Abacavir and lamivudine
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ABACAVIR and LAMIVUDINE TABLETS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ABACAVIR and LAMIVUDINE TABLETS. ABACAVIR and LAMIVUDINE tablets, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 2004
85071242-ccf6-43d7-8ee6-87273d21256f
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
May 15, 2023
Zydus Pharmaceuticals USA Inc.
DUNS: 156861945
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Abacavir and lamivudine
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (13)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 70710-1049-9
Abacavir and Lamivudine Tablets, 600 mg/300 mg
90 Tablets
Rx only
Zydus

Abacavir Sulfate and Lamivudine Tablet:
Warning Card

CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Abacavir and lamivudine is contraindicated in patients:
- who have the HLA-B*5701 allele [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] .
- with prior hypersensitivity reaction to abacavir [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] or lamivudine.
- with moderate or severe hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.7)] .
- Presence of HLA-B*5701 allele. (4)
- Prior hypersensitivity reaction to abacavir or lamivudine. (4)
- Moderate or severe hepatic impairment. (4, 8.7)
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Methadone
In a trial of 11 HIV-1-infected subjects receiving methadone-maintenance therapy with 600 mg of ZIAGEN twice daily (twice the currently recommended dose), oral methadone clearance increased [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. This alteration will not result in a methadone dose modification in the majority of patients; however, an increased methadone dose may be required in a small number of patients.
7.2 Sorbitol
Coadministration of single doses of lamivudine and sorbitol resulted in a sorbitol dose-dependent reduction in lamivudine exposures. When possible, avoid use of sorbitol-containing medicines with lamivudine-containing medicines [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- Methadone: An increased methadone dose may be required in a small number of patients. (7.1)
- Sorbitol: Coadministration of lamivudine and sorbitol may decrease lamivudine concentrations; when possible, avoid chronic coadministration. (7.2)
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Abacavir and lamivudine tablets, USP contain 600 mg of abacavir (equivalent to 702.00 mg abacavir sulfate) and 300 mg of lamivudine.
Abacavir and lamivudine tablets USP, 600 mg/300 mg are light yellow to yellow, modified capsule shaped, coated tablets, debossed with "1049" on one side and plain on the other side.
Tablets: 600 mg of abacavir and 300 mg of lamivudine. (3)
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Abacavir and Lamivudine Tablets, USP
Abacavir and lamivudine tablets contain the following 2 synthetic nucleoside analogues: abacavir sulfate and lamivudine with inhibitory activity against HIV-1.
Each tablet contains 600 mg of abacavir (equivalent to 702.00 mg abacavir sulfate, USP) and 300 mg of lamivudine, USP and the inactive ingredients: croscarmellose sodium, D&C yellow #10 aluminum lake, FD&C red #40 aluminum lake, hypromellose, iron oxide yellow, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose polysorbate 80, polyethylene glycol, povidone K-30 and titanium dioxide.
Abacavir Sulfate
The chemical name of abacavir sulfate is (1S,cis)-4-[2-amino-6 (cyclopropylamino)-9H-purin-9-yl]-2-cyclopentene-1-methanol sulfate (salt) (2:1). Abacavir sulfate is the enantiomer with 1S, 4R absolute configuration on the cyclopentene ring. It has a molecular formula of (C14H18N6O)2•H2SO4 and a molecular weight of 670.76 g per mol. It has the following structural formula:
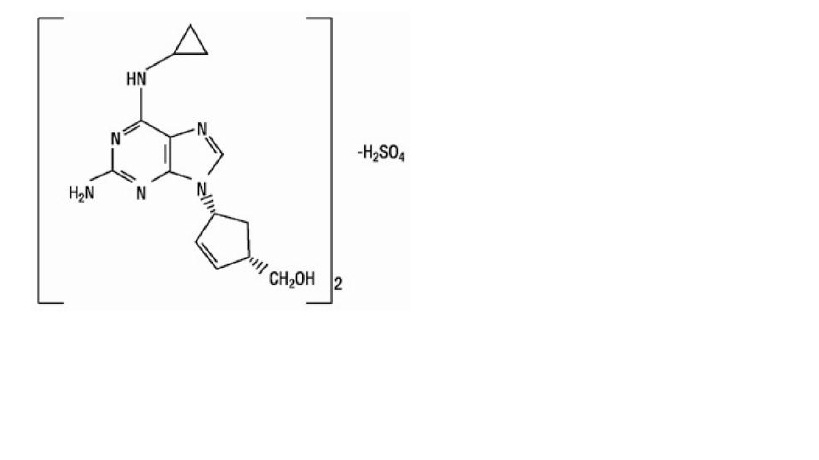
Abacavir sulfate, USP is white to almost white powder. It is soluble in water.
