Regulatory Information
HSA regulatory responsibility and product classification details
Regulatory Responsibility
Product Classification
Formulation Information
TABLET, FILM COATED
**4.2 Posology and method of administration** _Film-coated tablets:_ Voriconazole film-coated tablets are to be taken at least one hour before, or one hour following a meal. _Powder for oral suspension:_ Voriconazole oral suspension is to be taken at least one hour before, or two hours following a meal. _Powder for solution for infusion:_ Voriconazole requires reconstitution and dilution (see Section 6.6 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_) prior to administration as an intravenous infusion. Voriconazole powder for solution for infusion is **not** recommended for bolus injection. It is recommended that voriconazole be administered at a maximum rate of 3 mg/kg per hour over 1 to 3 hours. **Blood products and concentrated electrolytes** Voriconazole must not be infused concomitantly with any blood product or any short-term infusion of concentrated electrolytes, even if the two infusions are running in separate intravenous lines (or cannulas). Electrolyte disturbances such as hypokalaemia, hypomagnesemia and hypocalcaemia should be corrected prior to initiation of voriconazole therapy (see Section 4.4 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). **Intravenous solutions containing (non-concentrated) electrolytes** Voriconazole can be infused at the same time as other intravenous solutions containing (non-concentrated) electrolytes, but must be infused through a separate line. **Total parenteral nutrition (TPN)** Voriconazole can be infused at the same time as total parenteral nutrition, but must be infused in a separate line. If infused through a multiple-lumen catheter, TPN needs to be administered using a different port from the one used for voriconazole (see Section 6.2 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). **Other intravenous products** Voriconazole must not be infused into the same line or cannula concomitantly with other intravenous products. **Use in adults** Therapy must be initiated with the specified loading dose regimen of either intravenous or oral voriconazole to achieve plasma concentrations on Day 1 that are close to steady state. On the basis of the high oral bioavailability (96%; see Section 5.2 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_), switching between intravenous and oral administration is appropriate when clinically indicated. Detailed information on dosage recommendations is provided in the following table: 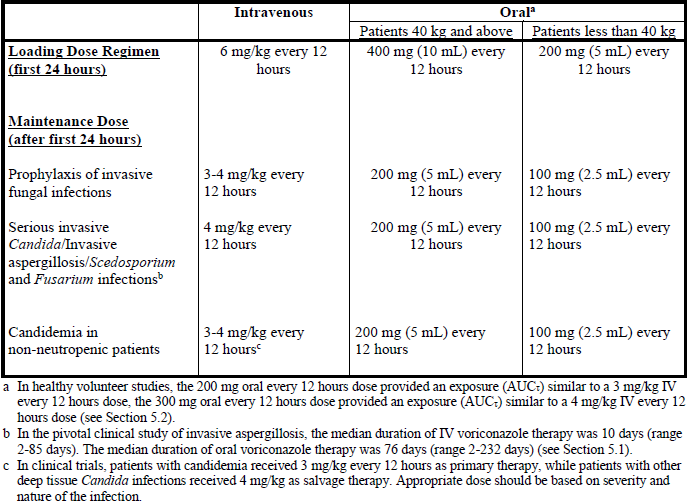 **Dosage adjustment** _Film-coated tablets/Powder for oral suspension:_ If patient response is inadequate, the maintenance dose may be increased from 200 mg every 12 hours (similar to 3 mg/kg IV every 12 hours) to 300 mg every 12 hours (similar to 4 mg/kg IV every 12 hours) for oral administration. For patients less than 40 kg the oral dose may be increased from 100 mg to 150 mg every 12 hours. If patients are unable to tolerate treatment at these higher doses, reduce the oral dose by 50 mg steps to a minimum of 200 mg every 12 hours (or 100 mg every 12 hours for patients less than 40 kg). Phenytoin may be co-administered with voriconazole if the maintenance dose of voriconazole is increased from 200 mg to 400 mg orally every 12 hours (from 100 mg to 200 mg orally, every 12 hours in patients less than 40 kg) (see Sections 4.4 and 4.5 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). When voriconazole is co-administered with adjusted doses of efavirenz, voriconazole maintenance dose should be increased to 400 mg every 12 hours (see Sections 4.3, 4.4 and 4.5 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Treatment duration depends upon patients’ clinical and mycological response. _Intravenous administration:_ If patient response at 3 mg/kg every 12 hours is inadequate, the intravenous maintenance dose may be increased to 4 mg/kg every 12 hours. If patients are unable