Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use SODIUM SULFATE, POTASSIUM SULFATE and MAGNESIUM SULFATE ORAL SOLUTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for SODIUM SULFATE, POTASSIUM SULFATE and MAGNESIUM SULFATE ORAL SOLUTION. SODIUM SULFATE, POTASSIUM SULFATE and MAGNESIUM SULFATE oral solution Initial U.S. Approval: 2010
2106d1aa-086e-4248-9a3d-ec138d492cf3
HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG LABEL
Mar 28, 2024
Ascend Laboratories, LLC
DUNS: 141250469
Products 1
Detailed information about drug products covered under this FDA approval, including NDC codes, dosage forms, ingredients, and administration routes.
Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate
Product Details
FDA regulatory identification and product classification information
FDA Identifiers
Product Classification
Product Specifications
INGREDIENTS (10)
Drug Labeling Information
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Bottle Label
NDC 67877-725-82
Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution (17.5
g/3.13 g/1.6 g) per 6 ounces
Rx only
6-ounce (177 mL) bottles

Carton Label
NDC 67877-725-92
Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate and Magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution (17.5
g/3.13 g/1.6 g) per 6 ounces
Rx only
6-ounce (177 mL) bottles

INDICATIONS & USAGE SECTION
1 INDICATIONS & USAGE
Sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution is indicated for cleansing of the colon as a preparation for colonoscopy in adult patients.
Pediatric use information is approved for Braintree Laboratories, Inc.’s SUPREP BOWEL PREP KIT (sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate, and magnesium sulfate) oral solution. However, due to Braintree Laboratories, Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
CONTRAINDICATIONS SECTION
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution is contraindicated in the following conditions:
-
Gastrointestinal obstruction or ileus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
-
Bowel perforation [see Warnings and Precaution (5.6)]
-
Toxic colitis or toxic megacolon
-
Gastric retention
-
Hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients in sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution
- Gastrointestinal obstruction or ileus (4, 5.6)
- Bowel perforation (4, 5.6)
- Toxic colitis or toxic megacolon (4)
- Gastric retention (4)
- Hypersensitivity to any ingredient (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS SECTION
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Serious Fluid and Serum Chemistry Abnormalities
Advise all patients to hydrate adequately before, during, and after the use of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution. If a patient develops significant vomiting or signs of dehydration after taking sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution, consider performing post-colonoscopy lab tests (electrolytes, creatinine, and BUN).
Fluid and electrolyte disturbances can lead to serious adverse events including cardiac arrhythmias, seizures and renal impairment. Correct fluid and electrolyte abnormalities before treatment with sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution. Use sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution with caution in patients with conditions, or who are using medications, that increase the risk for fluid and electrolyte disturbances or may increase the risk of adverse events of seizure, arrhythmias, and renal impairment [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution can cause temporary elevations in uric acid [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Uric acid fluctuations in patients with gout may precipitate an acute flare. The potential for uric acid elevation should be considered before administering sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution to patients with gout or other disorders of uric acid metabolism.
5.2 Cardiac Arrhythmias
There have been rare reports of serious arrhythmias associated with the use of ionic osmotic laxative products for bowel preparation. Use caution when prescribing sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution for patients at increased risk of arrhythmias (e.g., patients with a history of prolonged QT, uncontrolled arrhythmias, recent myocardial infarction, unstable angina, congestive heart failure, or cardiomyopathy). Consider pre-dose and post-colonoscopy ECGs in patients at increased risk of serious cardiac arrhythmias.
5.3 Seizures
There have been reports of generalized tonic-clonic seizures and/or loss of consciousness associated with use of bowel preparation products in patients with no prior history of seizures. The seizure cases were associated with electrolyte abnormalities (e.g., hyponatremia, hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, and hypomagnesemia) and low serum osmolality. The neurologic abnormalities resolved with correction of fluid and electrolyte abnormalities.
Use caution when prescribing sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution for patients with a history of seizures and in patients at increased risk of seizure, such as patients taking medications that lower the seizure threshold (e.g., tricyclic antidepressants), patients withdrawing from alcohol or benzodiazepines, or patients with known or suspected hyponatremia [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5.4 Use in Patients with Risk of Renal Injury
Use sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution with caution in patients with impaired renal function or patients taking concomitant medications that may affect renal function (such as diuretics, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers, or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) [see Drug Interactions (7.1)]. These patients may be at risk for renal injury. Advise these patients of the importance of adequate hydration with sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution and consider performing baseline and post- colonoscopy laboratory tests (electrolytes, creatinine, and BUN) in these patients [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6)].
