Regulatory Information
HSA regulatory responsibility and product classification details
Regulatory Responsibility
Product Classification
Formulation Information
INJECTION
**4.2 Posology and Method of Administration** Adults: Prophylaxis of venous thromboembolic disease in surgical patients: In patients with a moderate thromboembolism risk (e.g. abdominal surgery) the recommended dose of enoxaparin sodium is 2000 anti-Xa international units (0.2 ml) once daily by subcutaneous injection. In general surgery, the first injection should be given 2 hours before the surgical procedure. In patients with a high risk of thromboembolic (e.g. orthopedic surgery) the recommended dose of enoxaparin sodium given by subcutaneous injection is 4000 anti-Xa international units (0.4 ml) once daily initiated 12 hours preoperatively. For special recommendation concerning dosing intervals for spinal/ epidural anesthesia and PCI procedures, see Warnings – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_. Enoxaparin sodium treatment is usually prescribed for an average period of 7 to 10 days. Longer treatment duration may be appropriate in some patients and the treatment should be continued for as long as there is a risk of venous thromboembolism and until the patient is ambulatory. Therapy with 4000 anti-Xa international units once daily for 30 post-operative days has been proved to be beneficial in total hip replacement surgery. Prophylaxis of venous thromboembolic disease in medical patients: The recommended dose of enoxaparin sodium is 4000 anti-Xa international units (0.4 ml) once daily by subcutaneous injection. Treatment with enoxaparin sodium is prescribed for a minimum of 6 days and continued until the return to full ambulation, for a maximum of 14 days. Treatment of established deep vein thrombosis: Enoxaparin sodium is administered subcutaneously at the dose of 100 anti-Xa international units/kg every 12 hours. The treatment is prescribed until a therapeutic anticoagulant effect has been achieved with oral anticoagulant therapy, usually for an average period of 10 days. Prevention of extracorporeal thrombus formation during haemodialysis: A dose equivalent to 100 anti-Xa international units/kg (1mg/kg) introduced into the arterial line at the beginning of a dialysis session is usually sufficient for a 4 hour session. If fibrin rings are found, such as after a longer than normal session, a further dose of 50 to 100 anti-Xa international units/kg (0.5 to 1.0 mg/kg) may be given. For patients at a higher risk of haemorrhage the dose should be reduced to 50 anti-Xa international units/kg (0.5 mg/kg) for double vascular access or 75 anti-Xa international units/kg (0.75 mg/kg) for a single vascular access. Treatment of unstable angina and non-Q-wave myocardial infarction: The recommended dose is 100 anti-Xa international units/kg Clexane every 12 hours by subcutaneous injection, administered concurrently with oral aspirin (100 to 325 mg once daily). Treatment with Clexane in these patients should be prescribed for a minimum of 2 days and continued until clinical stabilisation. The usual duration of treatment is 2 to 8 days. Treatment of acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction in combination with a thrombolytic agent in patients eligible or not for subsequent PCI: An initial IV bolus injection of 3,000 anti-Xa international units (0.3 ml) followed by an SC injection of 100 anti-Xa international units/kg within 15 minutes, then every 12 hours (a maximum of 10000 anti-Xa international units (1.0 ml) for each of the first two SC doses only, followed by 100 anti-Xa international units/kg SC dosing for the remaining doses). For dosage in patients ≥75 years of age, see sub-section Elderly. The first dose of enoxaparin should be administered at any time between 15 minutes before 30 minutes after the start of thrombolytic treatment (whether fibrin-specific or not). Administration of aspirin must be instituted as soon as possible after symptoms appear, and maintained at a dosage of between 75 mg and 325 mg daily for at least 30 days, unless otherwise indicated. The recommended duration of **enoxaparin** treatment is 8 days, or until the patient is discharged from hospital if the hospitalization period is less than 8 days. Patients managed with Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI): If the last SC injection of enoxaparin was performed less than 8 hours before balloon inflation, no additional administration is necessary. If the last SC injection was performed more than 8 hours before balloon inflation, an IV bolus of 30 anti-Xa international units/kg of enoxaparin must be administered. In order to improve the accuracy of the volumes to be injected, it is recommended to dilute the drug to 300 anti-Xa international units/ml (see sub-section Intravenous (bolus) injection technique for the treatment of acute STEMI only). Elderly: Treatment of acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, in combination with a thrombolytic agent in patients eligible or not for subsequent PCI: In patients aged 75 and over, treated for acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, the initial IV bolus injection should not be administered. A SC dose of 75 anti-Xa international units/kg every 12 hours should be administered (maximum of 7500 anti-Xa international units for each of the first two SC doses only, followed by 75 anti-Xa international units/kg dosing for the remaining doses). For other therapeutic indications: No dose adjustment necessary in the elderly, unless kidney functions is impaired. Children: Not recommended, a dosage is not established. Renal impairment: See Special Warnings & Precautions for Use – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_ Severe renal impairment: A dosage adjustment is required for patients with severe renal impairment (creatinine clearance < 30 ml/min), since enoxaparin sodium exposure is significantly increased in this patient population.  