Regulatory Information
HSA regulatory responsibility and product classification details
Regulatory Responsibility
Product Classification
Formulation Information
INJECTION, SOLUTION
**4.2 Dose and method of administration** **Dosage** _**Local or regional anaesthesia (including intravenous regional anaesthesia)**_ The lowest dosage and volume that results in effective anaesthesia should be used and should be based on the status of the patient and the type of regional anaesthesia intended. Lidocaine should be administered with great caution to patients with impaired cardiovascular function as they may be less able to compensate for functional changes associated with the prolongation of AV conduction produced by these drugs. **Adults** Recommended dosages for LIDOCAINE AGUETTANT solution for injection in pre-filled syringe for various anaesthetic procedures in the average, healthy, 70 kg adult patient. 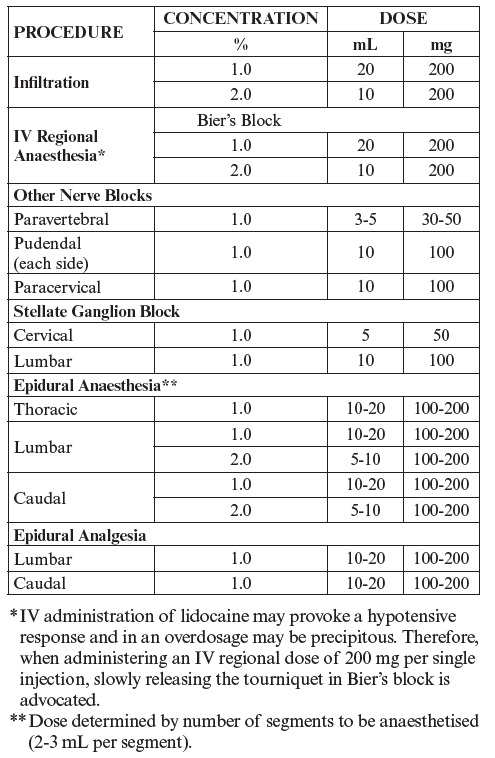 **Note:** 1. **Recommended doses** The above suggested concentrations and volumes serve only as a guide. Toxic doses vary widely between patients and toxic effects may occur after any local anaesthetic procedure. Careful observation of the patient must therefore be maintained. It is recommended that the dose of lidocaine at any one time should not exceed 3 mg/kg. However, the dose administered must be tailored to the individual patient and procedure, and the maximum doses here quoted should be used as a guide only. 2. **Hypotension** During thoracic, lumbar and caudal epidural anaesthesia, a marked fall in blood pressure and/or intercostal paralysis may be seen, possibly due to the use of excessive doses, improper positioning of the patient or accidental disposition of the anaesthetic within the subarachnoid space. Hypotension and bradycardia may occur as a result of sympathetic blockade. 3. **Test dose** For epidural anaesthesia, a 3–5 mL test dose of a local anaesthetic solution preferably containing up to 15 micrograms of adrenaline should be administered. Verbal contact and repeated monitoring of heart rate and blood pressure should be maintained for 5 minutes after the test dose after which, in the absence of signs of subarachnoid or intravascular injection, the main dose may be administered. Use of a test dose containing adrenaline may have further advantages in that an intravascular injection of adrenaline will be quickly recognised by an increase in heart rate, usually within about 40 seconds. To detect this, the heart rate and rhythm should be monitored with an electrocardiogram. Prior to administration of the total dose, aspiration should be repeated. The main dose should be injected slowly, with continual assessment of the patient. If toxic symptoms or signs occur, the injection should be stopped immediately. **Paediatrics** For children, a reduced dosage based on body weight or surface area should be used. The dosage should be calculated for each patient individually and modified in accordance with the physician’s experience and knowledge of the patient. In order to minimise the possibility of toxic effects, the strength 10 mg/mL is recommended for most anaesthetic procedures involving paediatric patients. In children, early signs of local anaesthetic toxicity may be difficult to detect in cases where the block is given during general anaesthesia. _**For intravenous use in cardiac arrhythmias:**_ **Adults** _Single Direct Intravenous injection (bolus)_ The usual dose is 50 to 100 mg of lidocaine hydrochloride (0.70 to 1.4 mg/kg) administered intravenously under ECG monitoring. This dose may be administered at the ratio of approximately 25 to 50 mg/min (0.35 to 0.70 mg/kg/min). Sufficient time should be allowed to enable a slow circulation to carry the drug to the site of action. If the initial injection of 50 to 100mg doses does not produce a desired response, a second dose may be injected after 5 minutes. No more than 200 to 300 mg of lidocaine hydrochloride should be administered