Bupivacaine Hydrochloride
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use BUPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION and BUPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE AND EPINEPHRINE INJECTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for BUPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE INJECTION and BUPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE AND EPINEPHRINE INJECTION. BUPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE injection, for infiltration, perineural, caudal, epidural, or retrobulbar use BUPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE AND EPINEPHRINE injection, for infiltration, perineural, caudal, or epidural use Initial U.S. Approval: 1972
02a845c3-4521-4926-e397-25ab536e7cf6
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Feb 23, 2024
Hospira, Inc.
DUNS: 141588017
Products 9
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
BUPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (5)
BUPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (6)
BUPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE AND EPINEPHRINE
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (7)
BUPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (5)
BUPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (5)
BUPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (6)
BUPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE AND EPINEPHRINE
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (8)
BUPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE AND EPINEPHRINE
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (8)
BUPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE AND EPINEPHRINE
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (7)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 150 mg/30 mL Vial Tray - 9045
30 mL Single-dose Teartop Vial
Sterile, Nonpyrogenic
Rx only
NDC 0409-9045-17
Contains 25 of NDC 0409-9045-16
0.5% Bupivacaine Hydrochloride
150 mg/30 mL (5 mg/mL)
and epinephrine 1:200,000 Injection
Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection, USP
FOR NERVE BLOCK, CAUDAL AND EPIDURAL ANESTHESIA ONLY.
Not for spinal anesthesia.
Warning: Contains Sulfites

Boxed Warning section
WARNING: RISK OF CARDIAC ARREST WITH USE OF BUPIVACAINE HYDROCHLORIDE
INJECTION IN OBSTETRICAL ANESTHESIA
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
There have been reports of cardiac arrest with difficult resuscitation or death during use of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection for epidural anesthesia in obstetrical patients. In most cases, this has followed use of the 0.75% (7.5 mg/mL) concentration. Resuscitation has been difficult or impossible despite apparently adequate preparation and appropriate management. Cardiac arrest has occurred after convulsions resulting from systemic toxicity, presumably following unintentional intravascular injection. The 0.75% (7.5 mg/mL) concentration of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection is not recommended for obstetrical anesthesia and should be reserved for surgical procedures where a high degree of muscle relaxation and prolonged effect are necessary (5.1).
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection is indicated in adults for the production of local or regional anesthesia or analgesia for surgery, dental and oral surgery procedures, diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, and for obstetrical procedures. Specific concentrations and presentations of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection are recommended for each type of block indicated to produce local or regional anesthesia or analgesia [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
Limitations of Use
Not all blocks are indicated for use with Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection given clinically significant risks associated with use [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.4, 5.5, 5.7, 5.9)].
Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection contains bupivacaine, an amide local anesthetic, and Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection is a combination of bupivacaine, an amide local anesthetic, and epinephrine, an alpha and beta-adrenergic agonist. Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection is indicated in adults for the production of local or regional anesthesia or analgesia for surgery, dental and oral surgery procedures, diagnostic and therapeutic procedures, and for obstetrical procedures. For each type of block indicated to produce local or regional anesthesia or analgesia, specific concentrations and presentations are recommended. (1, 2.2)
Limitations of Use
Not all blocks are indicated for use with Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection given clinically significant risks associated with use. (1, 2.2, 4, 5.1, 5.4, 5.5, 5.7, 5.9)
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection is contraindicated in:
•
obstetrical paracervical block anesthesia. Its use in this technique has resulted in fetal bradycardia and death.
•
intravenous regional anesthesia (Bier Block) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
•
patients with a known hypersensitivity to bupivacaine or to any local anesthetic agent of the amide-type or to other components of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection.
•
Obstetrical paracervical block anesthesia. Its use in this technique has resulted in fetal bradycardia and death. (4)
•
Intravenous regional anesthesia (Bier Block). (4)
•
Known hypersensitivity to bupivacaine or to any local anesthetic agent of the amide-type or to other components of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection. (4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions have been reported and described in the Warnings and Precautions section of the labeling:
•
Cardiac Arrest in Obstetrical Anesthesia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
•
Dose-Related Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
•
Methemoglobinemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
•
Chondrolysis with Intra-Articular Infusion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
•
Severe, Persistent Hypertension, Cerebrovascular Accidents, and Bradycardia Due to Drug Interactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
•
Cardiac Arrest with Intravenous Regional Anesthesia Use [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
•
Allergic-Type Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
•
Systemic Toxicities with Unintended Intravascular or Intrathecal Injection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
•
Respiratory Arrest Following Retrobulbar Block [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)]
The following adverse reactions from voluntary reports or clinical studies have been reported with bupivacaine or bupivacaine and epinephrine. Because many of these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Adverse reactions to Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection are characteristic of those associated with other amide-type local anesthetics. A major cause of adverse reactions to this group of drugs is excessive plasma levels, which may be due to overdosage, unintentional intravascular injection, or slow metabolic degradation.