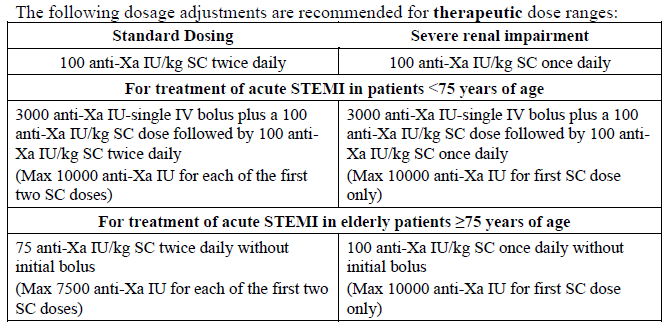 Moderate and mild renal impairment: Although no dose adjustment is recommended in patients with moderate (creatinine clearance 30–50 ml/min) and mild (creatinine clearance 50–80 ml/min) renal impairment, careful clinical monitoring is recommended. Hepatic impairment: In the absence of clinical studies, caution should be exercised. Administration: Clexane is administered by subcutaneous injection for the prevention of venous thromboembolic disease, treatment of deep vein thrombosis or for the treatment of unstable angina and non-Q-wave myocardial infarction, and through the arterial line of dialysis circuit for the prevention of thrombus formation in the extracorporeal circulation during haemodialysis. It must not be administered by the intramuscular route. Spinal/epidural anesthesia For patients receiving spinal/epidural anesthesia see Section 4.4 Warnings: Spinal/epidural anesthesia – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_. **Subcutaneous injection technique (except for patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction, in whom IV bolus administration is required for solution for injection containing 6000, 8000 and 10000 anti-Xa international units):** The prefilled disposable syringe is ready for immediate use. Clexane should be administered when the patient is lying down by deep subcutaneous injection. The administration should be alternated between the left and right anterolateral or postrolateral abdominal wall. The whole length of the needle should be introduced vertically into a skin fold held between the thumb and index finger. The skin fold should not be released until the injection is complete. Do not rub the injection site after administration. **Intravenous (bolus) injection technique for the treatment of acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction only:** Enoxaparin sodium should be administered through intravenous line. It should not be mixed or co-administered with other medications. To avoid the possible mixture of enoxaparin sodium with other drugs, the intravenous access chosen should be flushed with a sufficient amount of saline or dextrose solution prior to and following the intravenous bolus administration of enoxaparin sodium to clear the port of drug. Enoxaparin sodium may be safely administered with normal saline solution (0.9%) or 5% dextrose in water. - Initial 3000 anti-Xa international units (0.3 ml) bolus For the initial 3000 anti-Xa international units (0.3 ml) bolus, using an enoxaparin sodium graduated prefilled syringe, expel the excessive volume to retain only 3000 anti-Xa international units (0.3 ml) in the syringe. The 3000 anti-Xa international units (0.3 ml) dose can be directly injected into the intravenous line. - Additional bolus for patients treated by PCI when last SC administration was given more than 8 hours before balloon inflation For patients undergoing subsequent PCI an additional IV bolus of 30 anti-Xa international units/kg is to be administered if last SC administration was given more than 8 hours before balloon inflation (see Posology and Method of Administration: Treatment of acute STEMI). In order to assure the accuracy of the small volume to be injected, it is recommended to dilute the drug to 300 anti-Xa international units/ml. To obtain a 300 anti-Xa international units/ml solution, using a 6000 anti-Xa international units enoxaparin sodium prefilled syringe, it is recommended to use a 50 ml infusion bag (i.e. using either normal saline solution (0.9%) or 5% dextrose in water) as follows: Withdraw 30ml from the infusion bag with a syringe and discard the liquid. Inject the complete contents of the 6000 anti-Xa international units (0.6 ml) enoxaparin sodium prefilled syringe into the 20 ml remaining in the bag. Gently mix the contents of the bag. Withdraw the required volume of diluted solution with a syringe for administration into the intravenous line. After dilution is completed, the volume to be injected can be calculated using the following formula \[Volume of diluted solution (ml) = Patient weight (kg) x 0.1\] or using the table below. It is recommended to prepare the dilution immediately before use.  General recommendation: Regular monitoring of the platelet count is essential throughout the treatment due to the risk of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) (see Section 4.4 Special Warnings and Precautions for Use – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_).
SUBCUTANEOUS, INTRAVASCULAR
Medical Information
**4.1 Therapeutic Indications** Prophylaxis of venous thromboembolic disease (prevention of blood clot formation in the veins), in particular those which may be associated with orthopedic or general surgery. Prophylaxis of venous thromboembolic disease in medical patients bedridden due to acute illnesses. Treatment of established deep vein thrombosis. Prevention of thrombus formation in extracorporeal circulation during haemodialysis. Treatment of unstable angina and non-Q-wave myocardial infarction, administered concurrently with aspirin. Treatment of acute ST-segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction (STEMI), in combination with a thrombolytic agent, in patients to be managed medically or with subsequent Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI).
**4.3 Contra-indications** Contraindicated in patients with: - acute bacteria endocarditis; - active major bleeding disorders and conditions with a high risk of uncontrolled haemorrhage, including recent hemorrhagic stroke (unless due to systemic emboli); - thrombocytopenia in patients with a positive in-vitro aggregation test in the presence of enoxaparin; - acute gastric or duodenal ulceration; - hypersensitivity to either enoxaparin sodium, heparin or other low molecular weight heparins.
B01AB05
enoxaparin
Manufacturer Information
SANOFI-AVENTIS SINGAPORE PTE. LTD.
Sanofi Winthrop Industrie
Active Ingredients
Documents
Package Inserts
Clexane Injection PI.pdf
Approved: March 3, 2022
