Trimethobenzamide Hydrochloride
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use TRIMETHOBENZAMIDE HYDROCHLODIRE CAPSULES safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for TRIMETHOBENZAMIDE HYDROCHLODIRE CAPSULES Initial U.S. Approval:1974
c18073be-d52a-4347-a8d1-6be11bcb7824
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Jan 30, 2024
Lupin Pharmaceuticals,Inc.
DUNS: 089153071
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Trimethobenzamide Hydrochloride
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (13)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
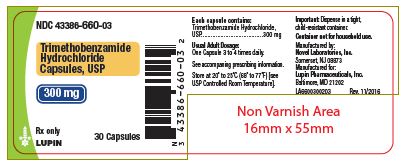
30count-label

100count-label

500count-label
INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules is indicated in adults for the treatment of postoperative nausea and vomiting and for nausea associated with gastroenteritis.
Limitation of Use:
Trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules is not recommended for use in pediatric patients due to the risk of extrapyramidal signs and symptoms and other serious central nervous system (CNS) effects, and the risk of exacerbation of the underlying disease in pediatric patients with Reye's syndrome or other hepatic impairment.
Trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules are an antiemetic indicated in adults for the treatment of postoperative nausea and vomiting and for nausea associated with gastroenteritis. (1)
Limitation of Use:
• Trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules are not recommended for use in pediatric patients due to the risk of extrapyramidal signs and symptoms and other serious central nervous system (CNS) effects and the risk of exacerbation of the underlying disease in pediatric patients with Reye's syndrome or other hepatic impairment. (1, 8.4)
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules are contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to trimethobenzamide [see Adverse Reactions (6)].
Known hypersensitivity to trimethobenzamide (4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions from voluntary reports or clinical studies have been reported with trimethobenzamide. Because many of these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- Nervous system disorders: Parkinson-like symptoms, coma, convulsions, opisthotonos, dizziness, drowsiness, headache, [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3)]
- Psychiatric disorders: disorientation, depression of mood
- Eye disorders: blurred vision
- Hematologic disorders: blood dyscrasias
- Hepatobiliary disorders: jaundice [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Immune system disorders: hypersensitivity, including angioedema and allergic-type skin reactions
- Gastrointestinal disorders: diarrhea
- Musculoskeletal disorders: muscle cramps
****Adverse reactions include hypersensitivity reactions and Parkinson-like symptoms; blood dyscrasias, blurring of vision, coma, convulsions, depression of mood, diarrhea, disorientation, dizziness, drowsiness, headache, jaundice, muscle cramps, and opisthotonos. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-866-403-7592 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 orWWW.FDA.GOV/MEDWATCH.
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Alcohol
Alcohol may increase the CNS depressant effects of trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules and may cause drowsiness [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.5)]. Avoid concomitant use of trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules with alcohol.
7.2 Other Drugs that Cause CNS Depression or EPS
The concurrent use of trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules with other drugs that cause CNS depression or EPS (e.g., sedatives, hypnotics, opiates, anxiolytics, antipsychotics, and anticholinergics, may potentiate the effects of trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.5)]. Either trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules or the other interacting drug should be chosen, depending on the importance of the drug to the patient. If CNS-acting drugs cannot be avoided, monitor patients for CNS adverse reactions.
• Alcohol: May cause drowsiness; avoid concomitant use. (7.1)
• Other Drugs that Cause CNS Depression or EPS: Either trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules or the other interacting drug should be chosen, depending on the importance of the drug to the patient. If CNS-acting drugs cannot be avoided, monitor patients for CNS adverse reactions. (7.2)
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Capsules: 300 mg trimethobenzamide hydrochloride; the capsule has an opaque lavender cap and opaque lavender body with a white imprint "Novel 660" on cap and "300 mg on body.