The most commonly encountered acute adverse reactions that demand immediate counter-measures were related to the CNS and the cardiovascular system. These adverse reactions were generally dose-related and due to high plasma levels which may have resulted from overdosage, rapid absorption from the injection site, diminished tolerance, or from unintentional intravascular injection of the local anesthetic solution. In addition to systemic dose-related toxicity, unintentional intrathecal injection of drug during the intended performance of caudal or lumbar epidural block or nerve blocks near the vertebral column (especially in the head and neck region) has resulted in underventilation or apnea ("Total or High Spinal"). Also, hypotension due to loss of sympathetic tone and respiratory paralysis or underventilation due to cephalad extension of the motor level of anesthesia have occurred. This has led to secondary cardiac arrest when untreated.
Nervous System Disorders
Adverse reactions were characterized by excitation and/or depression of the central nervous system and included restlessness, anxiety, dizziness, tinnitus, blurred vision, tremors, convulsions, drowsiness, unconsciousness, respiratory arrest, nausea, vomiting, chills, pupillary constriction.
In the practice of caudal or lumbar epidural block, unintentional penetration of the subarachnoid space by the catheter or needle has occurred. Subsequent adverse effects may have depended partially on the amount of drug administered intrathecally and the physiological and physical effects of a dural puncture. A high spinal has been characterized by paralysis of the legs, loss of consciousness, respiratory paralysis, and bradycardia.
Neurologic effects following epidural or caudal anesthesia have included spinal block of varying magnitude (including high or total spinal block); hypotension secondary to spinal block; urinary retention; fecal and urinary incontinence; loss of perineal sensation and sexual function; persistent anesthesia, paresthesia, weakness, paralysis of the lower extremities and loss of sphincter control, all of which had slow, incomplete, or no recovery; headache; backache; septic meningitis; meningismus; slowing of labor; increased incidence of forceps delivery; and cranial nerve palsies due to traction on nerves from loss of cerebrospinal fluid.
Neurologic effects following other procedures or routes of administration have included persistent anesthesia, paresthesia, weakness, paralysis, all with slow, incomplete, or no recovery.
Convulsions: Incidence varied with the procedure used and the total dose administered. In a survey of studies of epidural anesthesia, overt toxicity progressing to convulsions occurred in approximately 0.1% of local anesthetic administrations. The incidences of adverse neurologic reactions associated with the use of local anesthetics may be related to the total dose of local anesthetic administered and are also dependent upon the particular drug used, the route of administration, and the physical status of the patient.
Cardiac Disorders
High doses or unintentional intravascular injection have led to high plasma levels and related depression of the myocardium, decreased cardiac output, heartblock, hypotension, bradycardia, ventricular arrhythmias, including ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation, and cardiac arrest [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Immune System Disorders
Allergic-type reactions have occurred as a result of sensitivity to bupivacaine or to other formulation ingredients, such as the antimicrobial preservative methylparaben contained in multiple-dose vials or sulfites in epinephrine-containing solutions. These reactions were characterized by signs such as urticaria, pruritus, erythema, angioneurotic edema (including laryngeal edema), tachycardia, sneezing, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, syncope, excessive sweating, elevated temperature, and severe hypotension. Cross sensitivity among members of the amide-type local anesthetic group has been reported [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Most common adverse reactions are related to the central nervous system and the cardiovascular system. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Pfizer Inc. at 1-800-438-1985 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Bupivacaine blocks the generation and the conduction of nerve impulses, presumably by increasing the threshold for electrical excitation in the nerve, by slowing the propagation of the nerve impulse, and by reducing the rate of rise of the action potential. In general, the progression of anesthesia is related to the diameter, myelination, and conduction velocity of affected nerve fibers. Clinically, the order of loss of nerve function is as follows: (1) pain, (2) temperature, (3) touch, (4) proprioception, and (5) skeletal muscle tone.
Epinephrine is a vasoconstrictor added to bupivacaine to slow absorption into the general circulation and thus prolong maintenance of an active tissue concentration.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Systemic absorption of bupivacaine produces effects on the cardiovascular system and CNS. At blood concentrations achieved with normal therapeutic doses, changes in cardiac conduction, excitability, refractoriness, contractility, and peripheral vascular resistance are minimal. However, toxic blood concentrations depress cardiac conduction and excitability, which may lead to atrioventricular block, ventricular arrhythmias, and cardiac arrest, sometimes resulting in fatalities. In addition, myocardial contractility is depressed and peripheral vasodilation occurs, leading to decreased cardiac output and arterial blood pressure. These cardiovascular changes are more likely to occur after unintended intravascular injection of bupivacaine [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Following systemic absorption, bupivacaine can produce CNS stimulation, CNS depression, or both. Apparent central stimulation is manifested as restlessness, tremors, and shivering, progressing to convulsions, followed by CNS depression and coma progressing ultimately to respiratory arrest. However, bupivacaine has a primary depressant effect on the medulla and on higher centers. The depressed stage may occur without a prior excited state.
