Flecainide Acetate
Flecainide Acetate Tablets, USP Rx only
e56335c1-5508-4136-bd2e-18385623e497
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Jan 9, 2024
Rising Pharma Holdings, Inc.
DUNS: 116880195
Products 3
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Flecainide Acetate
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (6)
Flecainide Acetate
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (6)
Flecainide Acetate
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (6)
Drug Labeling Information
Adverse Reactions Section
ADVERSE REACTIONS
In post-myocardial infarction patients with asymptomatic PVCs and non- sustained ventricular tachycardia, flecainide acetate therapy was found to be associated with a 5.1% rate of death and non-fatal cardiac arrest, compared with a 2.3% rate in a matched placebo group. (SeeWARNINGS.)
Adverse effects reported for flecainide acetate, described in detail in the WARNINGS section, were new or worsened arrhythmias which occurred in 1% of 108 patients with PSVT and in 7% of 117 patients with PAF; and new or exacerbated ventricular arrhythmias which occurred in 7% of 1330 patients with PVCs, non-sustained or sustained VT. In patients treated with flecainide for sustained VT, 80% (51/64) of proarrhythmic events occurred within 14 days of the onset of therapy. 198 patients with sustained VT experienced a 13% incidence of new or exacerbated ventricular arrhythmias when dosage was initiated at 200 mg/day with slow upward titration, and did not exceed 300 mg/day in most patients. In some patients, flecainide acetate treatment has been associated with episodes of unresuscitatable VT or ventricular fibrillation (cardiac arrest). (SeeWARNINGS.) New or worsened CHF occurred in 6.3% of 1046 patients with PVCs, non-sustained or sustained VT. Of 297 patients with sustained VT, 9.1% experienced new or worsened CHF. New or worsened CHF was reported in 0.4% of 225 patients with supraventricular arrhythmias. There have also been instances of second- (0.5%) or third-degree (0.4%) AV block. Patients have developed sinus bradycardia, sinus pause, or sinus arrest, about 1.2% altogether (seeWARNINGS). The frequency of most of these serious adverse events probably increases with higher trough plasma levels, especially when these trough levels exceed 1 mcg/mL.
There have been rare reports of isolated elevations of serum alkaline phosphatase and isolated elevations of serum transaminase levels. These elevations have been asymptomatic and no cause and effect relationship with flecainide acetate has been established. In foreign postmarketing surveillance studies, there have been rare reports of hepatic dysfunction including reports of cholestasis and hepatic failure, and extremely rare reports of blood dyscrasias. Although no cause and effect relationship has been established, it is advisable to discontinue flecainide acetate in patients who develop unexplained jaundice or signs of hepatic dysfunction or blood dyscrasias in order to eliminate flecainide acetate as the possible causative agent.
Incidence figures for other adverse effects in patients with ventricular arrhythmias are based on a multicenter efficacy study, utilizing starting doses of 200 mg/day with gradual upward titration to 400 mg/day. Patients were treated for an average of 4.7 months, with some receiving up to 22 months of therapy. In this trial, 5.4% of patients discontinued due to non-cardiac adverse effects.
Table 1 Most Common Non-Cardiac Adverse Effects in Ventricular Arrhythmia Patients Treated with Flecainide Acetate in the Multicenter Study|
Adverse Effect |
Incidence |
Incidence by Dose | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
All 429 Patients at Any Dose |
200 mg/Day (N=426) |
300 mg/Day (N=293) |
400 mg/Day (N=100) | |
| ||||
|
Dizziness* |
18.9% |
11% |
10.6% |
13% |
|
Visual Disturbances† |
15.9% |
5.4% |
12.3% |
18% |
|
Dyspnea |
10.3% |
5.2% |
7.5% |
4% |
|
Headache |
9.6% |
4.5% |
6.1% |
9% |
|
Nausea |
8.9% |
4.9% |
4.8% |
6% |
|
Fatigue |
7.7% |
4.5% |
4.4% |
3% |
|
Palpitation |
6.1% |
3.5% |
2.4% |
7% |
|
Chest Pain |
5.4% |
3.1% |
3.8% |
1% |
|
Asthenia |
4.9% |
2.6% |
2% |
4% |
|
Tremor |
4.7% |
2.4% |
3.4% |
2% |
|
Constipation |
4.4% |
2.8% |
2.1% |
1% |
|
Edema |
3.5% |
1.9% |
1.4% |
2% |
|
Abdominal Pain |
3.3% |
1.9% |
2.4% |
1% |
The following additional adverse experiences, possibly related to flecainide acetate therapy and occurring in 1% to less than 3% of patients, have been reported in acute and chronic studies:
Body as a Whole – malaise, fever
Cardiovascular – tachycardia, sinus pause or arrest
Gastrointestinal – vomiting, diarrhea, dyspepsia, anorexia
Skin – rash
Visual – diplopia
Nervous System – hypoesthesia, paresthesia, paresis, ataxia, flushing, increased sweating, vertigo, syncope, somnolence, tinnitus
Psychiatric – anxiety, insomnia, depression.
The following additional adverse experiences, possibly related to flecainide acetate, have been reported in less than 1% of patients:
Body as a Whole – swollen lips, tongue and mouth; arthralgia, bronchospasm, myalgia
Cardiovascular – angina pectoris, second-degree and third-degree AV block, bradycardia, hypertension, hypotension
Gastrointestinal – flatulence
Urinary System – polyuria, urinary retention
Hematologic – leukopenia, granulocytopenia, thrombocytopenia
Skin – urticaria, exfoliative dermatitis, pruritis, alopecia
Visual – eye pain or irritation, photophobia, nystagmus
Nervous System – twitching, weakness, change in taste, dry mouth, convulsions, impotence, speech disorder, stupor, neuropathy
Respiratory – pneumonitis/pulmonary infiltration possibly due to chronic flecainide treatment
Psychiatric – amnesia, confusion, decreased libido, depersonalization, euphoria, morbid dreams, apathy.
For patients with supraventricular arrhythmias, the most commonly reported noncardiac adverse experiences remain consistent with those known for patients treated with flecainide acetate for ventricular arrhythmias. Dizziness is possibly more frequent in PAF patients.
Description Section
DESCRIPTION
Flecainide acetate is an antiarrhythmic drug available in tablets of 50 mg, 100 mg, or 150 mg for oral administration.
Flecainide acetate is benzamide, N-(2-piperidinyl-methyl)-2,5-bis (2,2,2-trifluoroethoxy)-monoacetate. The structural formula is given below.
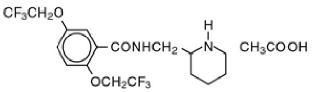
Flecainide acetate USP is a white to slightly off-white, crystalline powder with a pKa of 9.3. It has an aqueous solubility of 48.4 mg/mL at 37°C.
Flecainide acetate tablets, USP also contain: croscarmellose sodium, hydrogenated vegetable oil type 1, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, and pregelatinized starch.