5.5 Colonic Mucosal Ulcerations and Ischemic Colitis
Osmotic laxative products may produce colonic mucosal aphthous ulcerations, and there have been reports of more serious cases of ischemic colitis requiring hospitalization. Concurrent use of stimulant laxatives and sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution may increase these risks [see Drug Interactions (7.3)]. Consider the potential for mucosal ulcerations resulting from the bowel preparation when interpreting colonoscopy findings in patients with known or suspect inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
5.6 Use in Patients with Significant Gastrointestinal Disease
If gastrointestinal obstruction or perforation is suspected, perform appropriate diagnostic studies to rule out these conditions before administering sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution [see Contraindications (4)].
Use with caution in patients with severe active ulcerative colitis.
5.7 Aspiration
Patients with impaired gag reflex or other swallowing abnormalities are at risk for regurgitation or aspiration of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution. Observe these patients during administration of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution. Use with caution in these patients.
- Risk of fluid and electrolyte abnormalities: Encourage adequate hydration, assess concurrent medications, and consider laboratory assessments prior to and after each use. (5.1,7.1)
- Cardiac arrhythmias: Consider pre-dose and post-colonoscopy ECGs in patients at increased risk. (5.2)
- Seizures: Use caution in patients with a history of seizures and patients at increased risk of seizures, including medications that lower the seizure threshold. (5.3, 7.1)
- Patients with renal impairment or taking concomitant medications that affect renal function: Use caution, ensure adequate hydration and consider laboratory testing. (5.4, 7.1)
- Suspected GI obstruction or perforation: Rule out the diagnosis before administration. (4, 5.6)
- Patients at risk for aspiration: Observe during administration. (5.7)
ADVERSE REACTIONS SECTION
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following important adverse reactions for bowel preparations are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Serious Fluid and Serum Chemistry Abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Cardiac Arrhythmias [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Use in Patients with Risk of Renal Injury [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Colonic Mucosal Ulceration and Ischemic Colitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Patients with Significant Gastrointestinal Disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Aspiration [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adults
The safety of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution was evaluated in a multi-center, randomized, active controlled trial in 379 adult patients undergoing colonoscopy [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Most Common Adverse Reactions
Table 1 shows the most common adverse reactions reported in at least 2% of patients receiving sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution or the control (a bowel prep containing polyethylene glycol and electrolytes (PEG + E)) administered in split-dose (2-day) regimens.
Table 1: Common Adverse Reactions in Adult Patients Undergoing Colonoscopy in a Randomized, Active Controlled Trial*
|
Symptom |
Split-Dose (2-Day) Regimen | |
|
Sodium Sulfate, Potassium sulfate and magnesium Sulfate Oral Solution |
PEG + E product % | |
|
Overall Discomfort |
54 |
67 |
|
Abdominal Distension |
40 |
52 |
|
Abdominal Pain |
36 |
43 |
|
Nausea |
36 |
33 |
|
Vomiting |
8 |
4 |
- reported in at least 2% of patients
Laboratory Abnormalities
Table 2 shows the most common laboratory abnormalities (at least 10% in either treatment group and more than 2% difference between groups) for patients who developed new abnormalities of important electrolytes and uric acid after completing the bowel preparation with either sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution or PEG+E administered as a split-dose (2-day) regimen.
Table 2: Adult Patients with Normal Baseline Serum Chemistry with A Shift to an Abnormal Value While on the Split-Dose (2-Day) Regimen****1
|
Day of Colonoscopy |
Day 30 | ||
|
Bicarbonate (low) |
Sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution |
20 (13) |
7 (4) |
|
PEG + Electrolytes |
24 (15) |
4 (3) | |
|
Bilirubin, total (high) |
Sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution |
14 (9) |
0 (0) |
|
PEG + Electrolytes |
20 (12) |
3 (2) | |
|
BUN (high) |
Sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution |
2 (2) |
14 (11) |
|
PEG + Electrolytes |
4 (3) |
19 (15) | |
|
Calcium (high) |
Sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution |
16 (10) |
8 (5) |
|
PEG + Electrolytes |
6 (4) |
6 (4) | |
|
Chloride (high) |
Sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution |
4 (2) |
6 (4) |
|
PEG + Electrolytes |
20 (12) |
6 (4) | |
|
Osmolality (high) |
Sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution |
8 (6) |
NA |
|
PEG + Electrolytes |
19 (13) |
NA | |
|
Uric acid (high) |
Sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution |
27 (24) |
13 (12) |
|
PEG + Electrolytes |
12 (10) |
20 (17) |
1The study was not designed to support comparative claims for the laboratory abnormalities reported in this table.
