Lidotral 5 Percent and Hydrocortisone 1 Percent with Peptides and Arnica
Lidotral™ 5% + Hydrocortisone 1% Cream with Peptides & Arnica
0d871371-91ca-9ad7-e063-6294a90a5907
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Mar 15, 2024
PureTek Corporation
DUNS: 785961046
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Lidocaine HCl 5 % , Hydrocortisone Acetate 1%
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (32)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Lidotral™ 5% + Hydrocortisone 1% Cream with Peptides & Arnica
Manufactured in the USA by:
** PureTek Corporation**
Panorama City, CA 91402
For questions or information
call toll-free: 877-921-7873

INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
INDICATIONS:
The product is used for the anti-inflammatory and anesthetic relief of redness, pain, itching, and discoloration due to inflammation and skin burns. For the relief of redness, pain, itching, discoloration, inflammation and mild skin burns associated with radiation. For use after radiation treatment, cosmetic procedures, sun exposure, and for inflammatory skin conditions.
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
Product should not be used in patients with a history of sensitivity to any of
its ingredients or adverse reactions to lidocaine or amide
anesthetics, which usually do not cross-react with “caine” ester type
anesthetics. If excessive irritation and significant worsening occur,
discontinue use and seek the advice of your physician. Product and topical
lidocaine should be used cautiously in those with impaired liver function, as
well as the very ill or very elderly and those with significant liver disease.
Product should be used with caution in patients receiving antiarrhythmic drugs
of Class I since the adverse effects are additive and generally synergistic.
Product is contraindicated for tuberculous or fungal lesions or skin vaccinia,
varicella and acute herpes simplex. Topical corticosteroids are
contraindicated in those patients with a history of hypersensitivity to any of
the components of the preparation.
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
During or immediately following application of product, there may be transient stinging or burning from open areas of skin, or transient blanching (lightening), or erythema (redness) of the skin.
CARCINOGENESIS & MUTAGENESIS & IMPAIRMENT OF FERTILITY SECTION
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis and Impairment of Fertility:
Long-term animal studies have not been performed to evaluate the carcinogenic potential or the effect on fertility of topical corticosteroids. Studies to determine mutagenicity with prednisolone and hydrocortisone have revealed negative results. Studies of lidocaine in animals to evaluate the carcinogenic and mutagenic potential of the effect on fertility have not been conducted.
STORAGE AND HANDLING SECTION
KEEP THIS AND ALL MEDICATIONS OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN.
Store at 20º-25ºC (68º-77ºF) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
WARNINGS/PRECAUTIONS:
WARNINGS:
CONCERNS RELATED TO ADVERSE EFFECTS:
**Methemoglobinemia:**Has been reported with local anesthetics; clinically
significant methemoglobinemia requires immediate treatment along with
discontinuation of the anesthetic and other oxidizing agents. Onset may be
immediate or delayed (hours) after anesthetic exposure. Patients with G6PD
deficiency, congenital or idiopathic methemoglobinemia, cardiac or pulmonary
compromise, exposure to oxidizing agents or their metabolites, or infants <6
months of age are more susceptible and should be closely monitored for signs
and symptoms of methemoglobinemia (including pale, gray, or blue-colored skin
(cyanosis), headache, rapid pulse, shortness of breath, lightheadedness,
fatigue).
WARNINGS: For external use only. Not for ophthalmic use.
Stop use and ask a doctor if condition worsens or symptoms last more than 7
days or clear up and occur again within a few days.
Do not apply to wounds or damaged skin.
Do not use in large quantities, particularly over raw surfaces or blistered
areas.
If swallowed, get medical help or contact a Poison Control Center right away.
Keep out of reach of children.
Topical formulations of lidocaine may be absorbed to a greater extent through mucous membranes and abraded, fissured or irritated skin than through intact skin. Product should not be ingested or applied into the mouth, inside of the nose or in the eyes. Product should not be used in the ears. Any situation where lidocaine penetrates beyond the tympanic membrane into the middle ear is contraindicated because of ototoxicity associated with lidocaine observed in animals when instilled in the middle ear. Product should not come into contact with the eye or be applied into the eye because of the risk of severe eye irritation and the loss of eye surface sensation, which reduces protective reflexes and can lead to corneal irritation and possibly abrasion. If eye contact occurs, rinse out the eye immediately with saline or water and protect the eye surface until sensation is restored.
