent an 8-week washout period during which no vitamin D derivatives were administered to either group. Subsequently, all patients received doxercalciferol capsules in an open-label fashion for 16 weeks followed by a double-blind period of 8 weeks during which patients received either doxercalciferol capsules or placebo. Adverse reactions occurring in the doxercalciferol capsule groups at a frequency of 2% or greater, and more frequently than in the placebo group are presented in Table 2.
Table 2: Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥2% Doxercalciferol Capsule- Treated Patients with CKD on Dialysis and Greater than Placebo in Two Double- Blind Clinical Studies
| ||
|
** Adverse Reaction******* |
** Doxercalciferol (n=61)** |
** Placebo (n=61)** |
|
Edema |
34 |
21 |
|
Malaise |
28 |
20 |
|
Headache |
28 |
18 |
|
Nausea/Vomiting |
21 |
20 |
|
Dizziness |
12 |
10 |
|
Dyspnea |
12 |
7 |
|
Pruritus |
8 |
7 |
|
Bradycardia |
7 |
5 |
|
Anorexia |
5 |
3 |
|
Dyspepsia |
5 |
2 |
|
Arthralgia |
5 |
0 |
|
Weight increase |
5 |
0 |
|
Abscess |
3 |
0 |
|
Sleep disorder |
3 |
0 |
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of doxercalciferol. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to estimate their frequency or to establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Hypersensitivity reactions include anaphylaxis with symptoms of angioedema (involving face, lips, tongue and airways), hypotension, unresponsiveness, chest discomfort, shortness of breath, cardiopulmonary arrest, pruritus, and skin burning sensation.
The most common adverse reactions in patients with Stage 3 or 4 CKD (incidence
5%) were infection, urinary tract infection, chest pain, angina pectoris, constipation, dyspepsia, anemia, leucopenia, dehydration, edema, depression, hypertonia, insomnia, asthenia, paresthesia, cough increased, dyspnea, pruritus, sinusitis, and rhinitis. (6.1)
The most common adverse reactions in patients with CKD on dialysis (incidence
5%) were headache, malaise, edema, nausea/vomiting, dyspnea, dizziness, pruritus, and bradycardia. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Avet Pharmaceuticals Inc. at 1-866-901-DRUG (3784) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Tables 3 and 4 include clinically significant drug interactions with doxercalciferol.
Table 3: Clinically Significant Drug Interactions with Doxercalciferol Capsules|
** Drugs that May Increase the Risk of Hypercalcemia** | |
|
Clinical |
Concomitant administration of high doses of calcium-containing preparations or other vitamin D compounds may increase the risk of hypercalcemia. Thiazide diuretics are known to induce hypercalcemia by reducing excretion of calcium in the urine. |
|
Examples |
Calcium-containing products, other vitamin D compounds or thiazide diuretics |
|
Intervention |
Monitor serum calcium concentrations more frequently and adjust doxercalciferol dose as needed [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. |
|
** Digitalis Compounds** | |
|
Clinical |
Doxercalciferol can cause hypercalcemia which can potentiate the risk of digitalis toxicity. |
|
Intervention |
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of digitalis toxicity and increase frequency of serum calcium monitoring when initiating or adjusting the dose of doxercalciferol in patients receiving digitalis compounds [see Warnings andPrecautions (5.2)]. |
|
** Cytochrome P450 Inhibitors** | |
|
Clinical |
Doxercalciferol is activated by CYP 27 in the liver. Cytochrome P450 inhibitors may inhibit the 25-hydroxylation of doxercalciferol and thus reduce the formation of active doxercalciferol moiety [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
|
Examples |
Ketoconazole and erythromycin |
|
Intervention |
If a patient initiates or discontinues therapy with a cytochrome P450 inhibitor, dose adjustment of doxercalciferol may be necessary. Monitor intact PTH and serum calcium concentrations closely. |
|
** Enzyme Inducers** | |
|
Clinical |
Doxercalciferol is activated by CYP 27 in the liver. Enzyme inducers may affect the 25-hydroxylation of doxercalciferol [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. |