2Percent (n/N) of patients where N=number of patients with normal baseline who had abnormal values at the timepoint(s) of interest.
Less Common Adverse Reactions
AV Block (1 case) and CK increase.
Adverse Reactions with Unapproved Use
In another study of 408 adult patients, higher rates of the following adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities were reported in patients treated with sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution as an evening-only (1-day) regimen compared to the split-dose (2-day) regimen.
- overall discomfort, abdominal distention, nausea, and vomiting
- total bilirubin (high), BUN (high), creatinine (high), osmolality (high), potassium (high) and uric acid (high)
Administration of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution in an evening-only (1-day) dosing regimen is not recommended.
Pediatric use information is approved for Braintree Laboratories, Inc.’s SUPREP BOWEL PREP KIT (sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate, and magnesium sulfate) oral solution. However, due to Braintree Laboratories, Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
Most common adverse reactions are:
- Adults (>2%): overall discomfort, abdominal distention, abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Ascend Laboratories, LLC at 1-877-272-7901 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or****www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS SECTION
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Drugs That May Increase Risk of Fluid and Electrolyte Abnormalities
Use caution when prescribing sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution to patients taking medications that increase the risk of fluid and electrolyte disturbances or may increase the risk of adverse events of seizure, arrhythmias, and prolonged QT in the setting of fluid and electrolyte abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4 )].
7.2 Potential for Reduced Drug Absorption
Sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution can reduce the absorption of other co-administered drugs [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
- Administer oral medications at least one hour before starting each dose of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution.
- Administer tetracycline and fluoroquinolone antibiotics, iron, digoxin, chlorpromazine, and penicillamine at least 2 hours before and not less than 6 hours after administration of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution to avoid chelation with magnesium.
7.3 Stimulant Laxatives
Concurrent use of stimulant laxatives and sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution may increase the risk of mucosal ulceration or ischemic colitis. Avoid use of stimulant laxatives (e.g., bisacodyl, sodium picosulfate) while taking sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Drugs that increase risk of fluid and electrolyte imbalance. (7.1)
Pediatric use information is approved for Braintree Laboratories, Inc.’s SUPREP BOWEL PREP KIT (sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate, and magnesium sulfate) oral solution. However, due to Braintree Laboratories, Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION SECTION
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosage and Administration Overview
Administration of two bottles of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution and additional water is required for a complete preparation for colonoscopy. One bottle of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution is equivalent to one dose. Sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution is supplied in one dosage strength [see Dosage Forms and Strengths (3)]. The recommended dosage is:
***Adults:**Two 6-ounce doses [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Pediatric use information is approved for Braintree Laboratories, Inc.’s SUPREP BOWEL PREP KIT (sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate, and magnesium sulfate) oral solution. However, due to Braintree Laboratories, Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
2.2 Important Preparation and Administration Instructions
- Correct fluid and electrolyte abnormalities before treatment with sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Must dilute sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution in water before ingestion.
- Must consume additional water after each dose of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution.
- On the day before colonoscopy, consume only a light breakfast or clear liquids (e.g., water, strained fruit juice without pulp, lemonade, plain coffee or tea, chicken broth gelatin dessert without fruit). On the day of the colonoscopy only consume clear liquids up to two hours prior to colonoscopy.
- Do not eat solid food or drink milk or eat or drink anything colored red or purple.
- Do not drink alcohol.
- Do not take other laxatives while taking sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution.
- Do not take oral medications within one hour of starting each dose of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution.
- If taking tetracycline or fluoroquinolone antibiotics, iron, digoxin, chlorpromazine, or penicillamine, take these medications at least 2 hours before and not less than 6 hours after administration of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
- Stop consumption of all fluids at least 2 hours prior to the colonoscopy.
2.3 Recommended Dosage and Administration in Adults
The recommended Split-Dose (two-day) regimen foradultsconsists of two 6-ounce doses of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution: the first dose during the evening prior to colonoscopy and the second dose the next day, during the morning of the colonoscopy.
