Regulatory Information
HSA regulatory responsibility and product classification details
Regulatory Responsibility
Product Classification
Formulation Information
INJECTION, POWDER, FOR SOLUTION
**4.2 DOSE AND METHOD OF ADMINISTRATION** **Dosage** _**Adults**_ Therapy must be initiated with the specified loading dose regimen of either intravenous or oral voriconazole to achieve plasma concentrations on Day 1 that are close to steady state. On the basis of the high oral bioavailability, switching between intravenous and oral administration is appropriate when clinically indicated. Dosage recommendations are provided in the table below. 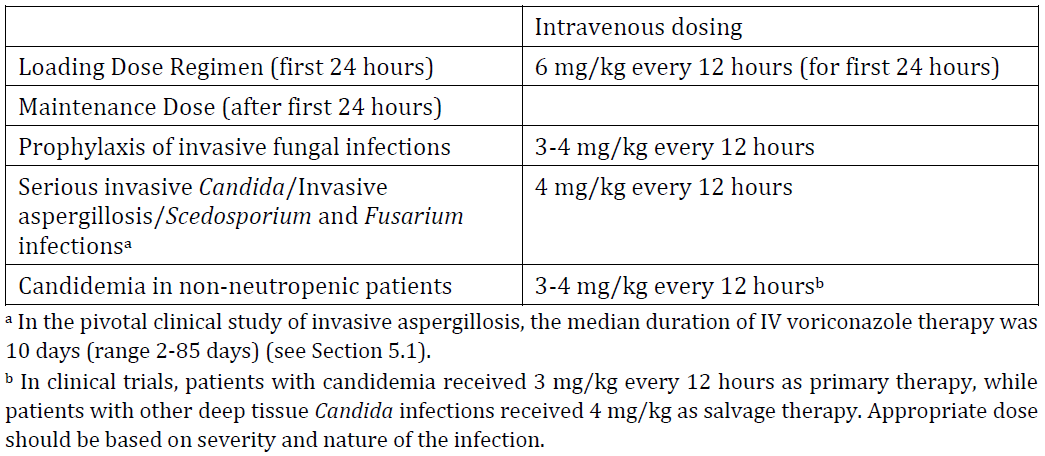 Clinical data to establish the safety of intravenously administered hydroxypropylbetadex in long-term treatment are limited. _**Paediatrics**_ Age of ≤ 2 years Safety and efficacy in paediatric subjects below the age of 2 years has not been established. Therefore, voriconazole is not recommended for children less than 2 years of age. Age ≥ 2 to 12 years The recommended maintenance dosing regimen in paediatric patients 2 to <12 years is as follows:  If paediatric patients are unable to tolerate an intravenous dose of 7 mg/kg twice daily, a dose reduction from 7 mg/kg to 4 mg/kg twice daily may be considered based on the population pharmacokinetic analysis and previous clinical experience. This provides equivalent exposure to 3 mg/kg twice daily in adults. Age 2 to < 12 years with hepatic or renal impairment Use in the patients aged 2 to < 12 years with hepatic or renal impairment have not been studied (see Section 4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Adolescents (12 – 16 years of age) Adolescents (12 – 16 years of age) should be dosed as adults. See dosing recommendation under the section heading, Adults. Clinical data to establish the safety of intravenously administered hydroxypropylbetadex in the paediatric population are limited. **Method of administration** Voriconazole – AFT powder for injection is not recommended for bolus injection. Voriconazole – AFT powder for injection requires reconstitution and dilution prior to administration as an intravenous infusion (see Section 6.2 Incompatibilities – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). It is recommended that Voriconazole – AFT powder for injection is administered at a maximum rate of 3 mg/kg per hour over 1 to 2 hours. Electrolyte disturbances such as hypokalaemia, hypomagnesaemia and hypocalcaemia should be corrected prior to initiation of voriconazole therapy (see Section 4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use, Cardiovascular – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). **_Reconstitution instructions_** Voriconazole-AFT 200mg powder for solution for infusion is stable in all of the following reconstitution solutions both at below 25 °C and at 5 °C for at least 72 hours: Water for injections, Sodium Chloride 0.9% solution, Compound Sodium Lactate solution, 5% Glucose and Lactate Ringer’s solution, 5% Glucose and 0.45% Sodium chloride solution, 5% Glucose solution, 5% Glucose in 20 mEq Potassium Chloride solution, 0.45% Sodium Chloride solution and 5% Glucose and 0.9% Sodium Chloride solution Product is for single use in one patient only. Discard any residue. Only clear solutions without particles should be used. **Dosage adjustment** _**Adults**_ If patient response at 3 mg/kg every 12 hours is inadequate, the intravenous maintenance dose may be increased to 4 mg/kg every 12 hours. If patients are unable to tolerate 4 mg/kg every 12 hours, reduce the intravenous dose to 3 mg/kg every 12 hours. Phenytoin may be co-administered with voriconazole if the maintenance dose of voriconazole is increased to 5 mg/kg IV every 12 hours. The loading dose regimen remains unchanged (see Section 4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use and Section 4.5 Interactions with other medicines and other forms of interactions – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). The dose recommendation for concomitant use of intravenous voriconazole and oral efavirenz has not been determined (see Section 4.5 Interactions with other medicines and other forms of interactions – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Treatment duration depends upon patients’ clinical and mycological response. _**Renal impairment**_ In patients with moderate to severe renal dysfunction (creatinine clearance < 50 mL/min), accumulation of the intravenous vehicle, hydroxypropylbetadex, occurs. Oral voriconazole should be administered to these patients, unless an assessment of the risk benefit to the patient justifies the use of intravenous voriconazole. Serum creatinine levels should be closely monitored in these patients and, if increases occur, consideration should be given to changing to oral voriconazole therapy (see Section 5.2 Pharmacokinetic properties, Renal impairment – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). _**Hepatic impairment**_ No dose adjustment is necessary in patients with acute hepatic injury, manifested by elevated liver function tests (ALT, AST) (but continued monitoring of liver function tests for further elevations is recommended). It is recommended that the standard loading dose regimens be used but that the maintenance dose be halved in patients with mild to moderate hepatic cirrhosis (Child-Pugh A and B) receiving voriconazole. Voriconazole has not been studied in patients with severe chronic hepatic cirrhosis (Child-Pugh C). Voriconazole has been associated with elevations in liver function tests and clinical signs of liver damage such as jaundice, and must only be used in patients with severe hepatic impairment if the benefit outweighs the potential risk. Patients with severe hepatic impairment must be carefully monitored for drug toxicity (see Section 4.8 Adverse effects (undesirable effects) – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). _**Elderly**_ No dose adjustment is necessary for elderly patients.