|
Examples |
Glutethimide and phenobarbital |
|
Intervention |
If a patient initiates or discontinues therapy with an enzyme inducer, dose adjustment of doxercalciferol may be necessary. Monitor intact PTH and serum calcium concentrations closely. |
|
** Magnesium-containing Products** | |
|
Clinical |
Concomitant administration of doxercalciferol and high doses of magnesium- containing products may increase the risk of hypermagnesemia. |
|
Examples |
Magnesium-containing products such as antacids |
|
Intervention |
Avoid use of magnesium-containing products and doxercalciferol in patients on chronic renal dialysis. |
|
** Cholestyramine** | |
|
Clinical |
Cholestyramine has been reported to reduce intestinal absorption of fat- soluble vitamins. Therefore, it may impair intestinal absorption of doxercalciferol capsules. |
|
Intervention |
Administer doxercalciferol capsules at least 1 hour before or 4 to 6 hours after taking cholestyramine. |
|
** Mineral Oil or other Substances that May Affect Absorption of Fat** | |
|
Clinical |
The use of mineral oil or other substances that may affect absorption of fat may influence the absorption and availability of doxercalciferol. |
|
Intervention |
Administer doxercalciferol capsules at least 1 hour before or 4 to 6 hours after taking mineral oil or other substances that may affect absorption of fat. |
- Cytochrome P450 inhibitors: Formation of the active doxercalciferol moiety may be hindered and may necessitate dosage adjustment. Monitor intact PTH and serum calcium concentrations closely. (7)
- Enzyme inducers: Formation of the active doxercalciferol moiety may be affected and may necessitate dosage adjustment. Monitor intact PTH and serum calcium concentrations closely. (7)
- Magnesium-containing products: Combined use may cause hypermagnesemia. Monitor serum magnesium concentrations more frequently and adjust dose as needed. (7)
- Cholestyramine: May impair absorption of doxercalciferol capsules. Administer doxercalciferol capsules at least 1 hour before or 4 to 6 hours after taking cholestyramine. (7)
- Mineral oil or other substances that may affect absorption of fat: May impair absorption of doxercalciferol capsules. Administer doxercalciferol capsules at least 1 hour before or 4 to 6 hours after taking substances that may affect absorption.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Prior to Initiation of Doxercalciferol Capsules
- Ensure serum calcium is not above the upper limit of normal before initiating treatment with doxercalciferol capsules [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
2.2 Dosage Recommendations for Doxercalciferol Capsules in Patients with
Stage 3 or 4 CKD
- Initiate doxercalciferol capsules at a dose of 1 mcg orally once daily.
- Target the maintenance dose of doxercalciferol to intact parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels within the desired therapeutic range and serum calcium within normal limits.
- Monitor serum calcium, phosphorus, and intact PTH levels at least every two weeks for 3 months after initiation of therapy or dose adjustment, then monthly for 3 months, and every 3 months thereafter.
- Titrate the dose of doxercalciferol capsules based on intact PTH. The dose may be increased at 2-week intervals by 0.5 mcg to achieve the desired therapeutic range of intact PTH. The maximum recommended dose of doxercalciferol capsules is 3.5 mcg administered once daily. Prior to raising the dose, ensure serum calcium is within normal limits.
- Suspend or decrease the dose if intact PTH is persistently and abnormally low to reduce the risk of adynamic bone disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] or if serum calcium is consistently above the normal range to reduce the risk of hypercalcemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. If suspended, the drug should be restarted after one week at a dose that is at least 0.5 mcg lower.
2.3 Dosage Recommendations for Doxercalciferol Capsules in Patients with
CKD on Dialysis
- Initiate doxercalciferol capsules at a dose of 10 mcg orally administered three times weekly at dialysis (no more frequently than every other day).