Each dose consists of one bottle of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution with additional water. The total volume of liquid required for colon cleansing (using two bottles) is 3 quarts. The following are recommended dosage and administration instructions for adults:
Dose 1 – On the Day Prior to Colonoscopy:
- May consume a light breakfast, or only clear liquids (no solid food).
- In the evening before the procedure, pour the contents of one bottle of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution into the mixing container provided.
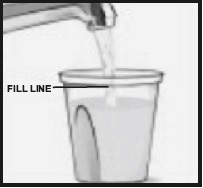
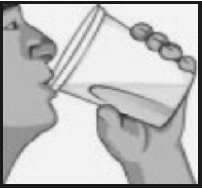
- Add cool drinking water to the 16-ounce fill line on the container, mix, and drink the entire amount.
- Drink two additional containers filled with water to the 16-ounce fill line over the next hour.
Dose 2 - Day of Colonoscopy:
- Continue to consume only clear liquids.
- In the morning (10 to 12 hours after the evening dose) on the day of the procedure, pour the contents of the second bottle of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution into the mixing container provided.
- Add cool drinking water to the 16-ounce fill line on the container, mix, and drink the entire amount.
- Drink two additional containers filled with water to the 16-ounce fill line over the next hour.
- Complete all solution of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution and required water at least two hours prior to colonoscopy.
Preparation and Administration (2.2)
- Must dilute in water prior to ingestion.
- Administration of two bottles of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution is required for a complete preparation for colonoscopy. One bottle is equivalent to one dose.
- Must consume additional water after each dose.
- Stop consumption of all fluids at least 2 hours before the colonoscopy.
Recommended Dosage and Administration
- Split-Dose (two-day) regimen consists of two doses of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution: first dose during the evening prior to colonoscopy and second dose the next day, during the morning of colonoscopy. (2.1, 2.3)
- Recommended sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution dosage is: o**Adults:**Two 6-ounce doses. (2.3)
- For complete information on preparation before colonoscopy and administration of the dosage regimen, see full prescribing Information. (2.1, 2.2, 2.3)
DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS SECTION
3 DOSAGE FORMS & STRENGTHS
- Sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution**(for adults):**Two bottles each containing 6 ounces of an oral solution of 17.5 grams sodium sulfate, 3.13 grams potassium sulfate, and 1.6 grams magnesium sulfate as a clear to slightly hazy liquid.
When diluted as directed, the solution is clear and colorless.
Pediatric use information is approved for Braintree Laboratories, Inc.’s SUPREP BOWEL PREP KIT (sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate, and magnesium sulfate) oral solution. However, due to Braintree Laboratories, Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS SECTION
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available data on sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution use in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug- associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. Animal reproductive studies have not been conducted with sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate, and magnesium sulfate (sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data available data on the presence of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution in human or animal milk, the effects on the breastfed child, or the effects on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution in pediatric patients less than 12 years of age have not been established.
****Pediatric use information is approved for Braintree Laboratories, Inc.’s SUPREP BOWEL PREP KIT (sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate, and magnesium sulfate) oral solution. However, due to Braintree Laboratories, Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 375 patients who received sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution in clinical trials, 94 (25%) were 65 years of age or older, and 25 (7%) were 75 years of age or older. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution, administered as the recommended split- dose (2-day) regimen, were observed between geriatric patients and younger patients. Geriatric patients reported more vomiting when sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution was given as a one-day preparation (not a recommended regimen).
Elderly patients are more likely to have decreased hepatic, renal or cardiac function and may be more susceptible to adverse reactions resulting from fluid and electrolyte abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
Use sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution with caution in patients with renal impairment or patients taking concomitant medications that may affect renal function. These patients may be at risk for renal injury. Advise these patients of the importance of adequate hydration before, during and after use of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution and consider performing baseline and post- colonoscopy laboratory tests (electrolytes, creatinine, and BUN) in these patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
OVERDOSAGE SECTION
10 OVERDOSAGE
Overdosage of more than the recommended dose of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution may lead to severe electrolyte disturbances, as well as dehydration and hypovolemia, with signs and symptoms of these disturbances. [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3)]. Monitor for fluid and electrolyte disturbances and treat symptomatically.
DESCRIPTION SECTION
11 DESCRIPTION
Sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate, and magnesium sulfate oral solution**(for adults)**is an osmotic laxative and is provided as two bottles each containing 6 ounces of solution.
