Calcium Chloride
8295039b-2559-4626-90c8-6ac7e896e41a
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Jul 7, 2023
International Medication Systems, Limited
DUNS: 055750020
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Calcium Chloride
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (3)
Drug Labeling Information
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
HOW SUPPLIED
10% Calcium Chloride Injection, USP is supplied in single-dose containers as follows:
|
NDC No. |
Stock No. |
Container Size |
Needle |
|---|---|---|---|
|
76329-3304-1 |
3304 |
10 mL |
None |
One shrink wrapped package containing 10 unit cartons, each containing a Luer-
Jet™ Luer-Lock Prefilled Syringe.
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C and 30°C
(59°F and 86°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
Syringe Assembly Directions:
USE ASEPTIC TECHNIQUE
Do not assemble until ready to use.
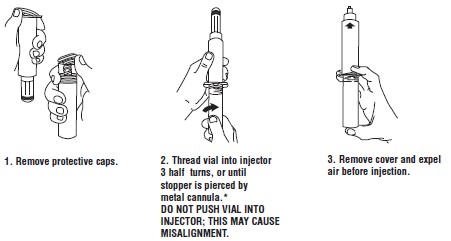
*CAUTION: IMPROPER ENGAGING MAY CAUSE GLASS BREAKAGE AND SUBSEQUENT INJURY.
PRECAUTIONS SECTION
PRECAUTIONS
Do not administer unless solution is clear and seal is intact. Discard unused portion.
Because of its additive effect, calcium should be administered very cautiously to a patient who is digitalized or who is taking effective doses of digitalis or digitalis-like preparations.
Injections should be made slowly through a small needle into a large vein to minimize venous irritation and avoid undesirable reactions. It is particularly important to prevent a high concentration of calcium from reaching the heart because of the danger of cardiac syncope.
Pediatric Use: Safety and effectiveness are based on similar clinical conditions in children and adults.
Pregnancy: Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with calcium chloride. It also is not known whether calcium chloride can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproductive capacity. Calcium chloride should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Geriatric Use: An evaluation of current literature revealed no clinical experience identifying differences in response between elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