The duration of local anesthesia after administration of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection is longer than that observed after administration of other commonly used short-acting local anesthetics. There appears to be a period of analgesia that persists after the resolution of the block and return of sensation.
The onset of action following dental injections is usually 2 to 10 minutes and may last up to 7 hours. The duration of anesthetic effect is prolonged by the addition of epinephrine 1:200,000.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Systemic plasma levels of bupivacaine following administration of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection do not correlate with local efficacy.
Absorption
The rate of systemic absorption of bupivacaine is dependent upon the total dose and concentration of drug administered, the route of administration, the vascularity of the administration site, and the presence or absence of epinephrine in the anesthetic solution. A dilute concentration of epinephrine (1:200,000) usually reduces the rate of absorption and peak plasma concentration of bupivacaine, permitting the use of moderately larger total doses and sometimes prolonging the duration of action [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
After injection of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection for caudal, epidural, or peripheral nerve block, peak levels of bupivacaine in the blood are reached in 30 to 45 minutes, followed by a decline to insignificant levels during the next three to six hours.
Distribution
Bupivacaine appears to cross the placenta by passive diffusion. The rate and degree of diffusion is governed by (1) the degree of plasma protein binding, (2) the degree of ionization, and (3) the degree of lipid solubility. Fetal/maternal ratios of bupivacaine appear to be inversely related to the degree of plasma protein binding, because only the free, unbound drug is available for placental transfer. Bupivacaine with a high protein binding capacity (95%) has a low fetal/maternal ratio (0.2 to 0.4). The extent of placental transfer is also determined by the degree of ionization and lipid solubility of the drug. Lipid soluble, nonionized drugs readily enter the fetal blood from the maternal circulation.
Depending upon the route of administration, bupivacaine is distributed to some extent to all body tissues, with high concentrations found in highly perfused organs such as the liver, lungs, heart, and brain.
Pharmacokinetic studies on the plasma profile of bupivacaine after direct intravenous injection (Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection is not approved for intravenous use) suggest a three-compartment open model. The first compartment is represented by the rapid intravascular distribution of the drug. The second compartment represents the equilibration of the drug throughout the highly perfused organs such as the brain, myocardium, lungs, kidneys, and liver. The third compartment represents an equilibration of the drug with poorly perfused tissues, such as muscle and fat.
Elimination
The half-life of bupivacaine in adults is 2.7 hours.
Metabolism
Amide-type local anesthetics such as bupivacaine are metabolized primarily in the liver via conjugation with glucuronic acid. Pipecoloxylidine is the major metabolite of bupivacaine. The elimination of drug from tissue distribution depends largely upon the availability of binding sites in the circulation to carry it to the liver where it is metabolized.
Excretion
The kidney is the main excretory organ for most local anesthetics and their metabolites. Urinary excretion is affected by urinary perfusion and factors affecting urinary pH. Only 6% of bupivacaine is excreted unchanged in the urine.
Specific Populations
Geriatric Patients
Elderly patients exhibited higher peak plasma concentrations than younger patients following administration of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection. The total plasma clearance was decreased in these patients [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Various pharmacokinetic parameters of the local anesthetics can be significantly altered by the presence of hepatic disease. Patients with hepatic disease, especially those with severe hepatic disease, may be more susceptible to the potential toxicities of the amide-type local anesthetics [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
Patients with Renal Impairment
Various pharmacokinetic parameters of the local anesthetics can be significantly altered by the presence of renal disease, factors affecting urinary pH, and renal blood flow [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5, 8.7)].
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Dosage and Administration Information
•
Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection is not for intrathecal use.
•
Avoid use of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection solutions containing antimicrobial preservatives (i.e., multiple-dose vials) for epidural or caudal anesthesia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
•
Discard unused portions of solution not containing preservatives, i.e., those supplied in single-dose vials, following initial use.
•
Visually inspect this product for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration whenever solution and container permit. Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection are clear, colorless solutions. Do not administer solutions which are discolored or contain particulate matter.
•
Mixing or the prior or intercurrent use of any other local anesthetic with Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection is not recommended because of insufficient data on the clinical use of such mixtures.
Administration Precautions
•
Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection are to be administered in carefully adjusted dosages by or under the supervision of experienced clinicians who are well versed in the diagnosis and management of dose-related toxicity and other acute emergencies which might arise from the block to be employed.
•
Use Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection only if the following are immediately available: oxygen, cardiopulmonary resuscitative equipment and drugs, and the personnel resources needed for proper management of toxic reactions and related emergencies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Adverse Reactions (6), Overdosage (10)].