- Target the maintenance dose of doxercalciferol to intact parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels within the desired therapeutic range and serum calcium within normal limits.
- Monitor serum calcium, phosphorus, and intact PTH levels frequently (e.g., weekly) after initiation of therapy or dose adjustment.
- Titrate the dose of doxercalciferol capsules based on intact PTH. The dose may be increased at 8-week intervals by 2.5 mcg to achieve the desired therapeutic range of intact PTH. The maximum recommended dose of doxercalciferol is 20 mcg administered three times weekly at dialysis for a total dose of 60 mcg weekly. Prior to raising the dose, ensure serum calcium is within normal limits.
- Suspend or decrease the dose if intact PTH is persistently and abnormally low to reduce the risk of adynamic bone disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] or if serum calcium is consistently above the normal range to reduce the risk of hypercalcemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. If suspended, the drug should be restarted one week later at a dose that is at least 2.5 mcg lower.
2.6 Drug Interactions that May Require Dosage Adjustments of
Doxercalciferol
- Increased monitoring of serum calcium and dose adjustment of doxercalciferol may be necessary when given concomitantly with drugs that may increase the risk of hypercalcemia [see Drug Interactions (7)].
- Increased monitoring of both serum calcium and intact PTH as well as dose adjustment of doxercalciferol may be necessary when given concomitantly with cytochrome P450 inhibitors or enzyme inducers [see Drug Interactions (7)].
- Before initiating treatment, ensure serum calcium is not above the upper limit of normal. (2.1)
- Dosage for doxercalciferol capsules in patients with:
- Stage 3 or 4 CKD: Initiate dosing at 1 mcg orally once daily. Maximum dose is 3.5 mcg once daily. (2.2)
- CKD on dialysis: Initiate dosing at 10 mcg orally three times weekly at dialysis (no more frequently than every other day). Maximum dose is 20 mcg three times weekly for a total of 60 mcg weekly. (2.3)
- Target the maintenance dose of doxercalciferol to intact parathyroid hormone (PTH) levels within the desired therapeutic range and serum calcium within normal limits. (2)
- See Full Prescribing Information for dose titration, laboratory monitoring, and important administration instructions. (2)
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 0.5 mcg – White, opaque, oval shaped soft gelatin capsules. Each capsule is imprinted with**"HP 538"** in black ink.
- 1 mcg – Beige, opaque, oval shaped soft gelatin capsules. Each capsule is imprinted with**"HP 539"** in black ink.
- 2.5 mcg – Red, opaque, oval shaped soft gelatin capsules. Each capsule is imprinted with**"HP 540"** in black ink.
- Capsules: 0.5 mcg, 1 mcg, and 2.5 mcg (3)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
The limited available data with doxercalciferol in pregnant women are insufficient to identify a drug-associated risk for major birth defects, miscarriage or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. There are risks to the mother and fetus associated with chronic kidney disease in pregnancy [see Clinical Considerations]. In reproduction studies in rats and rabbits administered doxercalciferol during organogenesis at up to 20 mcg/kg/day and 0.1 mcg/kg/day, respectively (approximately 25 times (rats) and less than (rabbits) the maximum recommended human oral dose of 60 mcg/week based on mcg/m2 body surface area), no adverse developmental effects were observed [see Data].
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and/or embryo/fetal risk
Chronic kidney disease in pregnancy increases the risk for maternal hypertension and preeclampsia,
miscarriage, preterm delivery polyhydramnios, stillbirth, and low-birth-weight infants.
Data
Animal data
There were no adverse effects on fetal development when doxercalciferol was administered at doses up to 20 mcg/kg/day in pregnant rats or doses up to 0.1 mcg/kg/day in pregnant rabbits during the period of organogenesis.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information available on the presence of doxercalciferol in human milk, the effects of the drug on the breastfed infant, or the effects of the drug on milk production. Infants exposed to doxercalciferol through breast milk should be monitored for signs and symptoms of hypercalcemia [see Clinical Considerations].