Capsule: 300 mg of trimethobenzamide hydrochloride (3)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
The limited available data with trimethobenzamide in pregnant women are not sufficient to inform a drug-associated risk for major birth defects and miscarriage. No adverse developmental effect was observed in animal reproduction studies with administration of trimethobenzamide hydrochloride during organogenesis in pregnant rats at doses 0.16 and 0.8 times the recommended human dose (RHD) and in pregnant rabbits at doses 1.6 times the RHD [see Data].
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2 to 4% and 15 to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
Reproduction studies with trimethobenzamide hydrochloride were conducted in rats and rabbits following administration of trimethobenzamide hydrochloride during organogenesis and no adverse developmental effect was observed in either species. The only effects observed were an increased percentage of embryonic resorptions or stillborn pups in rats administered 20 mg/kg and 100 mg/kg (0.16 and 0.8 times the RHD of 1200 mg/day, based on body surface area) and increased resorptions in rabbits receiving 100 mg/kg (1.6 times the RHD of 1200 mg/day, based on body surface area). In each study, these adverse effects were attributed to one or two dams.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information on the presence of trimethobenzamide in human milk, the effects of trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules on the breastfed infant or the effects of trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules on milk production. The lack of clinical data during lactation precludes a clear determination of the risk of trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules to an infant during lactation; therefore, the developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules in pediatric patients has not been established.
Trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules is not recommended for use in pediatric patients due to the risk of EPS and other serious CNS effects, and the risk of exacerbation of underlying disease in pediatric patients with Reye's Syndrome, or other hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of trimethobenzamide did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 years and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients. Although there are studies reported in the literature that included geriatric patients 65 years and older with younger patients, it is not known if there are differences in efficacy or safety parameters for geriatric and non-geriatric patients treated with trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules. Trimethobenzamide is excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because geriatric patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, reduce the daily dosage of trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules by increasing the dosing interval and adjust as needed based upon therapeutic response and tolerability. Monitor renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
Trimethobenzamide is eliminated by renal excretion [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. In patients with renal impairment (creatinine clearance 70 mL/min/1.73m2 or less), reduce the daily dosage by increasing the dosing interval and adjust as needed based upon therapeutic response and tolerability. Monitor renal function [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
Avoid trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules in patients whose signs and symptoms suggest the presence of hepatic impairment due to the risk of hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]. Discontinue trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules in patients who develop impaired liver function while taking trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules, USP are available as filled gelatin capsules size 1 lavender opaque cap/lavender opaque body with a white imprint "Novel 660" on cap and "300 mg" on body. Each capsule contains 300 mg of trimethobenzamide hydrochloride.
|
Package |
NDC Number |
|
Bottles of 30 |
43386-660-03 |
|
Bottles of 100 |
43386-660-24 |
|
Bottles of 500 |
43386-660-26 |
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68° to 77°F).
[See USP Controlled Room Temperature]
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Adult Dosage
The recommended adult dosage is 300 mg orally three or four times daily. Select the lowest effective daily dosage and adjust as needed based upon therapeutic response and tolerability.
2.2 Dosage Adjustment for Geriatric Patients and/or Patients with Renal
Impairment
In geriatric patients and/or in patients with renal impairment (creatinine clearance 70 mL/min/1.73m2 or less), reduce the daily dosage of trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules by increasing the dosing interval and adjust as needed based upon therapeutic response and tolerability. Monitor renal function [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5, 8.6)].