•
The toxic effects of local anesthetics are additive. Monitor for neurologic and cardiovascular effects related to local anesthetic systemic toxicity when additional local anesthetics are administered with Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Drug Interactions (7.1), Overdosage (10)].
•
Aspirate for blood or cerebrospinal fluid (where applicable) prior to injecting Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection, both the initial dose and all subsequent doses, to avoid intravascular or intrathecal injection. However, a negative aspiration for blood or cerebrospinal fluid does not ensure against an intravascular or intrathecal injection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
•
Avoid rapid injection of a large volume of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection and use fractional (incremental) doses when feasible.
•
During major regional nerve blocks, such as those of the brachial plexus or lower extremity, the patient should have an indwelling intravenous catheter to assure adequate intravenous access. The lowest dosage of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection that results in effective anesthesia should be used to avoid high plasma levels and serious adverse reactions.
•
Perform careful and constant monitoring of cardiovascular and respiratory (adequacy of oxygenation and ventilation) vital signs and the patient's level of consciousness after each local anesthetic injection.
•
Use Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection in carefully restricted quantities in areas of the body supplied by end arteries or having otherwise compromised blood supply such as digits, nose, external ear, or penis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)].
2.2 Recommended Concentrations and Dosages of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride
Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection
The dosage of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection administered varies with the anesthetic procedure, the area to be anesthetized, the vascularity of the tissues, the number of neuronal segments to be blocked, the depth of anesthesia and degree of muscle relaxation required, the duration of anesthesia desired, individual tolerance, and the physical condition of the patient. Administer the smallest dosage and concentration required to produce the desired result.
The types of block and recommended Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection concentrations are shown in Table 1.
Table 1. Types of Block and Recommended Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection Concentrations|
✓= indicated use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. | |||||
| |||||
|
Type of Block |
Bupivacaine Hydrochloride |
Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine | |||
|
0.25% |
0.5% |
0.75% |
0.25% |
0.5% | |
|
Local infiltration |
✓ |
✓ | |||
|
Peripheral nerve block |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ | |
|
Retrobulbar block |
✓ | ||||
|
Sympathetic block |
✓ | ||||
|
Caudal block† |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ | |
|
Lumbar epidural block† |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
✓ |
|
Epidural test dose |
✓ | ||||
|
Dental block |
✓ |
At recommended dosages, Bupivacaine Hydrochloride/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine produces complete sensory block, but the effect on motor function differs among the three concentrations. Table 2 provides information on the expected effect on motor function for the three concentrations.
Table 2. Types of Block and Recommended Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection Concentrations
| |
|
Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection Concentration |
Motor Function |
|
0.25% |
When used for caudal, epidural, or peripheral nerve block, produces incomplete motor block. Should be used for operations in which muscle relaxation is not important, or when another means of providing muscle relaxation is used concurrently. Onset of action may be slower than with the 0.5% (5 mg/mL) or 0.75% (7.5 mg/mL) solutions. |
|
0.5% |
Provides motor blockade for caudal, epidural, or nerve block, but muscle relaxation may be inadequate for operations in which complete muscle relaxation is essential. |
|
0.75% |
Produces complete motor block. Most useful for epidural block in abdominal operations requiring complete muscle relaxation, and for retrobulbar anesthesia. Not for obstetrical anesthesia. |
The duration of anesthesia with Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection is such that for most indications, a single dose is sufficient.
The maximum dosage limit within the recommended dosage range must be individualized in each case after evaluating the size and physical status of the patient, as well as the anticipated rate of systemic absorption from a particular injection site.
The dosages in Table 3 are recommended as a guide for use in the average adult. These doses may be repeated once every three hours. Do not exceed a total daily dosage of 400 mg in 24 hours. The duration of anesthetic effect may be prolonged by the addition of epinephrine.