Each bottle contains: 17.5 grams sodium sulfate, 3.13 grams potassium sulfate, and 1.6 grams magnesium sulfate. Inactive ingredients include: art cherry flavor, citric acid, dibasic sodium phosphate anhydrous, malic acid, monobasic sodium phosphate anhydrous, purified water, sodium benzoate, sucralose.
Sodium Sulfate, USP
The chemical name is Na2SO4. The average Molecular Weight is 142.04. The structural formula is:

Potassium Sulfate, FCC, purified
The chemical name is K2SO4. The average Molecular Weight is 174.26. The structural formula is:

Magnesium Sulfate, USP
The chemical name is MgSO4. The average Molecular Weight: 120.37. The structural formula is:

Each sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate, and magnesium sulfate oral solution also contains a polypropylene mixing container.
Pediatric use information is approved for Braintree Laboratories, Inc.’s SUPREP BOWEL PREP KIT (sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate, and magnesium sulfate) oral solution. However, due to Braintree Laboratories, Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY SECTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Sulfate salts provide sulfate anions, which are poorly absorbed. The osmotic effect of unabsorbed sulfate anions and the associated cations causes water to be retained within the gastrointestinal tract.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
No formal pharmacodynamic studies have been conducted with sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption and Elimination
After administration of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution in six healthy subjects, the time at which serum sulfate reached its highest point (Tmax) was approximately 17 hours after the first dose or approximately 5 hours after the second dose, and then declined with a half-life of 8.5 hours.
Excretion
Fecal excretion was the primary route of sulfate elimination.
Specific Populations
Patients with Renal Impairment
The disposition of sulfate after ingestion of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution was studied in patients (N=6) with moderate renal impairment (creatinine clearance of 30 to 49 mL/min). In patients with moderate renal impairment, mean AUC was 54% higher and mean Cmax was 44% higher, than healthy subjects.
The mean sulfate concentrations in healthy subjects and in patients with moderate renal impairment returned to their respective baselines by Day 6 after dose initiation. Urinary excretion of sulfate over 30 hours after the first dose was approximately 16% lower in patients with moderate renal impairment than in healthy subjects. These differences are not considered clinically meaningful.
Patients with Hepatic Impairment
The disposition of sulfate after ingestion of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution was studied in patients (N=6) with mild to moderate hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh grades A and B). Systemic exposure of serum sulfate (AUC and Cmax) was similar between healthy subjects and patients with hepatic impairment. The mean sulfate concentrations in healthy subjects and in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment returned to their respective baselines by Day 6 after dose initiation. Urinary excretion of sulfate over 30 hours after the first dose was similar between patients with hepatic impairment and healthy subjects.
HOW SUPPLIED SECTION
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Each sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate, and magnesium sulfate oral solution (for adults)(NDC 67877-725-92) contains:
- Two bottles (NDC 67877-725-82) each containing 6-ounces of an oral solution of 17.5 grams sodium sulfate, 3.13 grams potassium sulfate, and 1.6 grams magnesium sulfate as a clear to slightly hazy liquid. When diluted as directed, the solution is clear and colorless.
- One (1) mixing container with a 16-ounce fill line.
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). Excursions permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F). [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Pediatric use information is approved for Braintree Laboratories, Inc.’s SUPREP BOWEL PREP KIT (sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate, and magnesium sulfate) oral solution. However, due to Braintree Laboratories, Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS SECTION
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient and/or caregiver to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Instruct patients or caregivers:
- Must dilute sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution before ingestion.
- Must consume additional water after each dose of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution.
- On the day before colonoscopy, consume only a light breakfast or clear liquids (e.g., water, apple or orange juice without pulp, lemonade, coffee, tea, or chicken broth). On the day of the colonoscopy only consume clear liquids up to two hours prior to colonoscopy.
- Two doses of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution are required for a complete preparation for colonoscopy. One bottle of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution is equivalent to one dose.
- Do not to take other laxatives while taking sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution.
- Do not eat solid food or drink milk or eat or drink anything colored red or purple.
- Do not drink alcohol.
- Do not take oral medications within one hour of starting each dose of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution.
- If taking tetracycline or fluoroquinolone antibiotics, iron, digoxin, chlorpromazine, or penicillamine, take these medications at least 2 hours before and not less than 6 hours after administration of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution [see Drug Interactions (7.2)].
- Stop consumption of all fluids at least 2 hours prior to colonoscopy.
- Contact their healthcare provider if they develop significant vomiting or signs of dehydration after taking sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution or if they experience cardiac arrhythmias or seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3)].