** •**The recommended adult dosage is 300 mg orally three or four times daily. (2.1)
• Geriatric patients and/or patients with renal impairment (creatinine clearance 70 mL/min/1.73m2 or less): Reduce the daily dosage by increasing the dosing interval; monitor renal function. (2.2, 8.5, 8.6)
• Select the lowest effective daily dosage and adjust as needed based upon therapeutic response and tolerability. (2.1, 2.2)
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
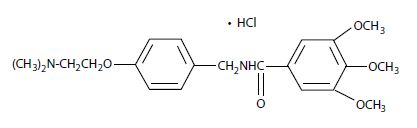
Chemically, trimethobenzamide hydrochloride is N-[p-[2-(dimethylamino)ethoxy]benzyl]-3,4,5-trimethoxybenzamide monohydrochloride. It has a molecular weight of 424.92 and the following structural formula:
Each capsule for oral use contains trimethobenzamide hydrochloride equivalent to 300 mg. The inactive ingredients are lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate and pregelatinized starch. The capsule shell contains the following ingredients: D&C Red # 28, FD&C Blue # 1, FD&C Red # 40, gelatin and titanium dioxide. White ink contains the following ingredients: 2-ethoxyethanol, industrial methylated spirit, lecithin, purified water, shellac glaze, simethicone emulsion and titanium dioxide.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of trimethobenzamide as determined in animals is obscure, but may involve the chemoreceptor trigger zone (CTZ), an area in the medulla oblongata through which emetic impulses are conveyed to the vomiting center; direct impulses to the vomiting center apparently are not similarly inhibited. In dogs pretreated with trimethobenzamide HCl, the emetic response to apomorphine is inhibited, while little or no protection is afforded against emesis induced by intragastric copper sulfate.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
The pharmacokinetics of trimethobenzamide in healthy adult subjects were compared when trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules was administered as a 300 mg oral capsule or a 200 mg (100 mg/mL) intramuscular injection. The time to reach maximum plasma concentration (Tmax) was about 30 minutes after intramuscular injection compared to about 45 minutes after oral capsule administration. The plasma concentration-time profile of trimethobenzamide was similar between the two formulations.
Elimination
The mean elimination half-life of trimethobenzamide is 7 to 9 hours.
Metabolism
The major pathway of trimethobenzamide metabolism is through oxidation resulting in the formation of trimethobenzamide N-oxide metabolite. The pharmacologic activity of this major metabolite has not been evaluated.
Excretion
Between 30 to 50% of a single dose in humans is excreted unchanged in the urine within 48 to72 hours.
Specific Populations
Sex
Systemic exposure to trimethobenzamide was similar between men (N=40) and women (N=28). Following a single 300 mg capsule oral administration, the respective mean (SD) Cmax of trimethobenzamide were 3.5 (1.1) and 4.2 (1.6) micrograms/mL in male and female subjects. The respective mean (SD) of AUC0-∞ of trimethobenzamide were 10 (2.7) and 10.4 (2.7) micrograms×hour/mL in male and female subjects.
Race
Pharmacokinetics appeared to be similar for Caucasians (N=53) and African Americans (N=12). Following a single 300 mg capsule oral administration, the respective mean (SD) Cmax of trimethobenzamide was 3.8 (1.3) micrograms/mL in Caucasians and 3.9 (1.7) micrograms/mL in African Americans. The respective mean (SD) AUC0-∞ of trimethobenzamide was 10.4 (2.8) micrograms×hour/mL in Caucasians and 9.8 (2.5) micrograms×hour/mL in African Americans.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Inform patients that trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules can cause serious adverse reactions. Instruct patients to discontinue trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules and contact a healthcare provider immediately if the following serious reactions occur:
Acute Dystonic Reactions and Other Extrapyramidal Symptoms [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
Other CNS Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2, 5.3)]
Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
Effects on the Ability to Drive or Operate Machinery
Advise patients that trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules can cause drowsiness and may impair their judgment, thinking, or motor skills required for tasks such as driving a motor vehicle or operating machinery. Inform patients not to operate motor vehicles or other dangerous machinery until they are reasonably certain that trimethobenzamide hydrochloride capsules does not affect them adversely [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Drug Interactions
Inform patients that use of alcohol or concomitant treatment with other CNS- acting drugs can precipitate or worsen CNS depression and/or EPS [see Drug Interactions (7.1, 7.2)]. Instruct patients avoid alcohol and to tell their health care providers when they start taking any concomitant medication.
Manufactured by:
Novel Laboratories, Inc.
Somerset, NJ 08873
Manufactured for:
Lupin Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Baltimore, MD 21202
PI6600000206
Rev. 01/2019