Table 3. Recommended Concentrations and Doses of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection in Adults
| ||||
|
Type of Block |
Concentration of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection |
Each Dose |
Motor Block* | |
|
mL |
mg of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection | |||
|
Local infiltration |
0.25% |
Up to 70 |
Up to 175 |
― |
|
Up to 90 |
Up to 225 | |||
|
Peripheral nerve block |
0.5% (5 mg/mL)† |
5–35 |
25–175 |
moderate to complete |
|
5–45 |
25–225 | |||
|
0.25% |
5–70 |
12.5–175 |
moderate to complete | |
|
5–90 |
12.5–225 | |||
|
Retrobulbar block |
0.75% |
2–4 |
15–30 |
complete |
|
Sympathetic block |
0.25% |
20–50 |
50–125 |
― |
|
Caudal block |
0.5% (5 mg/mL)† |
15–30 |
75–150 |
moderate to complete |
|
0.25% |
15–30 |
37.5–75 |
moderate | |
|
Lumbar epidural block |
0.75% |
10–20 |
75–150 |
complete |
|
0.5% (5 mg/mL)† |
10–20 |
50–100 |
moderate to complete | |
|
0.25% |
10–20 |
25–50 |
partial to moderate | |
|
Epidural test dose |
0.5% (5 mg/mL) with epinephrine |
2–3 |
10–15 |
― |
|
Dental |
0.5% (5 mg/mL) with epinephrine |
1.8–3.6 per site |
9–18 per site |
― |
2.3 Use in Epidural Anesthesia
During the administration of epidural anesthesia, it is recommended that a test dose of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection without antimicrobial preservative (0.5% bupivacaine with 1:200,000 epinephrine) be administered initially and the effects monitored before the full dose is given. When using a "continuous" catheter technique, test doses should be given prior to both the initial and all supplemental doses, because a catheter in the epidural space can migrate into a blood vessel or through the dura [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
During epidural administration, administer Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection, 0.5% (5 mg/mL) and Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection 0.75% (7.5 mg/mL) solutions in incremental doses of 3 mL to 5 mL with sufficient time between doses to detect toxic manifestations of unintentional intravascular or intrathecal injection. Administer injections slowly, with frequent aspirations before and during the injection to avoid intravascular injection. Perform syringe aspirations before and during each supplemental injection in continuous (intermittent) catheter techniques. In obstetrics, use ONLY the 0.5% (5 mg/mL) and 0.25% (2.5 mg/mL) concentrations of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]; incremental doses of 3 mL to 5 mL of the 0.5% (5 mg/mL) solution not exceeding 50 mg to 100 mg at any dosing interval are recommended. Repeat doses should be preceded by a test dose containing epinephrine if not clinically contraindicated. Use only the single-dose vials for caudal or epidural anesthesia; avoid use of the multiple-dose vials for these procedures, which contain a preservative [see Dosage and Administration (2.1, 2.4), Warnings and Precautions (5.4, 5.9)].
2.4 Test Dose for Caudal and Lumbar Epidural Blocks
Three mL of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection without antimicrobial preservative (0.5% bupivacaine with 1:200,000 epinephrine) is recommended for use as a test dose prior to caudal and lumbar epidural blocks when clinical conditions permit. This test dose may serve as a warning of unintended intravascular or intrathecal injection. Closely monitor for early clinical signs of toxicity following each test dose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]. Allot adequate time for onset of spinal block to detect possible intrathecal injection. An intravascular or intrathecal injection is still possible even if results of the test dose are negative. The test dose itself may produce a systemic toxic reaction, high spinal, or cardiovascular effects from the epinephrine [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.9), Overdosage (10)].
2.5 Use in Dentistry
Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection 0.5% (5 mg/mL) is recommended for infiltration and block injection in the maxillary and mandibular area when a longer duration of local anesthesia is desired, such as for procedures generally associated with significant postoperative pain. The average dose of 1.8 mL (9 mg) per injection site will usually suffice; an occasional second dose of 1.8 mL (9 mg) may be used if necessary to produce adequate anesthesia after allowing 2 to 10 minutes for block onset [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2)]. Use the lowest effective dose and allow time between injections; it is recommended that the total dose for all injection sites, spread out over a single dental sitting, not exceed 90 mg for a healthy adult patient (ten 1.8 mL injections of 0.5% (5 mg/mL) Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection). Inject slowly and with frequent aspirations.
2.6 Use in Ophthalmic Surgery
When Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection 0.75% (7.5 mg/mL) is used for retrobulbar block, complete corneal anesthesia usually precedes onset of clinically acceptable external ocular muscle akinesia. Therefore, presence of akinesia rather than anesthesia alone should determine readiness of the patient for surgery [see Warnings and Precautions (5.15)].
•
Not for intrathecal use. (2.1)
•
Avoid use of solutions containing antimicrobial preservatives (i.e., multiple-dose vials) for epidural or caudal anesthesia. (2.1, 5.4)
•
Three mL of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection without antimicrobial preservative (0.5% bupivacaine with 1:200,000 epinephrine) is recommended for use as a test dose prior to caudal and lumbar epidural blocks when clinical conditions permit. (2.4)
•
See full prescribing information for:
- Recommended concentrations and dosages of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection according to type of block. (2.2)
Additional dosage and administration information pertaining to use in epidural anesthesia, test dose for caudal and lumbar epidural blocks, use in dentistry, and use in ophthalmic surgery. (2.3, 2.4, 2.5, 2.6)
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP is a clear, colorless solution available as:
•
0.25% (25 mg/10 mL) (2.5 mg/mL) in single-dose teartop vials.
•
0.25% (75 mg/30 mL) (2.5 mg/mL) in single-dose teartop vials.