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for doxercalciferol and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from doxercalciferol or from the underlying maternal condition.
Clinical Considerations
Monitoring of serum calcium in the infant should be considered.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy of doxercalciferol in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of doxercalciferol did not include sufficient numbers of patients 65 years or over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
Patients with hepatic impairment may not metabolize doxercalciferol appropriately. More frequent monitoring of intact PTH, calcium, and phosphorus levels should be done in patients with hepatic impairment.
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
Overdosage of doxercalciferol may lead to hypercalcemia, hypercalciuria, and hyperphosphatemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. The treatment of acute overdosage should consist of supportive measures and discontinuation of doxercalciferol administration. Serum calcium levels should be measured until normal.
Based on similarities between doxercalciferol and its active metabolite, 1α,25-(OH)2D2, it is expected that doxercalciferol is not removed from the blood by dialysis.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Doxercalciferol Capsules contains doxercalciferol, which is a synthetic vitamin D2 analog. Doxercalciferol undergoes metabolic activation in vivo to form 1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D2 (1α,25-(OH)2D2), a naturally occurring, biologically active form of vitamin D2.
Doxercalciferol is a colorless crystalline compound with a calculated molecular weight of 412.66 and a molecular formula of C28H44O2. It is soluble in oils and organic solvents, but is relatively insoluble in water. Chemically, doxercalciferol is (1α,3β,5Z,7E,22E)-9,10-secoergosta-5,7,10(19),22-tetraene-1,3-diol. The structural formula is:
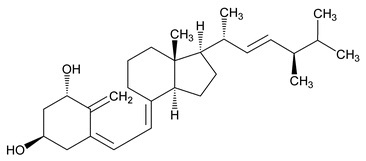
Doxercalciferol capsules are soft gelatin capsules containing 0.5 mcg, 1 mcg, or 2.5 mcg doxercalciferol for oral use. Each capsule also contains butylated hydroxyanisole (BHA), ethanol, and medium-chain triglycerides. The capsule shells contain gelatin, glycerin, iron oxide black and titanium dioxide. In addition, the 0.5 mcg capsule shells contain shellac glaze, the 1 mcg capsule shells contain FD&C Blue No. 1, FD&C Yellow No. 6, shellac and the 2.5 mcg capsule shells contain FD&C Red No. 40 and shellac.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Doxercalciferol is a synthetic vitamin D2 analog that requires metabolic activation to form the active 1α,25-(OH)2D2 metabolite, which binds to the vitamin D receptor (VDR) to result in the selective activation of vitamin D responsive pathways. Vitamin D and doxercalciferol have been shown to reduce PTH levels by inhibiting PTH synthesis and secretion.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
In healthy volunteers, peak blood levels of 1α,25-(OH)2D2, the major metabolite of doxercalciferol, are attained at 8 hours after a single intravenous dose of doxercalciferol and at 11 to 12 hours following capsule doses.
Elimination
The mean elimination half-life of 1α,25-(OH)2D2 after an oral dose is approximately 32 to 37 hours with a range of up to 96 hours.
Metabolism
Doxercalciferol is activated by CYP 27 in the liver to form 1α,25-(OH)2D2 (major metabolite) and 1α,24-dihydroxyvitamin D2 (minor metabolite). Activation of doxercalciferol does not require the involvement of the kidneys.