to tolerate 4 mg/kg every 12 hours, reduce the intravenous maintenance dose to a minimum of 3 mg/kg every 12 hours. Phenytoin may be co-administered with voriconazole if the maintenance dose of voriconazole is increased to 5 mg/kg intravenously every 12 hours (see Sections 4.4 and 4.5 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Treatment duration depends upon patients’ clinical and mycological response. **Use in the elderly** No dose adjustment is necessary for elderly patients. **Use in patients with renal impairment** _Film-coated tablets/Powder for oral suspension:_ The pharmacokinetics of orally administered voriconazole are not affected by renal impairment. Therefore, no adjustment is necessary for oral dosing for patients with mild to severe renal impairment. _Powder for solution for infusion:_ In patients with moderate to severe renal dysfunction (creatinine clearance <50 mL/min), accumulation of the intravenous vehicle, sulphobutylether β-cyclodextrin sodium (SBECD) occurs. Oral voriconazole should be administered to these patients, unless an assessment of the risk benefit to the patient justifies the use of intravenous voriconazole. Serum creatinine levels should be closely monitored in these patients and, if increases occur, consideration should be given to changing to oral voriconazole therapy. Voriconazole is haemodialysed with a clearance of 121 mL/min. A four-hour haemodialysis session does not remove a sufficient amount of voriconazole to warrant dose adjustment. The intravenous vehicle, SBECD, is haemodialysed with a clearance of 55 mL/min. **Use in patients with hepatic impairment** No dose adjustment is necessary in patients with acute hepatic injury, manifested by elevated liver function tests (ALT, AST). Continued monitoring of liver function tests for further elevations is recommended. It is recommended that the standard loading dose regimens be used but that the maintenance dose be halved in patients with mild to moderate hepatic cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A and B) receiving voriconazole. Voriconazole has not been studied in patients with severe chronic hepatic cirrhosis (Child-Pugh C). Voriconazole has been associated with elevations in liver function tests and clinical signs of liver damage, such as jaundice, and must only be used in patients with severe hepatic impairment if the benefit outweighs the potential risk. Patients with severe hepatic impairment must be carefully monitored for drug toxicity. **Use in paediatrics** Safety and effectiveness in paediatric patients below the age of 2 years has not been established (see also Section 5.1 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Therefore, voriconazole is not recommended for children less than 2 years of age. The recommended maintenance dosing regimen in paediatric patients 2 to <12 years is as follows: 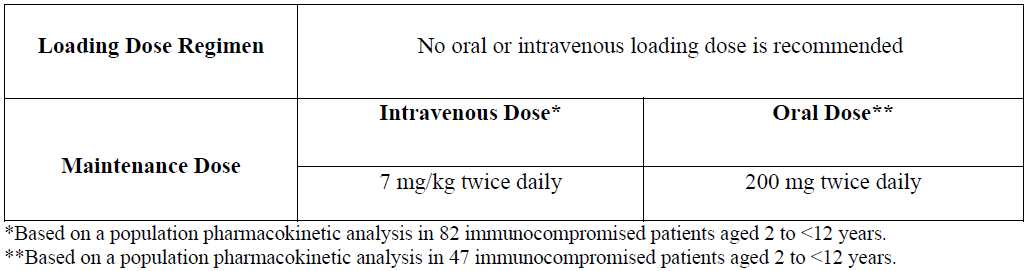 If paediatric patients are unable to tolerate an intravenous dose of 7 mg/kg twice daily, a dose reduction from 7 mg/kg to 4 mg/kg twice daily may be considered based on the population pharmacokinetic analysis and previous clinical experience. This provides equivalent exposure to 3 mg/kg twice daily in adults (see Section 4.2, Use in adults). Use in paediatric patients aged 2 to <12 years with hepatic or renal insufficiency has not been studied (see Sections 4.8 and 5.2 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). The oral dose recommendation for children is based on studies in which voriconazole was administered as the powder for oral suspension formulation. Bioequivalence between the powder for oral suspension and tablets has not been investigated in a paediatric population. Considering the assumed limited gastro-enteric transit time in paediatrics, the absorption of tablets may be different in paediatric compared to adult patients. It is therefore recommended to use the oral suspension formulation in children aged 2 to <12 years. **Adolescents** (12 to 16 years of age) should be dosed as adults.