•
0.25% (125 mg/50 mL) (2.5 mg/mL) in multiple-dose fliptop vials.
•
0.5% (50 mg/10 mL) (5 mg/mL) in single-dose teartop vials.
•
0.5% (150 mg/30 mL) (5 mg/mL) in single-dose teartop vials.
•
0.5% (250 mg/50 mL) (5 mg/mL) in multiple-dose fliptop vials.
•
0.75% (75 mg/10 mL) (7.5 mg/mL) in single-dose teartop vials.
•
0.75% (225 mg/30 mL) (7.5 mg/mL) in single-dose teartop vials.
Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection, USP is a clear, colorless solution available as:
•
0.25% (25 mg/10 mL) (2.5 mg/mL) in single-dose teartop vials.
•
0.25% (75 mg/30 mL) (2.5 mg/mL) in single-dose teartop vials.
•
0.25% (125 mg/50 mL) (2.5 mg/mL) in multiple-dose fliptop vials.
•
0.5% (50 mg/10 mL) (5 mg/mL) in single-dose teartop vials.
•
0.5% (150 mg/30 mL) (5 mg/mL) in single-dose teartop vials.
•
0.5% (250 mg/50 mL) (5 mg/mL) in multiple-dose fliptop vials.
Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP and Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection, USP are available in multiple concentrations. See full prescribing information for detailed description of each formulation. (3)
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection contains bupivacaine hydrochloride, an amide local anesthetic, as the active pharmaceutical ingredient. The route of administration for Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection (without epinephrine) is by injection, for infiltration, perineural, caudal, epidural, or retrobulbar use. The route of administration for Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection is by injection, for infiltration, perineural, caudal, or epidural use. Multiple- dose vials contain methylparaben [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
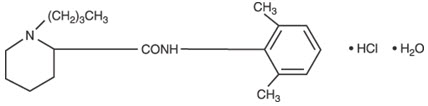
Bupivacaine hydrochloride is 2-piperidinecarboxamide, 1-butyl-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)-, monohydrochloride, monohydrate. It is a white crystalline powder that is freely soluble in 95 percent ethanol, soluble in water, and slightly soluble in chloroform or acetone. It has the following structural formula:
Bupivacaine hydrochloride with 1:200,000 epinephrine, contains bupivacaine hydrochloride and epinephrine (an alpha and beta-adrenergic agonist) as active pharmaceutical ingredients. This product is for injection via local infiltration, peripheral nerve block, and caudal and lumbar epidural blocks. Multiple-dose vials contain methylparaben and they should not be used for caudal and lumbar epidural blocks.
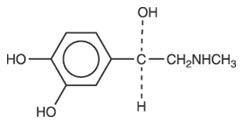
Epinephrine is (-)-3,4-Dihydroxy-α-[(methylamino)methyl] benzyl alcohol. Epinephrine is a vasoconstrictor. It has the following structural formula:
Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP is a clear and colorless sterile isotonic solution. Each mL of single-dose vial contains 2.5 mg, 5 mg, or 7.5 mg of bupivacaine hydrochloride (equivalent to 2.22 mg, 4.44 mg, or 6.66 mg of bupivacaine, respectively), sodium chloride for isotonicity, sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH between 4 and 6.5, in water for injection.
For the multiple-dose vials, each mL also contains 1 mg methylparaben as preservative.
Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection, USP is a clear and colorless sterile isotonic solution. Each mL contains 2.5 mg or 5 mg bupivacaine hydrochloride (equivalent to 2.22 mg or 4.44 mg of bupivacaine, respectively), and 0.005 mg of epinephrine, with sodium chloride for isotonicity, 0.1 mg sodium metabisulfite as antioxidant, and 0.1 mg edetate calcium disodium anhydrous as stabilizer. The pH of these solutions is adjusted to between 3.3 and 5.5 with sodium hydroxide or hydrochloric acid.
For the multiple-dose vials, each mL also contains 1 mg methylparaben as preservative.
The specific gravity of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection [0.5% (5 mg/mL) of bupivacaine] at 25 ºC is 1.007.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Store at 20 °C to 25 °C (68 °F to 77 °F); excursions permitted between 15 °C to 30 °C (59 °F to 86 °F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection, USP ─ Solutions of bupivacaine hydrochloride that do not contain epinephrine may be autoclaved. Autoclave at 15-pound pressure, 121 °C (250 °F) for 15 minutes. This product is clear and colorless. Do not use the solution if it is discolored or if it contains a precipitate.
|
Unit of Sale |
Concentration |
|
NDC 0409-1159-01 |
0.25% |
|
NDC 0409-1159-02 |
0.25% |
|
NDC 0409-1160-01 |
0.25% |
|
NDC 0409-1163-01 |
0.5% |
|
NDC 0409-1162-01 |
0.5% |
|
NDC 0409-1162-02 |
0.5% |
|
NDC 0409-1165-01 |
0.75% |
|
NDC 0409-1165-02 |
0.75% |
For single-dose vials: Discard unused portion.
Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection, USP ─ Do not autoclave solutions of bupivacaine hydrochloride that contain epinephrine and protect from light. This product is clear and colorless. Do not use the solution if it is discolored or if it contains a precipitate.
|
Unit of Sale |
Concentration |
|---|---|
|
NDC 0409-9042-01 |
0.25% |
|
NDC 0409-9042-17 |
0.25% |
|
NDC 0409-9043-01 |
0.25% |
|
NDC 0409-9045-01 |
0.5% |
|
NDC 0409-9045-17 |
0.5% |
|
NDC 0409-9046-01 |
0.5% |
For single-dose vials: Discard unused portion.
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
This product's labeling may have been updated. For the most recent prescribing information, please visit www.pfizer.com.
Distributed by Hospira, Inc., Lake Forest, IL 60045 USA

LAB-1176-6.0
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection is contraindicated for obstetrical paracervical block anesthesia. Its use in this technique has resulted in fetal bradycardia and death [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
There are no available data on use of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk of adverse developmental outcomes.
In animal studies, embryo-fetal lethality was noted when bupivacaine was administered subcutaneously to pregnant rabbits during organogenesis at clinically relevant doses. Decreased pup survival was observed in a rat pre- and post-natal developmental study (dosing from implantation through weaning) at a dose level comparable to the daily maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) on a body surface area (BSA) basis. Based on animal data, advise pregnant women of the potential risks to a fetus (see Data).
Local anesthetics rapidly cross the placenta, and when used for epidural, caudal, or pudendal block anesthesia, can cause varying degrees of maternal, fetal, and neonatal toxicity [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The incidence and degree of toxicity depend upon the procedure performed, the type, and amount of drug used, and the technique of drug administration. Adverse reactions in the parturient, fetus, and neonate involve alterations of the CNS, peripheral vascular tone, and cardiac function.
If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, inform the patient of the potential hazard to the fetus. The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations are unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2–4% and 15–20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Maternal Adverse Reactions
Maternal hypotension has resulted from regional anesthesia. Local anesthetics produce vasodilation by blocking sympathetic nerves. The supine position is dangerous in pregnant women at term because of aortocaval compression by the gravid uterus. Therefore, during treatment of systemic toxicity, maternal hypotension or fetal bradycardia following regional block, the parturient should be maintained in the left lateral decubitus position if possible, or manual displacement of the uterus off the great vessels be accomplished. Elevating the patient's legs will also help prevent decreases in blood pressure. The fetal heart rate also should be monitored continuously and electronic fetal monitoring is highly advisable.
Labor or Delivery
Epidural, caudal, or pudendal anesthesia may alter the forces of parturition through changes in uterine contractility or maternal expulsive efforts. Epidural anesthesia has been reported to prolong the second stage of labor by removing the parturient's reflex urge to bear down or by interfering with motor function. The use of obstetrical anesthesia may increase the need for forceps assistance.
The use of some local anesthetic drug products during labor and delivery may be followed by diminished muscle strength and tone for the first day or two of life. This has not been reported with bupivacaine.
It is extremely important to avoid aortocaval compression by the gravid uterus during administration of regional block to parturients. To do this, the patient must be maintained in the left lateral decubitus position or a blanket roll or sandbag may be placed beneath the right hip and gravid uterus displaced to the left.
Data
Animal Data
Bupivacaine hydrochloride produced developmental toxicity when administered subcutaneously to pregnant rats and rabbits at clinically relevant doses.
Bupivacaine hydrochloride was administered subcutaneously to rats at doses of 4.4, 13.3, & 40 mg/kg and to rabbits at doses of 1.3, 5.8, & 22.2 mg/kg during the period of organogenesis (implantation to closure of the hard palate). The high doses are comparable to the daily MRHD of 400 mg/day on a mg/m2 BSA basis. No embryo-fetal effects were observed in rats at the high dose which caused increased maternal lethality. An increase in embryo-fetal deaths was observed in rabbits at the high dose in the absence of maternal toxicity with the fetal No Observed Adverse Effect Level representing approximately 0.3 times the MRHD on a BSA basis.
In a rat pre- and post-natal developmental study (dosing from implantation through weaning) conducted at subcutaneous doses of 4.4, 13.3, & 40 mg/kg, decreased pup survival was observed at the high dose. The high dose is comparable to the daily MRHD of 400 mg/day on a BSA basis.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Lactation studies have not been conducted with bupivacaine. Bupivacaine has been reported to be excreted in human milk suggesting that the nursing infant could be theoretically exposed to a dose of the drug. Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection should be administered to lactating women only if clearly indicated. Studies assessing the effects of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection in breastfed children have not been performed. Studies to assess the effect of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection on milk production or excretion have not been performed. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for bupivacaine and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from bupivacaine or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection is approved for use in adults. Administration of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection in pediatric patients younger than 12 years is not recommended.