In vivo, abacavir sulfate dissociates to its free base, abacavir. All dosages for abacavir sulfate are expressed in terms of abacavir.
Lamivudine
The chemical name of lamivudine is (2R,cis)-4-amino-1-(2-hydroxymethyl-1,3 oxathiolan-5-yl)-(1H)-pyrimidin-2-one. Lamivudine is the (-)enantiomer of a dideoxy analogue of cytidine. Lamivudine has also been referred to as (-)2′,3′-dideoxy, 3′-thiacytidine. It has a molecular formula of C8H11N3O3S and a molecular weight of 229.3 g per mol. It has the following structural formula:
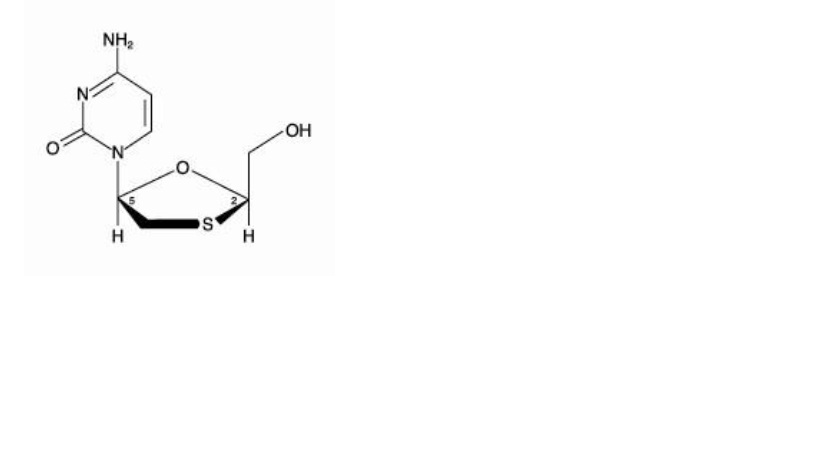
Lamivudine, USP is a white to off-white solid, melts at about 176°C. It is soluble in water.
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.3 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity
Abacavir
Abacavir was administered orally at 3 dosage levels to separate groups of mice and rats in 2-year carcinogenicity studies. Results showed an increase in the incidence of malignant and non-malignant tumors. Malignant tumors occurred in the preputial gland of males and the clitoral gland of females of both species, and in the liver of female rats. In addition, non-malignant tumors also occurred in the liver and thyroid gland of female rats. These observations were made at systemic exposures in the range of 6 to 32 times the human exposure at the recommended dose of 600 mg.
Lamivudine
Long-term carcinogenicity studies with lamivudine in mice and rats showed no evidence of carcinogenic potential at exposures up to 10 times (mice) and 58 times (rats) the human exposures at the recommended dose of 300 mg.
Mutagenicity
Abacavir
Abacavir induced chromosomal aberrations both in the presence and absence of metabolic activation in an in vitro cytogenetic study in human lymphocytes. Abacavir was mutagenic in the absence of metabolic activation, although it was not mutagenic in the presence of metabolic activation in an L5178Y mouse lymphoma assay. Abacavir was clastogenic in males and not clastogenic in females in an in vivo mouse bone marrow micronucleus assay. Abacavir was not mutagenic in bacterial mutagenicity assays in the presence and absence of metabolic activation.