Manufactured by:
Alkem Laboratories Ltd.,
INDIA.
Distributed by:
Ascend Laboratories, LLC
Parsippany, NJ 07054
Revised: December, 2022
NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
The sulfate salts of sodium, potassium, and magnesium contained in sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution were administered orally (gavage) to rats and dogs up to 28 days up to a maximum daily dose of 5 grams/kg/day (approximately 0.9 and 3 times for rats and dogs, respectively, the recommended human dose of 44 grams/day or 0.89 grams/kg based on the body surface area). In rats, the sulfate salts caused diarrhea and electrolyte and metabolic changes, including hypochloremia, hypokalemia, hyponatremia, lower serum osmolality, and high serum bicarbonate. Significant renal changes included increased fractional sodium excretion, increased urinary sodium and potassium excretion, and alkaline urine in both males and females. In addition, creatinine clearance was significantly decreased in females at the highest dose. No microscopic renal changes were seen. In dogs, the sulfate salts caused emesis, excessive salivation, excessive drinking of water, and abnormal excreta (soft and/or mucoid feces and/or diarrhea) and increased urine pH and sodium excretion.
CLINICAL STUDIES SECTION
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Adults
The colon cleansing efficacy of sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution was evaluated in a randomized, single-blind, active-controlled, multicenter study in adult patients scheduled to have a colonoscopy. There were 363 adult patients included in the efficacy analysis. Patients ranged in age from 20 to 84 years (mean age 55 years) and 54% were female. Race distribution was 86% Caucasian, 9% African-American, and 5% other.
Patients were randomized to one of the following two colon preparation regimens: sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution or a marketed polyethylene glycol (PEG) plus electrolytes bowel preparation. In the Study sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution was administered as a split-dose (two-day) regimen. The PEG bowel prep was also given as a split-dose preparation according to its labeled instructions. Patients receiving sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution were limited to a light breakfast followed by clear liquids on the day prior to the day of colonoscopy; patients receiving the PEG bowel prep were allowed to have a normal breakfast and a light lunch, followed by clear liquids.
The primary efficacy endpoint was the proportion of patients with successful colon cleansing as assessed by the colonoscopists, who were not informed about the type of preparation received, as shown in Table 3. In the study, no clinically or statistically significant differences were seen between the group treated with sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution and the group treated with the PEG bowel prep.
Table 3: Proportion of Adult Patients with Successful Colon Cleansing Response Rates
|
Treat****ment Group |
Regimen |
N |
Responders****1 |
Sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution –
PEG |
|
Sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate oral solution |
Split-Dose |
180 |
97% |
**2%**2 |
|
(with light breakfast) | ||||
|
PEG bowel prep |
Split-Dose |
183 |
96% |
1 Responders were patients whose colon preparations were graded excellent (no more than small bits of adherent feces/fluid) or good (small amounts of feces or fluid not interfering with the exam) by the colonoscopist.
2Does not equal difference in tabled responder rates due to rounding effects.
Pediatric use information is approved for Braintree Laboratories, Inc.’s SUPREP BOWEL PREP KIT (sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate, and magnesium sulfate) oral solution. However, due to Braintree Laboratories, Inc.’s marketing exclusivity rights, this drug product is not labeled with that pediatric information.
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Dispense the enclosed Medication Guide to each patient.
** Sodium Sulfate, Potassium Sulfate**
** and Magnesium Sulfate**
** Oral Solution**



Booklet Includes:
1- Patient Instrutions
2- Full Prescribing Information
3- Medication Guide

On the day before your procedure
• You may have a light breakfast or have clear liquids ONLY; please have
nothing for dinner
•DO NOT drink milk
•DO NOTeat or drink anything colored red or purple
•DO NOTdrink alcoholic beverages
Any of the following clear liquids are OK
• Water
• Strained fruit juices (without pulp) including apple, orange, white grape,
or white cranberry
• Limeade or lemonade
• Coffee or tea (DO NOT use any dairy or non-dairy creamer)
• Chicken broth
• Gelatin desserts without added fruit or topping (NO RED OR PURPLE)

• In the evening before the procedure complete steps 1 through 4 using one (1)
6-ounce bottle before going to bed
• In the morning on the day of the procedure, repeat steps 1 through 4 using
the other 6-ounce bottle
|
STEP 1 |
STEP 2 |
STEP 3 |
STEP 4 |
|
|