Regulatory Information
HSA regulatory responsibility and product classification details
Regulatory Responsibility
Product Classification
Formulation Information
INJECTION, POWDER, FOR SOLUTION
**4.2 Posology and Method of Administration** Sulbactam sodium/ampicillin sodium IM/IV can be administered by either intravenous or intramuscular routes. The following dilutions may be used: 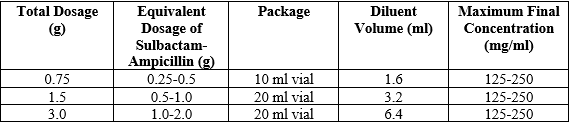 For intravenous administration, sulbactam sodium/ampicillin sodium IM/IV should be reconstituted with sterile water for injection or any compatible solution (see section 6.6 - **Special Precautions for Disposal and Other Handling** – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). To ensure complete dissolution, allow foaming to dissipate in order to visually inspect. The dose can be given by bolus injection over a minimum of 3 minutes or can be used in greater dilutions as an intravenous infusion over 15–30 minutes. Sulbactam sodium/ampicillin sodium parenteral may also be administered by deep intramuscular injection; if pain is experienced, 0.5% sterile solution for injection of lignocaine hydrochloride anhydrous may be used for reconstitution of the powder. Use in Adults The usual dosage range of sulbactam sodium/ampicillin sodium IM/IV is 1.5 g to 12 g per day in divided doses every 6 or 8 hours up to a maximum daily dosage of sulbactam of 4 g. Less severe infections may be treated on an every-12-hours schedule.  More or less frequent dosing may be indicated depending on the severity of the illness and the renal function of the patient. Treatment is usually continued until 48 hours after pyrexia and other abnormal signs have resolved. Treatment is normally given for 5 to 14 days, but the treatment period may be extended or additional ampicillin may be administered in severely ill cases. In treating patients on restricted sodium intake, it should be noted that 1,500 mg of sulbactam sodium/ampicillin sodium IM/IV contains approximately 115 mg (5 mmol) of sodium. For the prophylaxis of surgical infections, 1.5–3 g of sulbactam sodium/ampicillin sodium IM/IV should be given at induction of anesthesia, which allows sufficient time to achieve effective serum and tissue concentrations during the procedure. The dose may be repeated every 6–8 hours; administration is usually stopped 24 hours after the majority of surgical procedures, unless a therapeutic course of sulbactam sodium/ampicillin sodium IM/IV is indicated. In the treatment of uncomplicated gonorrhea, sulbactam sodium/ampicillin sodium IM/IV can be given as a single dose of 1.5 g. Concomitant probenecid 1.0 g orally should be administered in order to prolong plasma concentrations of sulbactam and ampicillin. Use in Children, Infants and Neonates The dosage of sulbactam sodium/ampicillin sodium IM/IV for most infections in children, infants and neonates is 150 mg/kg/day (corresponding to sulbactam 50 mg/kg/day and ampicillin 100 mg/kg/day). In children, infants and neonates, dosing is usually every 6 or 8 hours in accordance with the usual practice for ampicillin. In neonates during the first week of life (especially preterms), the recommended dose is 75 mg/kg/day (corresponding to 25 mg/kg/day sulbactam and 50 mg/kg/day ampicillin) in divided doses every 12 hours. Use in Patients with Renal Impairment In patients with severe impairment of renal function (creatinine clearance ≤30 ml/min), the elimination kinetics of sulbactam and ampicillin are similarly affected and hence the plasma ratio of one to the other will remain constant. The dose of sulbactam sodium/ampicillin sodium IM/IV in such patients should be administered less frequently in accordance with the usual practice for ampicillin.
INTRAVENOUS, INTRAMUSCULAR
Medical Information
**4.1 Therapeutic Indications** Sulbactam sodium/ampicillin sodium IM/IV is indicated for infections caused by susceptible microorganisms. Typical indications are upper and lower respiratory tract infections including sinusitis, otitis media and epiglottitis; bacterial pneumonias; urinary tract infections and pyelonephritis; intra-abdominal infections including peritonitis, cholecystitis, endometritis and pelvic cellulitis; bacterial septicemia; skin, soft tissue, bone and joint infections and gonococcal infections. Sulbactam sodium/ampicillin sodium IM/IV may also be administered peri-operatively to reduce the incidence of post-operative wound infections in patients undergoing abdominal or pelvic surgery, in which peritoneal contamination may be present. In termination of pregnancy or cesarean section, sulbactam sodium/ampicillin sodium IM/IV may be used prophylactically to reduce post-operative sepsis.
**4.3 Contraindications** The use of this combination is contraindicated in individuals with a history of an allergic reaction to any of the penicillins.
J01CR01
ampicillin and beta-lactamase inhibitor
Manufacturer Information
PFIZER PRIVATE LIMITED
Haupt Pharma Latina S.r.L
Active Ingredients
Documents
Package Inserts
1.4.3 Package Insert (PI) - Proposed Pristine.doc
Approved: March 16, 2020