PRECAUTIONS:
If irritation or sensitivity occurs or infection appears, discontinue use and institute appropriate therapy. If extensive areas are treated, the possibility of systemic absorption exists. Systemic absorption of topical steroids has produced reversible hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis suppression, manifestation of Cushing’s syndrome, hyperglycemia, and glycosuria in some patients. Conditions which augment systemic absorption include the application of the more potent steroids, use over large surface areas, prolonged use, and the addition of occlusive dressings. Therefore, patients receiving a large dose of potent topical steroids applied to a large surface area, or under an occlusive dressing, should be evaluated periodically for evidence of HPA axis suppression. If noted, an attempt should be made to withdraw the drug, to reduce the frequency of application, or to substitute a less potent steroid. Recovery of the HPA axis function is generally prompt and complete upon discontinuation of the drug. Infrequently, signs and symptoms of steroid withdrawal may occur, requiring supplemental systemic corticosteroids. Children may absorb proportionately larger amounts of topical corticosteroids and thus be more susceptible to systemic toxicity. If irritation develops, topical steroids should be discontinued and appropriate therapy instituted. In the presence of dermatological infections, the use of an appropriate antifungal or antibacterial agent should be instituted. If a favorable response does not occur promptly, the corticosteroid should be discontinued until the infection has been adequately controlled.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
DESCRIPTION:
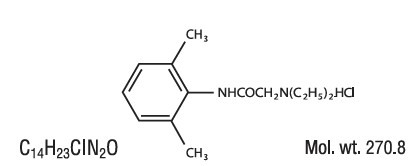
Lidocaine HCl is chemically designated as acetamide, 2-(diethylamino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl), and has the following structure:
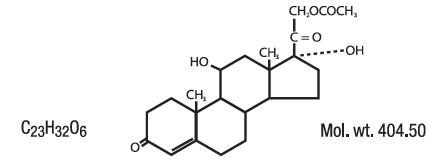
Hydrocortisone acetate has a chemical name pregn-4-ene-3, 20-dione, 21-(acetyloxy)-11, 17-dihydroxy-(11β)-, It has the following structural formula:
Lidotral™ 5% + Hydrocortisone 1% Cream with Peptides & Arnica Each gram contains Lidocaine HCl 50 mg, Hydrocortisone Acetate 10 mg.
ACTIVE INGREDIENTS:
Lidocaine HCl 5%
Hydrocortisone Acetate 1%
INACTIVE INGREDIENT SECTION
INACTIVE INGREDIENTS:
Aloe Barbadensis (Aloe) Leaf Juice, Aqua (Purified Water), Arnica Montana (Arnica) Flower Extract, Bis(Tripeptide-1) Copper Acetate, Brassica Campestris (Rapeseed) Sterols, Butyrospermum Parkii (Shea) Butter, Camellia Sinensis (Green Tea) Leaf Extract, Cetearyl Alcohol, Cetyl Alcohol, Coco- Caprylate/Caprate, Coconut Alkanes, Cucumis Sativus (Cucumber) Fruit Extract, Curcuma Longa (Turmeric) Root Extract, D-Alpha-Tocopherol, Glycerin, Glyceryl Stearate, Glycine Soja (Soybean) Oil, Glycine Soja (Soybean) Sterols, Glycolipids, Hydroxyethylcellulose, Menthyl Lactate, PEG-100 Stearate, Phenoxyethanol, Phospholipids, Polyglyceryl-3 Diisostearate, Simmondsia Chinensis (Jojoba) Seed Oil, Sodium Hydroxide, Sorbitan Stearate, Stearic Acid, Stearyl Alcohol, Tetrahexyldecyl Ascorbate
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY:
Mechanism of Action:
Product releases lidocaine to stabilize the neuronal membrane by inhibiting the ionic fluxes required for initiation and conduction of impulses, thereby affecting local anesthetic action. Hydrocortisone acetate providesrelief of inflammatory and pruritic manifestations of corticosteroid responsive dermatoses.
Pharmacokinetics:
Lidocaine may be absorbed following topical administration to mucous membranes, its rate and extent of absorption depending upon the specific site of application, duration of exposure, concentration, and total dosage. In general, the rate of absorption of local anesthetic agents following topical application occurs most rapidly after intratracheal administration. Lidocaine is also well-absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, but little intact drug appears in the circulation because of biotransformation of the liver.