Specific Populations
Patients with renal impairment
The mean elimination half-life of 1α,25-(OH)2D2 in patients with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) and in healthy volunteers appears to be similar following an oral dose. Hemodialysis causes a temporary increase in 1α,25- (OH)2D2 mean concentrations, presumably due to volume contraction. 1α,25-(OH)2D2 is not removed from blood during hemodialysis.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In a 104-week carcinogenicity study in rats, there was an increased incidence of benign and malignant adrenal pheochromocytomas in both males and females at oral doses of 0.04, 0.13, and 0.39 mcg/kg/day (less than the maximum recommended human oral dose of 60 mcg/week based on mcg/m2 body surface area). This increased incidence of pheochromocytomas in rats may be due to altered calcium homeostasis by doxercalciferol. No evidence of genetic toxicity was observed in an in vitro bacterial mutagenicity assay (Ames test) or a mouse lymphoma gene mutation assay. Doxercalciferol caused structural chromatid and chromosome aberrations in an in vitro human lymphocyte clastogenicity assay with metabolic activation. However, doxercalciferol was negative in an in vivo mouse micronucleus clastogenicity assay.
Doxercalciferol had no effect on male or female fertility in rats at oral doses up to 2.5 mcg/kg/day (approximately 3 times the maximum recommended human oral dose of 60 mcg/week based on mcg/m2 body surface area).
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Clinical Studies of Doxercalciferol Capsules in Patients with Stage 3
or 4 CKD
The safety and effectiveness of doxercalciferol capsules were evaluated in two clinical studies in 55 patients with Stage 3 or 4 CKD. Eighty-two percent of the patients were male, the average age was 65 years, 51% were Caucasian, 40% African-American, and the average serum intact PTH level at baseline was 195 pg/mL. While levels of 25-(OH) vitamin D were not evaluated at baseline, retrospective assessments of stored serum revealed that the mean ± SD serum 25-(OH) vitamin D was 19 ± 8 ng/mL (range: <5 to 54 ng/mL) in the study population.
After randomization to two groups, eligible patients underwent an 8-week washout period during which no vitamin D derivatives were administered to either group. Subsequently, one group received doxercalciferol capsules and the other placebo during the double-blind period of 24 weeks. The initial dose of doxercalciferol capsules was 1 mcg per day. The dosage of doxercalciferol capsules was adjusted as necessary by the investigator to reduce intact PTH levels to a target of ≥30% below post-washout baseline. The maximum dosage was limited to 3.5 mcg per day. If at any time during the trial intact PTH fell below 15 pg/mL, doxercalciferol capsules were immediately suspended and restarted at a lower dosage the following week.
Decreases in the mean plasma intact PTH from baseline values were calculated using as baseline the average of the last 2 values obtained during the 8-week washout phase. In analyses of pooled data from the two studies, intact PTH levels decreased from baseline by an average of 101 pg/mL in the doxercalciferol capsules group and by 4 pg/mL in the placebo group (p<0.001). Twenty (74%) of 27 subjects in the doxercalciferol capsules group achieved mean plasma intact PTH suppression of ≥30% from baseline for the last four weeks of treatment, whereas two (7%) of the 28 subjects treated with placebo achieved this level of intact PTH suppression.
14.2 Clinical Studies of Doxercalciferol Capsules in Patients with CKD on
Dialysis
The safety and effectiveness of doxercalciferol capsules were evaluated in two double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter clinical studies (Study A and Study B) in a total of 138 patients with CKD on hemodialysis. Patients in Study A were an average age of 52 years (range: 22 to 75), were 55% male, and were 58% African-American, 31% Caucasian, and 11% Hispanic, and had been on hemodialysis for an average of 53 months. Patients in Study B were an average of 52 years (range: 27 to 75), were 45% male, and 99% African-American, and 1% Caucasian, and had been on hemodialysis for an average of 56 months. After randomization to two groups, eligible patients underwent an 8-week washout period during which no vitamin D derivatives were administered to either group. Subsequently, all patients received doxercalciferol capsules in an open-label fashion for 16 weeks followed by a double-blind period of 8 weeks during which patients received either doxercalciferol capsules or placebo. The initial dose of doxercalciferol capsules during the open-label phase was 10 mcg after each dialysis session (3 times weekly) for a total of 30 mcg per week. The dosage of doxercalciferol was adjusted as necessary by the investigator to achieve intact PTH levels within 150 pg/mL to 300 pg/mL. The maximum dosage was limited to 20 mcg after each dialysis session (60 mcg/week). If at any time during the trial intact PTH fell below 150 pg/mL, Doxercalciferol was immediately suspended and restarted at a lower dosage the following week. Mean weekly doses during the 16-week open-label period ranged from 15 mcg to 29 mcg in Study A and from 19 mcg to 28 mcg in Study B.