Continuous infusions of bupivacaine in pediatric patients have been reported to result in high systemic levels of bupivacaine and seizures; high plasma levels may also be associated with cardiovascular abnormalities.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Patients 65 years and over, particularly those with hypertension, may be at increased risk for developing hypotension while undergoing anesthesia with Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection.
In clinical studies of bupivacaine, elderly patients reached the maximal spread of analgesia and maximal motor blockade more rapidly than younger adult patients.
Differences in various pharmacokinetic parameters have been observed between elderly and younger adult patients [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
This product is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function. Elderly patients may require lower doses of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection.
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
Amide-type local anesthetics, such as bupivacaine, are metabolized by the liver. Patients with severe hepatic impairment, because of their inability to metabolize local anesthetics normally, are at a greater risk of developing toxic plasma concentrations, and potentially local anesthetic systemic toxicity. Therefore, consider reduced dosing and increased monitoring for local anesthetic systemic toxicity in patients with moderate to severe hepatic impairment treated with Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection, especially with repeat doses [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
8.7 Renal Impairment
Bupivacaine is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with renal impairment. This should be considered when selecting the Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection dosage [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
•
Pediatric Use: Administration of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection in pediatric patients younger than 12 years is not recommended. (8.4)
•
Geriatric Use: Patients 65 years and over, particularly those with hypertension, may be at increased risk for developing hypotension while undergoing anesthesia with Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection. (8.5)
•
Moderate to Severe Hepatic Impairment: Consider increased monitoring for bupivacaine systemic toxicity. (8.6)
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
Clinical Presentation
Acute emergencies from use of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection are generally related to high plasma levels encountered during therapeutic use or to unintended intrathecal injection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.9), Adverse Reactions (6)].
If not treated immediately, convulsions with simultaneous hypoxia, hypercarbia, and acidosis plus myocardial depression from the direct effects of bupivacaine may result in cardiac arrhythmias, bradycardia, asystole, ventricular fibrillation, or cardiac arrest. Respiratory abnormalities, including apnea, may occur. Hypoventilation or apnea due to unintentional intrathecal injection of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection may produce these same signs and also lead to cardiac arrest if ventilatory support is not instituted. If cardiac arrest should occur, successful outcome may require prolonged resuscitative efforts.
Management
The first step in the management of systemic toxic reactions, as well as hypoventilation or apnea due to unintentional intrathecal injection of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection/Bupivacaine Hydrochloride and Epinephrine Injection, consists of immediate attention to the establishment and maintenance of a patent airway and effective assisted or controlled ventilation with 100% oxygen with a delivery system capable of permitting immediate positive airway pressure by mask. Endotracheal intubation, using drugs and techniques familiar to the clinician, may be indicated after initial administration of oxygen by mask if difficulty is encountered in the maintenance of a patent airway, or if prolonged ventilatory support (assisted or controlled) is indicated.
If necessary, use drugs to manage the convulsions. A bolus intravenous dose of a benzodiazepine will counteract CNS stimulation related to Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection. Immediately after the institution of ventilatory measures, evaluate the adequacy of the circulation. Supportive treatment of circulatory depression may require Advanced Cardiac Life Support measures.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Long-term studies in animals to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of bupivacaine hydrochloride have not been conducted.
Mutagenesis
The mutagenic potential of bupivacaine hydrochloride has not been determined.
Impairment of Fertility
The effect of bupivacaine on fertility has not been determined.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Allergic-Type Reactions
Assess if the patient has had allergic-type reactions to amide-type local anesthetics or to other formulation ingredients, such as the antimicrobial preservative methylparaben contained in multiple-dose vials or sulfites in epinephrine-containing solutions [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.8), Adverse Reactions (6)].
Temporary Loss of Sensation and Motor Activity After Caudal or Epidural Anesthesia
When appropriate, patients should be informed in advance that they may experience temporary loss of sensation and motor activity, usually in the lower half of the body, following proper administration of caudal or epidural anesthesia.
Instructions After Dental Injection of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection
Advise patients receiving dental injections of Bupivacaine Hydrochloride Injection not to chew solid foods or to test the anesthetized area by biting or probing until anesthesia has worn off (up to 7 hours) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.16)].
Methemoglobinemia
Inform patients that use of local anesthetics may cause methemoglobinemia, a serious condition that must be treated promptly. Advise patients or caregivers to seek immediate medical attention if they or someone in their care experience the following signs or symptoms: pale, gray, or blue colored skin (cyanosis); headache; rapid heart rate; shortness of breath; lightheadedness; or fatigue [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