Lidocaine is metabolized rapidly by the liver, and metabolites and unchanged drug are excreted by the kidneys. Biotransformation includes oxidative N-dealkylation, ring hydroxylation, cleavage of the amide linkage, and conjungation. N-dealkylation, a major pathway of biotransformation, yields the metabolites monoethylglycinexylidide and glycinexylidide. The pharmacological/toxicological actions of these metabolites are similar to, but less potent than, those of lidocaine. Approximately 90% of lidocaine administered is excreted in the form of various metabolites, and less than 10% is excreted unchanged. The primary metabolite in urine is a conjugate of 4-hydroxy-2, 6-dimethylaniline.
The plasma binding of lidocaine is dependent of drug concentration, and the fraction bound decreases with increasing concentration. At concentrations of 1 to 4 g of free base per mL, 60 to 80 percent of lidocaine is protein bound. Binding is also dependent on the plasma concentration of the alpha-1-acid- glycoprotein.
Lidocaine crosses the blood-brain and placental barriers, presumably by passive diffusion.
Studies of lidocaine metabolism following intravenous bolus injections have shown that the elimination half-life of this agent is typically 1.5 to 2 hours. Because of the rapid rate at which lidocaine is metabolized, any condition that affects liver function may alter lidocaine kinetics. The half- life may be prolonged two-fold or more in patients with liver dysfunction. Renal dysfunction does not affect lidocaine kinetics but may increase the accumulation of metabolites.
Factors such as acidosis and the use of CNS stimulants and depressants affect the CNS levels of lidocaine required to produce overt systemic effects. Objective adverse manifestations become increasingly apparent with increasing venous plasma levels above 6 g free base per mL. In the rhesus monkey arterial blood levels of 18-21 g/mL have been shown to be the threshold for convulsive activity.
The extent of percutaneous absorption of topical corticosteroids is determined by many factors including the vehicle, the integrity of the epidermal barrier, and the use of occlusive dressings.
Topical corticosteroids can be absorbed from normal intact skin. Inflammation and/or other disease processes in the skin increase percutaneous absorption. Occlusive dressings substantially increase the percutaneous absorption of topical corticosteroids. Thus, occlusive dressings may be a valuable therapeutic adjunct for treatment of resistant dermatoses.
Once absorbed through the skin, topical corticosteroids are handled through pharmacokinetic pathways similar to systemically administered corticosteroids. Corticosteroids are bound to plasma protein in varying degrees. Corticosteroids are metabolized primarily in the liver and are then excreted by the kidneys. Some of the topical corticosteroids and their metabolites are also excreted into the bile.
PEDIATRIC USE SECTION
PEDIATRIC USE:
Safety and efficacy in children have not been established.
NURSING MOTHERS SECTION
NURSING MOTHERS:
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when this drug is administered to a nursing mother.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION:
Apply product to the affected area(s) twice daily or as directed by a licensed healthcare practitioner. If the condition does not respond to repeated courses of product or should worsen, discontinue use and seek the advice of your physician. Wash hands before and after application.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
HOW SUPPLIED:
Lidotral™ 5% + Hydrocortisone 1% Cream with Peptides & Arnica (Lidocaine HCl 5% - Hydrocortisone Acetate 1%) is supplied as a beige cream in a 3 oz. (85 g) tube - NDC 59088-319-07
PREGNANCY SECTION
Use in Pregnancy:
Teratogenic Effects:
Pregnancy Category C. Reproduction studies have been performed for lidocaine in rats at doses up to 6.6 times the human dose and have revealed no evidence of harm to the fetus caused by lidocaine. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response. General consideration should be given to this fact before administering lidocaine to women of childbearing potential, especially during early pregnancy when maximum organogenesis takes place. Corticosteroids are generally teratogenic in laboratory animals when administered systemically at relatively low dosage levels. The more potent corticosteroids have been shown to be teratogenic after dermal application in laboratory animals. There are no adequate and well controlled studies in pregnant women on teratogenic effects from topically applied corticosteroids. Therefore, topical corticosteroids should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus. Drugs of this class should not be used extensively on pregnant patients, in large amounts, or for prolonged periods of time.