One hundred and six (77%) of the 138 patients who were treated with doxercalciferol capsules during the 16- week open-label phase achieved intact PTH levels ≤300 pg/mL. Ninety-four (68%) of these patients exhibited plasma intact PTH levels ≤300 pg/mL on at least 3 occasions. Eighty-seven (63%) patients had plasma intact PTH levels <150 pg/mL on at least one occasion during the open-label phase of study participation.
Decreases in plasma intact PTH from baseline values were calculated using as baseline the average of the last 3 values obtained during the 8-week washout phase and are displayed in Table 5.
Table 5: Intact PTH Summary Data for Patients with CKD on Dialysis Receiving Doxercalciferol Capsules in Studies A and B
| |||
|
NA = not applicable | |||
|
** Intact PTH (pg/mL)** | |||
|
** means** ±** SD (n)*** | |||
|
** Doxercalciferol Capsules** |
** Placebo** | ||
|
Study A |
Baseline |
797.2 ± 443.8 (30) |
847.1 ± 765.5 (32) |
|
Week 16 |
384.3 ± 397.8 (24) |
526.5 ± 872.2 (29) | |
|
Week 24 |
404.4 ± 262.9 (21) |
672.6 ± 356.9 (24) | |
|
Study B |
Baseline |
973.9 ± 567.0 (41) |
990.4 ± 488.3 (35) |
|
Week 16 |
476.1 ± 444.5 (37) |
485.9 ± 443.4 (32) | |
|
Week 24 |
459.8 ± 443.0 (35) |
871.9 ± 623.6 (30) |
Doxercalciferol capsules treatment resulted in a statistically significant reduction from baseline in mean intact PTH levels during the 16-week open- label treatment period in more than 94% of the 138 treated patients. During the double-blind period (weeks 17 to 24), the reduction in mean intact PTH levels was maintained in the doxercalciferol capsules treatment group compared to a return to near baseline in the placebo group.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
How Supplied
Doxercalciferol capsules are oval, soft gelatin capsules supplied as follows.
|
** Strength** |
** Capsule Color** |
** Imprint Code** |
** Package Size** |
** NDC** |
|
0.5 mcg |
White, Opaque |
HP 538 |
Bottle of 50 capsules |
23155-538-25 |
|
1 mcg |
Beige, Opaque |
HP 539 |
Bottle of 50 capsules |
23155-539-25 |
|
2.5 mcg |
Red, Opaque |
HP 540 |
Bottle of 50 capsules |
23155-540-25 |
Storage and Handling
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F)
[see USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Hypercalcemia
Advise patients to contact a health care provider if they develop symptoms of elevated calcium (e.g. feeling tired, difficulty thinking clearly, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, constipation, increased thirst, increased urination and weight loss) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Hypersensitivity
Inform patients that hypersensitivity reactions can occur with doxercalciferol [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Monitoring
Inform patients that they will need routine monitoring of laboratory parameters such as calcium and intact PTH while receiving doxercalciferol. Inform patients that more frequent monitoring is necessary during the initiation of therapy, following dose changes or when potentially interacting medications are started or discontinued [see Dosage and Administration (2), Drug Interactions (7)].
Drug Interactions
Advise patients to inform their physician of all medications, including prescription and nonprescription drugs, and supplements they are taking. Advise patients to also inform their physician that they are receiving doxercalciferol if a new medication is prescribed [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Distributed by:
Avet Pharmaceuticals Inc.
East Brunswick, NJ 08816
1.866.901.DRUG (3784)
51U000000118US04
Revised: 09/2020