Lamivudine
Lamivudine was mutagenic in an L5178Y mouse lymphoma assay and clastogenic in a cytogenetic assay using cultured human lymphocytes. Lamivudine was not mutagenic in a microbial mutagenicity assay, in an in vitro cell transformation assay, in a rat micronucleus test, in a rat bone marrow cytogenetic assay, and in an assay for unscheduled DNA synthesis in rat liver.
Impairment of Fertility
Abacavir: Abacavir did not affect male or female fertility in rats at a dose associated with exposures (AUC) approximately 3.3 times (male) or 4.1 times (female) those in humans at the clinically recommended dose.
Lamivudine: Lamivudine did not affect male or female fertility in rats at doses up to 4,000 mg per kg per day, associated with concentrations approximately 42 times (male) or 63 times (female) higher than the concentrations (Cmax) in humans at the dose of 300 mg.
13.4 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Myocardial degeneration was found in mice and rats following administration of abacavir for 2 years. The systemic exposures were equivalent to 7 to 24 times the expected systemic exposure in humans at a dose of 600 mg. The clinical relevance of this finding has not been determined.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Inform patients:
- that a Medication Guide and Warning Card summarizing the symptoms of the abacavir hypersensitivity reaction and other product information will be dispensed by the pharmacist with each new prescription and refill of abacavir and lamivudine and instruct the patient to read the Medication Guide and Warning Card every time to obtain any new information that may be present about abacavir and lamivudine. The complete text of the Medication Guide is reprinted at the end of this document.
- to carry the Warning Card with them.
- how to identify a hypersensitivity reaction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1),Medication Guide ].
- that if they develop symptoms consistent with a hypersensitivity reaction they should call their healthcare provider right away to determine if they should stop taking abacavir and lamivudine.
- that a hypersensitivity reaction can worsen and lead to hospitalization or death if abacavir and lamivudine is not immediately discontinued.
- to not restart abacavir and lamivudine or any other abacavir-containing product following a hypersensitivity reaction because more severe symptoms can occur within hours and may include life-threatening hypotension and death.
- that if they have a hypersensitivity reaction, they should dispose of any unused abacavir and lamivudine tablets to avoid restarting abacavir.
- that a hypersensitivity reaction is usually reversible if it is detected promptly and abacavir and lamivudine is stopped right away.
- that if they have interrupted abacavir and lamivudine for reasons other than symptoms of hypersensitivity (for example, those who have an interruption in drug supply), a serious or fatal hypersensitivity reaction may occur with reintroduction of abacavir.
- to not restart abacavir and lamivudine or any other abacavir-containing product without medical consultation and only if medical care can be readily accessed by the patient or others.
Patients with Hepatitis B or C Co-infection
Advise patients co-infected with HIV-1 and HBV that worsening of liver disease has occurred in some cases when treatment with lamivudine was discontinued. Advise patients to discuss any changes in regimen with their physician [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Lactic Acidosis/Hepatomegaly with Steatosis
Advise patients that lactic acidosis and severe hepatomegaly with steatosis have been reported with use of nucleoside analogues and other antiretrovirals. Advise patients to stop taking abacavir and lamivudine tablets if they develop clinical symptoms suggestive of lactic acidosis or pronounced hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
Advise patients to inform their healthcare provider immediately of any signs and symptoms of infection as inflammation from previous infection may occur soon after combination antiretroviral therapy, including when abacavir and lamivudine tablets is started [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Pregnancy Registry
Advise patients that there is a pregnancy exposure registry that monitors pregnancy outcomes in women exposed to abacavir and lamivudine tablets during pregnancy [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Lactation
Instruct women with HIV-1 infection not to breastfeed because HIV-1 can be passed to the baby in the breast milk [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Missed Dose
Instruct patients that if they miss a dose of abacavir and lamivudine tablets, to take it as soon as they remember. Advise patients not to double their next dose or take more than the prescribed dose [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
Availability of Medication Guide
Instruct patients to read the Medication Guide before starting abacavir and lamivudine tablets and to re-read it each time the prescription is renewed. Instruct patients to inform their physician or pharmacist if they develop any unusual symptom, or if any known symptom persists or worsens.
The brands listed are trademarks of their respective owners.