INTRAVENOUS
Medical Information
**4.1 THERAPEUTIC INDICATIONS** Voriconazole is a broad spectrum, triazole antifungal agent and is indicated as follows: Treatment of invasive aspergillosis; Treatment of candidemia in non-neutropenic patients; Treatment of fluconazole-resistant serious invasive _Candida_ infections (including _C. krusei_); Treatment of serious fungal infections caused by _Scedosporium_ spp. and _Fusarium_ spp.; Prophylaxis in patients ≥12 years old who are at high risk of developing invasive fungal infections. The indication is based on a study which includes patients ≥12 years old undergoing allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation (see Section 5.1 – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_).
**4.3 CONTRAINDICATIONS** Voriconazole – AFT is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to voriconazole or to any of the excipients. Coadministration of the CYP3A4 substrates, terfenadine, ivabradine, pimozide or quinidine with voriconazole is contraindicated since increased plasma concentrations of these medicinal products can lead to QTc prolongation and rare occurrences of torsades de pointes (see Section 4.5 Interactions with other medicines and other forms of interactions – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Coadministration of voriconazole with rifabutin, rifampicin, carbamazepine and longacting barbiturates (e.g., phenobarbitone) is contraindicated since these medicinal products are likely to decrease plasma voriconazole concentrations significantly (see Section 4.5 Interactions with other medicines and other forms of interactions – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Coadministration of standard doses of voriconazole with patients receiving efavirenz doses of 400 mg once daily or higher is contraindicated, because efavirenz significantly decreases plasma voriconazole concentrations in healthy subjects at these doses. Voriconazole also significantly increases efavirenz plasma concentrations (see Section 4.5 Interactions with other medicines and other forms of interactions – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Coadministration of voriconazole with patients receiving high doses of ritonavir (400 mg and higher twice daily) is contraindicated, because ritonavir significantly decreases plasma voriconazole concentrations in healthy subjects at these doses (see Section 4.5 Interactions with other medicines and other forms of interactions – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). For information pertaining to lower doses of ritonavir see Section 4.4 Special warnings and precautions for use – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_. Coadministration of ergot alkaloids (ergotamine, dihydroergotamine), which are CYP3A4 substrates, is contraindicated since increased plasma concentrations of these medicinal products can lead to ergotism (see 4.5 Section Interactions with other medicines and other forms of interactions – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Coadministration of voriconazole and sirolimus is contraindicated, since voriconazole is likely to increase plasma concentrations of sirolimus significantly (see Section 4.5 Interactions with other medicines and other forms of interactions – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Coadministration of voriconazole with St John’s Wort is contraindicated (see Section 4.5 Interactions with other medicines and other forms of interactions – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Co-administration of voriconazole with naloxegol is contraindicated because voriconazole may significantly increase plasma concentrations of naloxegol which may precipitate opioid withdrawal symptoms (see Section 4.5 Interactions with other medicines and other forms of interactions – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Co-administration of voriconazole with tolvaptan is contraindicated because voriconazole may significantly increase plasma concentrations of tolvaptan (see Section 4.5 Interactions with other medicines and other forms of interactions – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Co-administration of voriconazole with venetoclax is contraindicated at initiation and during the venetoclax dose titration phase since voriconazole is likely to significantly increase plasma concentrations of venetoclax and increase risk of tumour lysis syndrome (see Section 4.5 Interactions with other medicines and other forms of interactions – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_). Co-administration of voriconazole with lurasidone is contraindicated since it may result in significant increases in lurasidone exposure and the potential for serious adverse reactions (see Section 4.5 Interactions with other medicines and other forms of interactions – _please refer to the Product Insert/Patient Information Leaflet published on HSA for the full drug information_).
J02AC03
voriconazole
Manufacturer Information
APEX PHARMA MARKETING PTE. LTD.
ANFARM HELLAS S.A
Active Ingredients
Documents
Package Inserts
VORICONAZOLE – AFT INJECTION PI.pdf
Approved: December 8, 2023