ORAL
Medical Information
**4.1 Therapeutic indications** Voriconazole is a broad spectrum, triazole antifungal agent and is indicated as follows: Treatment of invasive aspergillosis; Treatment of candidemia in non-neutropenic patients; Treatment of fluconazole-resistant serious invasive _Candida_ infections (including _C. krusei_); Treatment of serious fungal infections caused by _Scedosporium_ spp. and _Fusarium_ spp.; Prophylaxis in patients ≥12 years old who are at high risk of developing invasive fungal infections. The indication is based on a study which includes patients ≥12 years old undergoing allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation (see Section on ‘Clinical experience’ – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_).
**4.3 Contraindications** Voriconazole is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to voriconazole or to any of the excipients. Co-administration of the CYP3A4 substrates, terfenadine, astemizole, cisapride, pimozide, quinidine or ivabradine with voriconazole is contraindicated since increased plasma concentrations of these medicinal products can lead to QTc prolongation and rare occurrences of _torsades de pointes_ (see Section 4.5 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Co-administration of voriconazole and sirolimus is contraindicated, since voriconazole has been shown to significantly increase plasma concentrations of sirolimus in healthy subjects (see Section 4.5 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Co-administration of voriconazole with rifabutin, rifampicin, carbamazepine, long-acting barbiturates (e.g., phenobarbital) and St John’s Wort is contraindicated since these medicinal products are likely to decrease plasma voriconazole concentrations significantly (see Section 4.5 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Co-administration of standard doses of voriconazole with efavirenz doses of 400 mg QD or higher is contraindicated because efavirenz significantly decreases plasma voriconazole concentrations in healthy subjects at these doses. Voriconazole also significantly increases efavirenz plasma concentrations (see Section 4.5, for lower doses see Section 4.4 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Co-administration of ergot alkaloids (ergotamine, dihydroergotamine), which are CYP3A4 substrates, is contraindicated since increased plasma concentrations of these medicinal products can lead to ergotism (see Section 4.5 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Co-administration of voriconazole with high-dose ritonavir (400 mg and above twice daily) is contraindicated because ritonavir significantly decreases plasma voriconazole concentrations in healthy subjects at this dose (see Section 4.5, for lower doses see Section 4.4 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Co-administration of voriconazole with naloxegol is contraindicated because voriconazole may significantly increase plasma concentrations of naloxegol which may precipitate opioid withdrawal symptoms (see Section 4.5 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Co-administration of voriconazole with tolvaptan is contraindicated because voriconazole may significantly increase plasma concentrations of tolvaptan (see Section 4.5 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Co-administration of voriconazole with venetoclax is contraindicated at initiation and during the venetoclax dose titration phase since voriconazole is likely to significantly increase plasma concentrations of venetoclax and increase risk of tumour lysis syndrome (see Section 4.5 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Co-administration of voriconazole with lurasidone is contraindicated since it may result in significant increases in lurasidone exposure and the potential for serious adverse reactions (see Section 4.5 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_).
J02AC03
voriconazole
Manufacturer Information
PFIZER PRIVATE LIMITED
R-Pharm Germany GmbH
Pfizer Italia S.r.l.
Active Ingredients
Documents
Package Inserts
Vfend_PI.pdf
Approved: February 13, 2023