during one hour period. **Paediatrics** For children, a reduced dose based on body weight or surface area should be used. It is recommended that the 1% solution be used to minimise the possibility of toxic effects. Experience with lidocaine is limited. The suggested loading dose is a bolus dose of 1 mg/kg. Then, continuous infusions of 20 to 50 mcg/kg/min are recommended however it is reminded that LIDOCAINE AGUETTANT is a ready to administer pre-filled syringe not adapted to continuous infusions (see next § Method of administration). **Method of administration** In local or regional anaesthesia, the method of administration of LIDOCAINE AGUETTANT varies according to the procedure. In cardiac arrhythmias, LIDOCAINE AGUETTANT should be administered as a slow intravenous injection. LIDOCAINE AGUETTANT is a ready to administer pre-filled syringe which is not designed for administration with an electronic syringe pump (for continuous infusion or patient controlled repeated bolus epidural administration). **Dosage adjustment** - _**Use in Elderly**_ A reduction in dosage may be necessary for elderly patients especially those with compromised cardiovascular and/or hepatic function. In epidural anaesthesia, a smaller dose may provide adequate anaesthesia. - _**With impaired hepatic function**_ Although lidocaine is metabolised by the liver, dosage reduction for local anaesthesia is probably not warranted. However, caution should be exercised with repeated doses. - _**With impaired renal function**_ Impairment of renal function is unlikely to affect lidocaine clearance in the short term (24 hours). However, toxicity due to accumulation may develop with prolonged or repeated administration.
INTRAVENOUS, INFILTRATION
Medical Information
**4.1 Therapeutic indications** LIDOCAINE AGUETTANT solution for injection in pre-filled syringe is indicated for the production of local or regional anaesthesia by the following techniques: - infiltration, - intravenous regional anaesthesia – excluding solutions with adrenaline, - peripheral nerve block such as intercostal block, - major plexus block such as brachial plexus block, - epidural block, - subarachnoid block. LIDOCAINE AGUETTANT solution for injection in pre-filled syringe administered intravenously is specially indicated in the acute management of ventricular arrythmias such as those occurring in relation to acute myocardial infarction or during cardiac manipulation, such as cardiac surgery.
**4.3 Contraindications** - Allergy or hypersensitivity to amide type local anaesthetics or to any excipients. Detection of suspected hypersensitivity by skin testing is of limited value. - Hypersensitivity to methyl and/or propyl parahydroxybensoate (methyl-/propyl paraben), or to their metabolite para amino benzoic acid (PABA). Formulations of lidocaine containing parabens should be avoided in patients allergic to ester local anaesthetics or its metabolite PABA. - Local anaesthetics are contraindicated for epidural and spinal anaesthesia in patients with uncorrected hypotension or coagulation disorders or in patients receiving anti‑coagulation treatment. - Local anaesthetic techniques must not be used when there is inflammation and/or sepsis in the region of the proposed injection and/or in the presence of septicaemia. - LIDOCAINE AGUETTANT solution for injection in pre-filled syringe should not be used in patients with Stokes-Adam syndrome, Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome, or with severe degrees of sinoatrial, atrioventricular, or intraventricular block in the absence of an artificial pacemaker. - General contraindications related to epidural anaesthesia, regardless of the local anaesthetic used, should be taken into account.
C01BB01, N01BB02
xc 01 bb 01, n 01 bb 02
Manufacturer Information
AGUETTANT ASIA PACIFIC PTE. LTD.
Laboratoire AGUETTANT
Active Ingredients
Documents
Package Inserts
Lidocaine Aguettant Solution for Injection in PFS PI.pdf
Approved: September 12, 2023
